Madang languages
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Engkalak Litsea garciae Status konservasiRisiko rendahIUCN153109975 TaksonomiDivisiTracheophytaSubdivisiSpermatophytesKladAngiospermaeKladmagnoliidsOrdoLauralesFamiliLauraceaeGenusLitseaSpesiesLitsea garciae S.Vidal, 1886 lbs Litsea garciae, juga dikenal sebagai engkala, enkkalak, kangkala, pangalaban, tangkalak, kalangkala, dan alpukat Kalimantan merupakan pohon berbunga penghasil buah dalam keluarga Lauraceae.[2] Distribusi Litsea garciae berasal dari Taiwan, Filipina, Brunei, Malay...

William ChanChan on Hot Blood Dance CrewNama asal陳 偉霆Lahir21 November 1985 (umur 38)Hong Kong BritaniaKebangsaanBritania (Hong Kong)Hong KongPendidikanSecondary 7, Yew Chung International SchoolPekerjaanPenyanyipenariaktorTahun aktif2004–kiniPenghargaanRTHK Top 10 Gold Songs AwardsBest Prospect Award (Gold)2008 (untuk penampilan tahun 2008) William Chan Hanzi tradisional: 陳偉霆 Hanzi sederhana: 陈伟霆 Alih aksara Mandarin - Hanyu Pinyin: Chén Wěitíng Yue (Kan...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Annual hurling competition season 2000 Cork Senior Hurling ChampionshipDates6 May 2000 – 8 October 2000Teams23SponsorTSB BankChampions Newtownshandrum (1st title)Donal Mulcahy (captain)Bernie O'Connor (manager)Runners-up Erin's OwnTony O'Keeffe (captain)P. J. Murphy (manager)Tournament statisticsMatches played32Goals scored92 (2.88 per match)Points scored827 (25.84 per match)Top scorer(s) Joe Deane (6-32) ← 1999 (Previous) (Next) 2001 → The 2000 Cork Senior Hurling Championship was the ...

Mazmur 132Naskah Gulungan Mazmur 11Q5 di antara Naskah Laut Mati memuat salinan sejumlah besar mazmur Alkitab yang diperkirakan dibuat pada abad ke-2 SM.KitabKitab MazmurKategoriKetuvimBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen19← Mazmur 131 Mazmur 133 → Mazmur 132 (disingkat Maz 132 atau Mz 132; penomoran Septuaginta: Mazmur 131) adalah sebuah mazmur dalam bagian ke-5 Kitab Mazmur di Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama dalam Alkitab Kristen. Tidak ada catatan n...

العلاقات المكسيكية الليبية المكسيك ليبيا المكسيك ليبيا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات المكسيكية الليبية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين المكسيك وليبيا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارنة الم�...

County in Texas, United States County in TexasCalhoun CountyCountyCalhoun County CourthouseLocation within the U.S. state of TexasTexas's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 28°26′N 96°37′W / 28.44°N 96.61°W / 28.44; -96.61Country United StatesState TexasFounded1846Named forJohn C. CalhounSeatPort LavacaLargest cityPort LavacaArea • Total1,033 sq mi (2,680 km2) • Land507 sq mi (1,310 km2) •...

ThilakanOil Painting Of ThilakanLahirK. Surendranatha Thilakan(1935-06-15)15 Juni 1935Ayroor,[1] TravancoreMeninggal24 September 2012(2012-09-24) (umur 77)Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, IndiaKebangsaanIndianTahun aktif1956–1978 (stage)1972, 1979–2012 (film)Karya terkenalYavanika (1982)Panchagni (1986)Thaniyavarthanam (1987)Dhwani (1988)Moonnam pakkam (1988)Hrithubhedam (1988)Kireedam (1989)Perumthachan (1990)Gamanam (1994)PasanganShanthaSarojamAnakShaji (Son)Shammi (Son)Sh...

Statue formerly installed in Nashville, Tennessee, U.S. Statue of Edward W. CarmackThe statue in 2016ArtistNancy Cox-McCormackYear1927SubjectEdward W. CarmackLocationNashville, Tennessee, U.S. A statue of Edward W. Carmack was installed in Nashville, Tennessee, United States in 1924. The statue was the work of American sculptor Nancy Cox-McCormack.[citation needed] Carmack was an opponent of Ida B. Wells and encouraged retaliation for her support of the civil rights movement.[1 ...

Military museum in London, England The Guards MuseumA Ferret armoured car on display outside the Guards Museum (January 2006)Shown in WestminsterEstablished1988LocationWellington BarracksCoordinates51°29′59″N 0°8′16″W / 51.49972°N 0.13778°W / 51.49972; -0.13778TypeMilitaryWebsitewww.theguardsmuseum.com The Guards Museum is a military museum in Central London, England. It is in Wellington Barracks on Birdcage Walk near Buckingham Palace, which is the home of...

Antoine de LalouvèreVeterum geometria promota in septem de cycloide libris, 1660BiographieNaissance 24 août 1600AuchDécès 2 septembre 1664 (à 64 ans)ToulouseActivité MathématicienAutres informationsOrdre religieux Compagnie de Jésusmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Antoine de Lalouvère (ou Antoine de Laloubère) né à Auch, Gers (France), le 24 août 1600 et décédé à Toulouse le 2 septembre 1664, est un prêtre jésuite français et mathématicien de renom. On...

Italian film director and screenwriter (1895–1981) Mario CameriniBorn(1895-02-06)6 February 1895Rome, Kingdom of ItalyDied4 February 1981(1981-02-04) (aged 85)Gardone Riviera, ItalyOccupation(s)Film director, screenwriterYears active1920–1972Spouse Assia Noris (m. 1940; ann. 1943) Mario Camerini (6 February 1895 – 4 February 1981) was an Italian film director and screenwriter. The cousin of Augusto Genina, Camerini made the m...

American economist (born 1940) For other uses, see Peter Diamond (disambiguation). Peter DiamondDiamond in 2010BornPeter Arthur Diamond (1940-04-29) April 29, 1940 (age 84)New York City, New York, U.S.EducationYale University (BA)Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MA, PhD)SpouseKate MyrickAcademic careerInstitutionsMassachusetts Institute of TechnologyUniversity of California, BerkeleyUniversity of CambridgeFieldPolitical economicsWelfare economicsBehavioral economicsDoctoraladvisorR...

Portland Timbers 2023 soccer seasonPortland Timbers2023 seasonCEOHeather DavisInterim Head coachMiles JosephStadiumProvidence ParkPortland, Oregon(Capacity: 25,218)Major League SoccerConference: 10thOverall: 18thMLS Cup PlayoffsDNQHighest home attendance25,218[1]Lowest home attendance21,320[1]Average home league attendance23,102[2]Biggest win4–1 SEA (April 15)Biggest defeat5-0 HOU (August 20) Primary colors Secondary colors ← 20222024 →All stat...
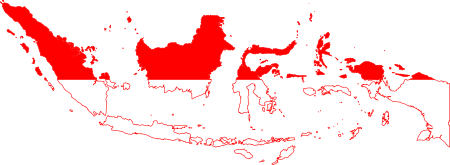
Pemilihan Presiden Indonesia 19681963197327 Maret 1968616 suara anggota Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat SementaraDitetapkan berdasarkan perolehan suara terbanyak untuk menangKandidat Calon Soeharto Partai Golkar Suara elektoral 616 Persentase 100,00% Hasil suara Peta persebaran suara Suara Majelis Permusyawaratan Rakyat Sementara Soeharto: 616 kursi Presiden petahanaSoeharto (Pejabat) ABRI Presiden terpilih Soeharto ABRI Pemilihan presiden Indonesia 1968 adalah suatu p...

TagbanwaDaerah dengan populasi signifikan Filipina: PalawanBahasaBahasa Tagbanwa Agborlan, Tagbanwa Calamian, Tagbanwa Tengah, Cuyonon, TagalogAgamaKatolik Roma, paganismeKelompok etnik terkaitOrang Filipina lain, Orang Austronesia lain Suku Tagbanwa atau Tagbanua adalah salah satu kelompok etnis tertua di Filipina yang banyak berada di bagian tengah dan utara Palawan. Penelitian telah menunjukkan bahwa suku Tagbanwa mungkin keturunan Orang Tabon. Sehingga, mereka merupakan salah satu pendudu...

Paradoks Pinokio menyebabkan hidung Pinokio tumbuh memanjang jika dan hanya jika hidungnya tidak tumbuh memanjang. Paradoks Pinokio muncul saat Pinokio mengatakan Hidung saya tumbuh sekarang dan merupakan versi dari paradoks pembohong.[1] Paradoks pembohong didefinisikan dalam filsafat dan logika sebagai pernyataan Kalimat ini salah. Setiap upaya untuk menetapkan biner klasik nilai kebenaran ke pernyataan ini menyebabkan kontradiksi, atau paradoks. Hal ini terjadi karena jika pernyata...

Sculpture from ancient Greece and Rome Leochares: Belvedere Apollo. Roman copy of 130–140 AD after a Greek bronze original of 330–320 BC. Vatican Museums Classical sculpture (usually with a lower case c) refers generally to sculpture from Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome, as well as the Hellenized and Romanized civilizations under their rule or influence, from about 500 BC to around 200 AD. It may also refer more precisely a period within Ancient Greek sculpture from around 500 BC to the o...

Diamonds Are ForeverPoster film karya Robert McGinnisSutradaraGuy HamiltonProduserHarry SaltzmanAlbert R. BroccoliSkenarioRichard MaibaumTom MankiewiczBerdasarkanDiamonds Are Foreveroleh Ian FlemingPemeran Sean Connery Jill St. John Charles Gray Lana Wood Jimmy Dean Bruce Cabot Penata musikJohn BarrySinematograferTed MoorePenyuntingBert BatesJohn HolmesPerusahaanproduksiEon ProductionsDistributorUnited ArtistsTanggal rilis 14 Desember 1971 (1971-12-14) (Jerman Barat) 17 Desembe...

Notes available on a koncovka made in the key of G. Notes played with the end closed are marked with ●, and notes played with the end open are marked with ○.[1] Nature look koncovka. Koncovka, a Slovak overtone flute The koncovka is a Slovak duct-blown[2] overtone fipple flute without finger holes,[3] traditionally played by shepherds.[4] The koncovka is played by closing and opening the bottom hole of the flute.[3] By increasing the air speed, two ...
