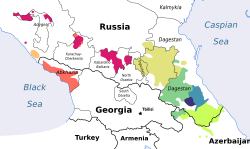
Northwest Caucasian languages
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

BudimanDidirikan1992; 32 tahun lalu (1992)PendiriH. Saleh BudimanKantor pusatJl. Ir. H. Juanda no. 31, Indihiang, Tasikmalaya, Jawa BaratWilayah layananJawaJenis layananBus AntarkotaBus PariwisataShuttleTaksiKargoKelasKelas SatuKelas PrimerEksekutifBisnisGarasiTasikmalaya, Bandung, Banjarsari, Karangpucung dan PangandaranArmadaMercedes-BenzRute terpendekBandung-TasikmalayaRute terpanjangSukabumi-YogyakartaJenis bahan bakarSolarOperatorPT HS Budiman 45CEODede SudrajatSitus webSitus resmi ...

Air Tahiti Nui IATA ICAO Kode panggil TN THT TAHITI NUI Didirikan31 Oktober 1996Mulai beroperasi20 November 1998PenghubungBandar Udara Internasional Faa'aProgram penumpang setiaClub TiareLounge bandaraInternational LoungeArmada5Tujuan4SloganWhere the Journey BeginPerusahaan indukPemerintah Polinesia PrancisKantor pusatImmeuble Dexter-Pont de L’Est, Papeete,Tokoh utamaEtienne Howan (CEO)Situs webhttps://www.airtahitinui.com Air Tahiti Nui adalah maskapai penerbangan nasional Polinesia Pranci...

Jacob MosselJacob Mossel Gubernur Jenderal Hindia Belanda ke-28Masa jabatan1 November 1750 – 15 Mei 1761 PendahuluGustaaf Willem baron van ImhoffPenggantiPetrus Albertus van der Parra Informasi pribadiLahir28 November 1704 Enkhuizen, Republik BelandaMeninggal15 Mei 1761 (umur 56 tahun) Batavia, Hindia BelandaSunting kotak info • L • B Jacob Mossel (28 November 1704 – 15 Mei 1761) adalah Gubernur-Jenderal Hindia Belanda yang ke-28. Ia memerintah antara ...

Bandar Udara Internasional Ferenc Liszt BudapestBudapest Liszt Ferenc Nemzetközi RepülőtérIATA: BUDICAO: LHBPInformasiJenisPublikPemilik/PengelolaBudapest Airport Ltd.[1]MelayaniWilayah metropolitan BudapestLokasi16 km (9,9 mi) south-east of center of BudapestMaskapai penghubung Smartwings Hungary Wizz Air Ketinggian dpl151 mdplKoordinat47°26′22″N 019°15′43″E / 47.43944°N 19.26194°E / 47.43944; 19.26194Koordinat: 47°26′22�...

Extinct species of reptile SilvisaurusTemporal range: Early-Late Cretaceous, 104–93.5 Ma PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Skull Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Clade: Dinosauria Clade: †Ornithischia Clade: †Thyreophora Clade: †Ankylosauria Family: †Nodosauridae Subfamily: †Nodosaurinae Genus: †SilvisaurusEaton, 1960 Species: †S. condrayi Binomial name †Silvisaurus condrayiEaton, 1960 Silvisaurus, from the Latin ...

2022 FIFA World Cup qualification (UEFA)Tournament detailsDates24 March 2021 – 5 June 2022Teams55 (from 1 confederation)Tournament statisticsMatches played258Goals scored781 (3.03 per match)Attendance3,036,083 (11,768 per match)Top scorer(s) Harry Kane Memphis Depay(12 goals each)← 2018 2026 → International football competition UEFA European Qualifiers FIFA World Cup 1958 1962 1966 1970 1974 1978 1982 1986 1990 1994 1998 2002 2006 2010 2014 2018 2022 2026 UE...

For the former KIRO-FM at 100.7 MHz, see KKWF. Radio station in Tacoma, WashingtonKIRO-FMTacoma, WashingtonBroadcast areaPuget Sound region, WashingtonFrequency97.3 MHz (HD Radio)BrandingKIRO Newsradio 97.3 FM(KIRO pronounced as Cairo)ProgrammingFormatNews/talkSubchannelsHD2: Sports (KIRO simulcast)HD3: Conservative talk (KTTH simulcast)AffiliationsCBS News RadioCompass Media NetworksPremiere NetworksKIRO-TVSeattle Seahawks Radio NetworkOwnershipOwnerBonneville International(Bonneville Intern...

2008 film directed by Joe Conti Army of the DeadDirected byJoseph ContiWritten by Michael Ciccolini Tom Woosley Produced by Joseph Conti Paul Conti Fred Tepper Starring Ross Kelly Stephanie Marchese Miguel Martinez CinematographyJohn GraceEdited byRichard ByardJoseph ContiMusic byWilliam T. StrombergProductioncompanyContifilmsDistributed byMaverick Entertainment GroupRelease date January 15, 2008 (2008-01-15) (US) Running time90 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglish Ar...

Wagering of money on a game of chance or event with an uncertain outcome Several terms redirect here. For other uses, see Gamble (disambiguation), Gambler (disambiguation), Betting (disambiguation), and Bets (disambiguation). Caravaggio, The Cardsharps (c. 1594), depicting card sharps. Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of value (the stakes) on a random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of ...

Participation in the Kyoto Protocol Annex B parties with binding targets in the second period Annex B parties with binding targets in the first period but not the second non-Annex B parties without binding targets Annex B parties with binding targets in the first period but which withdrew from the Protocol Signatories to the Protocol that have not ratified Other UN member states and observers that are not party to the Pr...

Voce principale: Martiri del Vietnam. San Théophane Vénard Sacerdote e martire NascitaPoitiers, 21 febbraio 1829 MorteHanoi, 2 febbraio 1861 (31 anni) Venerato daChiesa cattolica Beatificazione1909 Canonizzazioneda papa Giovanni Paolo II nel 1988 Ricorrenza2 febbraio Manuale Théophane Vénard (Poitiers, 21 febbraio 1829 – Hanoi, 2 febbraio 1861) è stato un presbitero e missionario francese, morto martire nel Vietnam. Beatificato nel 1909, è stato proclamato santo da pa...

Городская клиническая больница № 23 Расположение Таганский район Дата основания 1878 Главный врач Васильева Елена Юрьевна Сайт gkb-23.ru Медиафайлы на Викискладе Ворота — первоклассный памятник московского ампира Городская клиническая больница № 23 (ГКБ им. И. �...

Biological process in primates Breast development, also known as mammogenesis, is a complex biological process in primates that takes place throughout a female's life. It occurs across several phases, including prenatal development, puberty, and pregnancy. At menopause, breast development ceases and the breasts atrophy. Breast development results in prominent and developed structures on the chest known as breasts in primates, which serve primarily as mammary glands. The process is mediated by...

この名前は、ポルトガル語圏の人名慣習に従っています。第一姓(母方の姓)はヴァス、第二姓(父方の姓)はレアルです。 ブランコ 名前本名 クラウジオ・イブライム・ヴァス・レアルCláudio Ibraim Vaz Lealラテン文字 Branco基本情報国籍 ブラジル生年月日 (1964-04-04) 1964年4月4日(60歳)出身地 リオグランデ・ド・スル州バジェ選手情報ポジション DF(LB)ユース バゲ グアラ...

Парк «Ибирапуэра»порт. Parque do Ibirapuera Обелиск Сан-Паулу в парке Основная информация Площадь140 га Дата основания1954 год parqueibirapuera.org Расположение 23°35′18″ ю. ш. 46°39′32″ з. д.HGЯO Страна Бразилия ГородСан-Паулу Парк «Ибирапуэра» Медиафайлы на Викисклад...

Fernpass Passhöhe, Blick nach Osten Passhöhe, Blick nach Osten Himmelsrichtung Nord Süd Passhöhe 1216 m ü. A. Bezirk Reutte, Tirol Imst Wasserscheide Loisach Briglbach, Gurglbach Talorte Biberwier Nassereith Ausbau Fernpassstraße Gebirge Lechtaler Alpen (W)Mieminger Gebirge (O) Karte Fernpass (Österreich) Koordinaten 47° 21′ 45″ N, 10° 49′ 52″ O47.362510.8311216Koordinaten: 47° 21′ 45″ N, 10° 49′ 5...

Study of the development of social production For the study of political economy on an international level, see International political economy. For the study of political science through economic analysis, see Public choice theory. For the effects of politics on the economy, see Economic policy. Part of a series onEconomics History Outline Index Branches and classifications Applied Econometrics Heterodox International Micro / Macro Mainstream Mathematical Methodology Political JEL classifica...

Victor-Amédée II (it) Vittorio Amedeo II Portrait de Victor-Amédée II en 1728 par Martin van Meytens. Titre Roi de Sardaigne 17 février 1720 – 3 septembre 1730(10 ans, 6 mois et 17 jours) Prédécesseur Charles III Successeur Charles-Emmanuel III Roi de Sicile(Victor-Amédée Ier) 22 septembre 1713 – 17 février 1720(6 ans, 4 mois et 26 jours) Prédécesseur Philippe IV Successeur Charles IV Prince de Piémont et Duc de Savoie 12 juin 1675 – 3 septemb...

Harriet Shaw WeaverHarriet Shaw Weaver pada 1907Lahir(1876-09-01)1 September 1876Frodsham, Cheshire, Inggris, Britania RayaMeninggal14 Oktober 1961(1961-10-14) (umur 85)Saffron Walden, Essex, Inggris, Britania RayaKebangsaanBritania RayaPendidikanPrivatPekerjaanAktivis politik, penyunting jurnalOrang tuaDr Frederic Poynton WeaverMary (née Wright) WeaverHarriet Shaw Weaver (1 September 1876 – 14 Oktober 1961) adalah seorang aktiv politik dan penyunting majalah asal Inggr...

Public space in ancient Greek cities This article is about the ancient marketplace. For other uses, see Agora (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Agora – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) View of the Ancient A...