The Return of the King (1980 film)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Albenga (disambigua). Albengacomune Albenga – VedutaPanorama di Albenga LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Liguria Provincia Savona AmministrazioneSindacoRiccardo Tomatis (liste civiche di centro-sinistra) dal 9-6-2019 Data di istituzione1861 TerritorioCoordinate44°02′56.81″N 8°12′46.86″E / 44.049114°N 8.213017°E44.049114; 8.213017 (Albenga)Coordinate: 44°02′56.81″N 8°...

Strada extraurbana principale o strada di tipo B, meglio conosciuta come superstrada, è un tipo di strada definito all'interno del codice stradale italiano. Indice 1 Caratteristiche 2 Restrizioni al transito 3 Limiti di velocità 4 Classificazione amministrativa e segnaletica 5 Tipologie di strade omologhe in altri paesi 6 Note 7 Voci correlate 8 Altri progetti 9 Collegamenti esterni Caratteristiche La Variante Aurelia della Strada statale 1, classificata come strada extraurbana principale �...

Tugu PahlawanNama sebagaimana tercantum dalamSistem Registrasi Nasional Cagar Budaya Cagar budaya IndonesiaPeringkatNasionalKategoriStrukturNo. RegnasRNCB.20140117.03.000015LokasikeberadaanSurabaya, Jawa TimurTanggal SK1996 & 2014Pemilik IndonesiaPengelolaUPTD Tugu Pahlawan dan Museum Sepuluh NovemberTugu PahlawanLokasi Tugu Pahlawan di Kota Surabaya Tugu Pahlawan adalah sebuah monumen yang menjadi markah tanah Kota Surabaya. Tinggi monumen ini adalah 41,15 meter dan berbentuk lingga...

Medical conditionApraxiaApraxia is characterized by loss of the ability to execute or carry out learned purposeful movements.SpecialtyNeurology, psychiatryTreatmentOccupational therapy, physical therapy Apraxia is a motor disorder caused by damage to the brain (specifically the posterior parietal cortex or corpus callosum[1]), which causes difficulty with motor planning to perform tasks or movements. The nature of the damage determines the disorder's severity, and the absence of senso...

Biduk-BidukKecamatanKantor kecamatan Biduk-BidukNegara IndonesiaProvinsiKalimantan TimurKabupatenBerauPemerintahan • Camat...Populasi • Total5,631 jiwaKode Kemendagri64.03.08 Kode BPS6405030 Luas3.002,99 km²Desa/kelurahan6/- Danau Labuan Cermin di wilayah Biduk-Biduk. Biduk-Biduk adalah salah satu kecamatan di Kabupaten Berau, Provinsi Kalimantan Timur, Indonesia yang terdiri dari 6 desa. Kekayaan hayati Kecamatan yang terletak di ujung timur Kabupaten Berau ini ...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Il segno del comando (disambigua). Il segno del comandoLa sigla d'aperturaPaeseItalia Anno1971 Formatominiserie TV Generegiallo, fantastico Puntate5 Durata60 min (ad episodio) Lingua originaleitaliano Dati tecniciB/N1.33:1 (4/3) CreditiIdeatoreFlaminio Bollini e Dante Guardamagna RegiaDaniele D'Anza SceneggiaturaGiuseppe D'Agata, Flaminio Bollini, Dante Guardamagna e Lucio Mandarà Interpreti e personaggi Ugo Pagliai: Lancelot ...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento attori italiani non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Luigi Cimara Luigi Cimara (Roma, 19 luglio 1891 – Roma, 26 gennaio 1962) è stato un attore italiano di cinema, televisione, radio e teatro. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Filmografia parziale 3 Prosa radiofonica ...

American professional golfer Rose ZhangZhang in 2020Personal informationBorn (2003-05-24) May 24, 2003 (age 20)Arcadia, California, U.S.Height5 ft 6.5 in (169 cm)Sporting nationality United StatesResidenceIrvine, California, U.S.CareerCollegeStanford UniversityTurned professional2023Current tour(s)LPGA Tour (joined 2023)Professional wins1Number of wins by tourLPGA Tour1Best results in LPGA major championshipsChevron ChampionshipT11: 2020Women's PGA C'shipT8: 2023U.S. ...

Football clubDeportivo PucallpaFull nameClub Deportivo PucallpaFounded1946GroundAliardo Soria Pérez, PucallpaCapacity15,000LeagueCopa Perú Home colours Away colours Deportivo Pucallpa is a Peruvian football club, playing in the city of Pucallpa, Ucayali, Peru. History They were originally called Deportivo COOPTRIP,[1] and played in the 1985 Torneo Descentralizado. The club participated in 1985 Torneo Descentralizado until 1986 Torneo Descentralizado when was relegated. Deportivo Puc...

Governor of California This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Romualdo Pacheco – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Romualdo Pacheco12th Governor of CaliforniaIn officeFebruary 27, 1875 – December 9, 1875LieutenantWilli...

Знак «Для цветных», зал ожидания пассажиров в штате Джорджия, 1943 год Расовая сегрегация в США — отделение белого населения США от иных этнических групп (главным образом чернокожих и индейцев). Осуществлялась через различные социальные преграды: раздельное обучение и ...

هذه المقالة عن ولاية بجاية. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع بجاية (توضيح). ولاية بجاية ولاية بجايةولاية بجاية ولاية بجاية الإدارة عاصمة الولاية بجاية رمز الولاية 06 ولاية منذ 1974 الموقع الرسمي Wbejaia.gov.dz بعض الأرقام مساحة 3223.50 كم² (37) تعداد السكان 912577 نسمة (12) إحصاء سنة 2008 م كثافة 276 نسمة/�...
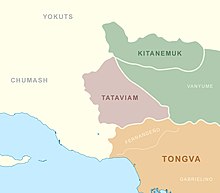
Native American group in Southern California, United States For the language, see Tataviam language. TataviamThe general area where the Tataviam language was spoken prior to European colonization (shown in red)Regions with significant populations United States ( California)LanguagesEnglish, Spanish formerly TataviamReligionTraditional tribal religion, ChristianityRelated ethnic groupsTongva, Chumash, Serrano, Kitanemuk, Luiseño, Vanyume The Tataviam (Kitanemuk: people on the south slope) are...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (نوفمبر 2019) الدوري التشيكي لكرة القدم 1993–94 تفاصيل الموسم الدوري التشيكي لكرة القدم النسخة 1 البلد جمهورية الت...
هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (نوفمبر 2019) بطولة الأمم الخمس 1982 تفاصيل الموسم بطولة الأمم الست النسخة 88 التاريخ بد...

习近平 习近平自2012年出任中共中央总书记成为最高领导人期间,因其废除国家主席任期限制、开启总书记第三任期、集权统治、公共政策与理念、知识水平和自述经历等争议,被中国大陸及其他地区的民众以其争议事件、个人特征及姓名谐音创作负面称呼,用以恶搞、讽刺或批评习近平。对习近平的相关负面称呼在互联网上已经形成了一种活跃、独特的辱包亚文化。 权力�...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant une localité du Nouveau-Mexique. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. AlamogordoNom officiel (en) AlamogordoNom local (en) AlamogordoGéographiePays États-UnisÉtat Nouveau-MexiqueComté comté d'Otero (siège)Superficie 55,43 km2 (2020)Surface en eau 0,06 %Altitude 1 323 mCoordonnées 32° 54′ 17″ N, 105° ...

倫敦的一個垃圾搜尋者 垃圾搜尋(dumpster diving)、垃圾桶尋寶、翻垃圾桶等,是指從別人拋棄的東西(有時不一定是垃圾桶)中收集自己有用的東西(例如食物)作為自己用途。進行這種行為的人不一定是因為貧窮,部份人是為了響應環境保護意識,更有部份人是以抗議及痛心資本主義社會的浪費;甚至有視之為嗜好者。 垃圾搜尋是一種行為,從垃圾堆中搜尋個人喜好的「寶�...

Vietnamese fermented pork dish Nem chua Nem chua is a fermented pork dish from Vietnamese cuisine.[1] It is mainly composed of a mixture of lean pork and thin strips of cooked rind, garnished with garlic and chilli. It can take the form of bite-size pieces wrapped individually in aluminum foil and paper, or a kind of cervelat in sealed plastic. Traditionally the leaves of star gooseberry tree (chùm ruột), strawberry guava (cây ổi, ổi sẻ), cluster fig (sung), Ming aralia (đi...

George Digby, II conte di BristolRitratto di George Digby, II conte di Bristol di Antoon van Dyck, 1638 circa, Dulwich Picture GalleryConte di BristolStemma In carica1653 –1676 PredecessoreJohn Digby, I conte di Bristol SuccessoreJohn Digby, III conte di Bristol NascitaMadrid, 22 febbraio 1612 MorteLondra, 20 maggio 1677 (65 anni) DinastiaDigby PadreFrancis Digby, I conte di Bristol MadreBeatrice Walcott ConsorteAnne Russell Religioneanglicanesimo poi cattolicesimo George Di...

