火星的地下水
|
Read other articles:

Brad Guzan Guzan saat bermain untuk Hull CityInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Bradley Edwin Guzan[1]Tanggal lahir 9 September 1984 (umur 39)Tempat lahir Evergreen Park, Illinois, United StatesTinggi 6 ft 4 in (1,93 m)Posisi bermain penjaga gawangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Atlanta UnitedNomor 1Karier junior2003–2004 South Carolina GamecocksKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2004 Chicago Fire Premier 13 (0)2005–2008 Chivas USA 79 (0)2008–2016 Aston Villa 144 (0...

Thai Catholic prelate and cardinal His EminenceFrancis Xavier Kriengsak KovitvanitCardinal, Archbishop of BangkokKovitvanit as cardinalNative nameฟรังซิสเซเวียร์ เกรียงศักดิ์ โกวิทวาณิช[citation needed]ChurchRoman Catholic ChurchArchdioceseBangkokSeeBangkokAppointed14 May 2009Installed16 August 2009PredecessorMichael Michai KitbunchuOther post(s)Cardinal-Priest of Santa Maria AddolorataOrdersOrdination11 July 19...

DukuhturiKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan DukuhturiNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenTegalKode Kemendagri33.28.13 Kode BPS3328130 Desa/kelurahan18 Dukuhturi (Jawa: ꦢꦸꦏꦸꦃꦠꦸꦫꦶ) adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Tegal, Jawa Tengah, Indonesia. Kecamatan Dukuhturi berbatasan dengan Kota Tegal di sebelah utara, Kecamatan Kramat dan Talang di timur, Kecamatan Adiwerna di selatan dan Kabupaten Brebes di barat. Pembagian administratif Dukuhturi terdiri dari 18 des...

Species of bat Robust yellow bat Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Chiroptera Family: Vespertilionidae Genus: Scotophilus Species: S. robustus Binomial name Scotophilus robustusMilne-Edwards, 1881 Robust yellow bat range The robust yellow bat (Scotophilus robustus) is a species of vesper bat. It is found only in Madagascar. References ^ Monadjem, A.; Razafiman...

Town in Florida, United States Town in FloridaLauderdale-by-the-SeaTownTown of Lauderdale-by-the-SeaThe beach is the main visitor attraction of Lauderdale-by-the-SeaNickname: LBTSLocation of Lauderdale-by-the-Sea in Broward County, FloridaCoordinates: 26°11′22″N 80°5′52″W / 26.18944°N 80.09778°W / 26.18944; -80.09778Country United StatesState FloridaCountyBrowardSettledc. 1920s–1924[1]IncorporatedNovember 30, 1927[1][2&#...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori rumeni è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Marcel Răducanu Răducanu nel 2014 Nazionalità Romania Altezza 178 cm Peso 74 kg Calcio Ruolo Centrocampista offensivo Carriera Giovanili 1964-1972 Steaua Bucarest Squadre di club1 1972-1981 Steaua Bucarest229 (94)1982-1988 Borussia Dortmund163 (31)1988-1990 Zurigo47 (12) Nazionale 1...

Airline of the United States IBC Airways IATA ICAO Callsign II CSQ CHASQUI Founded1991HubsMiami International AirportFleet size13Destinations13HeadquartersFort Lauderdale, Florida, United StatesKey peopleJoe Costigan, PresidentWebsitewww.ibcairways.comwww.flyibcair.com IBC Airways is an FAR Part 135 on-demand airline headquartered in unincorporated Broward County, Florida, near Fort Lauderdale.[1] IBC Airways operates on-demand cargo services to the Caribbean. Its main base is Miami I...
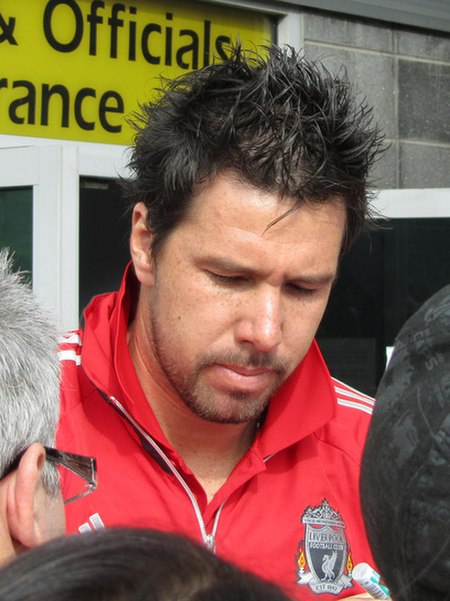

Doni Doni pada tahun 2011Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Doniéber Alexander Marangon[1]Tanggal lahir 22 Oktober 1979 (umur 44)Tempat lahir Jundiaí, São Paulo, BrasilTinggi 194 m (636 ft 6 in)Posisi bermain Penjaga gawangKarier junior1999–2001 Botafogo-SPKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2001 Botafogo-SP 0 (0)2001–2003 Corinthians 59 (0)2004 Santos 0 (0)2004–2005 Cruzeiro 6 (0)2005 Juventude 20 (0)2005–2011 Roma 147 (0)2011–2013 Liverpool 4 (0)2013 Bot...

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. You can help. The talk page may contain suggestions. (August 2023) Myneni Hariprasada Rao, (Edlalanka, 21 July 1927 – 5 April 2016) was a retired Director of the Nuclea...

Biografi ini memerlukan lebih banyak catatan kaki untuk pemastian. Bantulah untuk menambahkan referensi atau sumber tepercaya. Materi kontroversial atau trivial yang sumbernya tidak memadai atau tidak bisa dipercaya harus segera dihapus, khususnya jika berpotensi memfitnah.Cari sumber: Kuntz Agus – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Kuntz AgusLahirAgus NugrohoBoyolali, I...

Запрос «Пугачёва» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. Алла Пугачёва На фестивале «Славянский базар в Витебске», 2016 год Основная информация Полное имя Алла Борисовна Пугачёва Дата рождения 15 апреля 1949(1949-04-15) (75 лет) Место рождения Москва, СССР[1]...

Archaeological site in Xiangfen County, Shanxi, China Taosi陶寺Location in north ChinaLocationChinaRegionShanxiCoordinates35°53′26.17″N 111°29′49.82″E / 35.8906028°N 111.4971722°E / 35.8906028; 111.4971722Area280 haHistoryFoundedc. 2300 BCAbandonedc. 1900 BCCulturesLongshan culture A painted pottery jar excavated from the Taosi site. Exhibit of the Shanxi Museum. Taosi (Chinese: 陶寺; pinyin: Táosì) is an archaeological site in Xia...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Aleaume. Aléaume de Burgos Saint catholique Tombeau de San Lesmes à Burgos saint Naissance vers 1035Loudun (Vienne) Décès 1097 à Burgos (Espagne) Ordre religieux Ordre de Saint-Benoît Vénéré à Burgos Fête 30 janvier Attributs Mitre, livre, crosse Saint patron Burgos et Loudun modifier Aléaume († 1097) (Alleaume, Lesmes en espagnol, Adelhem en germanique ou Adelelme en espagnol médiéval) est un saint chrétien fêté le 30 janvier....

此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2021年5月6日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 约翰斯顿环礁Kalama Atoll 美國本土外小島嶼 Johnston Atoll 旗幟颂歌:《星條旗》The Star-Spangled Banner約翰斯頓環礁�...

English botanist and zoologist (1751–1813) George ShawBornGeorge Kearsley Shaw(1751-12-10)10 December 1751Bierton, BuckinghamshireDied22 July 1813(1813-07-22) (aged 61)LondonNationalityEnglishAlma materMagdalen College, Oxford (MA)Scientific careerFieldsBotany, ZoologyInstitutionsUniversity of Oxford George Kearsley Shaw[1] (10 December 1751 – 22 July 1813) was an English botanist and zoologist. Life Shaw was born at Bierton, Buckinghamshire, and was educated at Magdalen...

San Beda il VenerabileThe Last Chapter di James Doyle Penrose, 1902, Royal Academy of Arts Dottore della Chiesa Nascita672-673 circa MorteJarrow, 26 maggio 735 Venerato daTutte le Chiese cristiane che ammettono il culto dei santi Canonizzazione13 novembre 1899 da papa Leone XIII Ricorrenza23, 25 e 27 maggio Patrono distudiosi Manuale Beda, anche noto come Beda il Venerabile (in latino Beda Venerabilis, in antico inglese Baeda o Bēda; 672-673 circa – Jarrow, 26 maggio 735), ...

Swimsuit, clothing, equipment and accessories used in the aquatic competitive sports A mixed-sex pair in their swimsuits, participating in FINA World Championships of synchronised swimming.A woman wearing a racing competitive racerback bikini Competitive swimwear refers to the swimsuit, clothing, equipment, and accessories used in the aquatic sports of swimming, diving, synchronized swimming, triathlon, and water polo. Some swimsuits are designed specifically for swimming competitions where t...
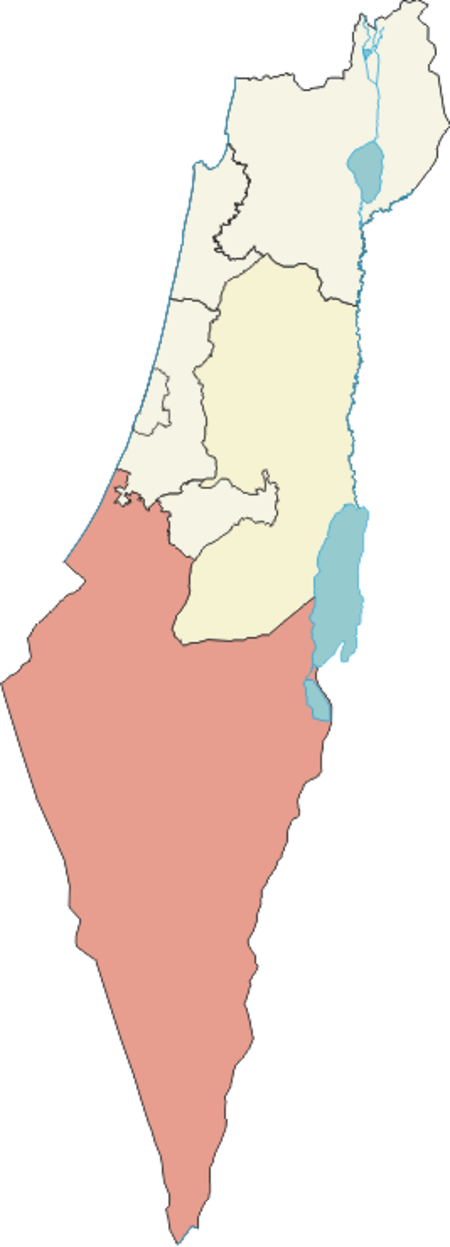
عنتالمنطقة الجنوبية في إسرائيلمدن عراد أشدود عسقلان بئر السبع ديمونا إيلات كريات جات كريات ملاخي نتيفوت أوفاكيم رهط سديروت مجالس محلية عرعرة النقب حورة كسيفة اللقية لهافيم ميتار متسبي ريمون عومر شقيب السلام تل السبع يروحام المجالس الإقليمية القيصوم بير توفيا بني شمعون و...

Austrian composer (1819–1895) Suppé, 1846 Franz von Suppé, born Francesco Ezechiele Ermenegildo de Suppé (18 April 1819 – 21 May 1895) was an Austrian composer of light operas and other theatre music. He came from the Kingdom of Dalmatia, Austro-Hungarian Empire (now part of Croatia). A composer and conductor of the Romantic period, he is notable for his four dozen operettas, including the first operetta to a German libretto. Some of them remain in the repertory, particula...

وسام القديسة حنة Star of the Order مؤسس الإمبراطورية الروسية البلد الإمبراطورية الروسية يُمنح من طرف رئيس بيت رومانوف سميت باسم حنة، وآنا بيتروفنا نوع الوسام ترتيب الأسرة الحالة نادرًا ما يتم منحها المراتب الدرجة الأولى والثانية والثالثة ، مع ميدالية آنا الممنوحة �...



















