Rustam Muradov
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يونيو 2019) نورشهرول إدلان معلومات شخصية الميلاد 8 يونيو 1986 (العمر 37 سنة)بسوت [لغات أخرى] الطول 1.72 م (5 قدم 7 1⁄2 بوصة) مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية مال�...

هذه المقالة عن جمهورية غينيا أو غينيا كوناكري. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع غينيا (توضيح). جمهورية غينيا République de Guinée (فرنسية) غينياعلم غينيا غينياشعار غينيا الشعار الوطنيعمل وعدل وإخاء النشيد: نشيد غينيا الوطني الأرض والسكان إحداثيات 10°N 11°W / 10°N 11°W / 10; -11 ...

Olahraga elektronik pada Pesta Olahraga Asia 2018LokasiBritAma ArenaJakartaTanggal26 Agustus – 1 September 2018Jumlah disiplin6Peserta131 dari 18 negara2022 → Olahraga elektronik padaPesta Olahraga Asia 2018Turnamen Arena of Valor Clash Royale Hearthstone League of Legends Pro Evolution Soccer StarCraft IIlbs Olahraga elektronik pada Pesta Olahraga Asia 2018 adalah pelaksanaan cabang olahraga olahraga elektronik pada penyelenggaraan Pesta Olahraga Asia 2018 sebagai...

Pseudohistorical theory according to which Belarusians founded the Grand Duchy of Lithuania Map of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the main foundation of the Litvin identity, at its greatest extent from the 13th to 15th centuries. Litvinism (Belarusian: Літвінізм, romanized: Litvinizm; Russian: Литвинизм, romanized: Litvinizm) is a branch of nationalism, philosophy and political current in Belarus, which bases the history of its state on the heritage of the Grand Duc...

Route of Via Praenestina from Rome in a map of ancient Latium. Roman Ponte di Nona Ponte amato Via Praenestina near Ponte Amato The Via Praenestina (modern Italian: Via Prenestina) was an ancient Roman road in central Italy. Initially called Via Gabiana, from Gabii, the ancient city of Old Latium to which it ran, it received a new name having been extended as far as Praeneste (modern Palestrina). Once past Praeneste the road continued towards the Apennines and the source of the Anio River. At...

Unicameral legislature of the Indian state of Kerala Niyamasabha redirects here. For the building that houses the Niyamasabha, see Niyamasabha Mandiram. This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (April 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Kerala Legislative Assembly Kerala Niyamasabha15th Kerala AssemblyTypeTypeUnicameral Term limits5 yearsH...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Contoh gaya talud-tablero Talud-tablero adalah langgam arsitektur yang paling lazim digunakan di landasan, kuil, dan piramida di Mesoamerika pada zaman pra-Kolumbus. Langgam ini pertama kali muncul pada zaman Klasik Awal di Teotihuacan, dan kemudian menyebar luas hingga ke wilayah peradaban Maya. Talud-tablero terdiri dari permukaan atau panel yang condong ke arah dalam yang disebut talud, dengan panel atau struktur di tengahnya yang tegak lurus dengan tanah yang disebut tablero. Referensi Br...

Period within the Cold War Part of a series onHistory of the Cold War Origins World War II Hiroshima and Nagasaki Eastern Bloc Western Bloc Iron Curtain Periods Cold War (1947–1948) Cold War (1948–1953) Cold War (1953–1962) Cold War (1962–1979) Cold War (1979–1985) Cold War (1985–1991) Frozen conflicts Related topics Arab Cold War Cold War in Asia Historiography List of related conflicts Post-Soviet conflicts Reagan Doctrine Second Cold War Timeline of events vte The Cold War from...

مؤنس الخادم معلومات شخصية تاريخ الميلاد سنة 844 [1] الوفاة سنة 933 (88–89 سنة) بغداد الحياة العملية المهنة وصي العرش الخدمة العسكرية المعارك والحروب ثورة الزنج الحروب الإسلامية البيزنطية معارك ضد القرامطة الغزو الفاطمي لمصر تعديل مصدري - تعديل أبو الحَسَ...

此條目翻譯品質不佳。 (2023年1月25日)翻譯者可能不熟悉中文或原文語言,也可能使用了機器翻譯。請協助翻譯本條目或重新編寫,并注意避免翻译腔的问题。明顯拙劣的翻譯請改掛{{d|G13}}提交刪除。 減色混合 法國彩色攝影的先驅路易斯·阿瑟·杜科斯·杜豪伦(Louis Ducos du Hauron)於1877年拍攝的阿讓市景彩色照片。可以清楚地看出以重疊消減黃色,青色以及洋紅色(紫色�...

Laboratory apparatus Clamp HolderA clamp holderOther namesClamp Fastener, Boss Head, Right Angle Clamp HolderUsesElevate and move attached clampStabilize equipmentComponentsRing stand rod jaw and extension clamp jaw A clamp holder or clamp fastener is a piece of laboratory apparatus that is used to secure laboratory clamps, such as extension-type utility clamps, or other attachments to a retort stand or lab frame.[1] The material can be made up of brass, cast iron, stainless steel, al...

СелоВерхняя Кутузовкаукр. Верхня Кутузовка, крымскотат. Yuqarı Şuma 44°43′20″ с. ш. 34°22′35″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Россия/ Украина[1] Регион Республика Крым[2]/Автономная Республика Крым[3] Район Городской округ Алушта[2]/Алуштинский горсовет[3] Истори...

Katusha-AlpecinInformationsStatuts UCI ProTeam (2009-2012)continentale pro (1er janvier - 14 février 2013)UCI ProTeam (15 février 2013 - 31 décembre 2014)UCI WorldTeam (2015-2019)Codes UCI KAT (de 2009 à 2017) et TKA (de 2018 à 2019)Discipline Cyclisme sur routePays Russie (2009-2016) Suisse (2017-2019)Création 2009Disparition 2019Saisons 11Budget 15 M€ (2014)Marque de cycles Canyon (2012-2019)EncadrementDirecteur général Viatcheslav Ekimov (2013-2016)José Azevedo (2017-2019)Direct...

Questa voce sull'argomento attori statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Gail Ann O'Grady Gail Ann O'Grady (Detroit, 23 gennaio 1963) è un'attrice statunitense, nota soprattutto per la sua partecipazione alle serie NYPD - New York Police Department, American Dreams e Hellcats, quest'ultima accanto all'attrice e cantante Ashley Tisdale. Indice 1 Filmografia parziale 1.1 Cinema 1.2...

Spiaggia di Travemünde, con le caratteristiche sedie da spiaggia a baldacchino (Strandkörbe in tedesco) Veliero Passat a Travemünde Travemünde: edifici a graticcio nell'Altstadt (città vecchia) Travemünde è un distretto di Lubecca, in Germania, alla foce del fiume Trave nella Baia di Lubecca. Famosa meta balneare del turismo locale sia attualmente che già in passato. Infatti Travemünde era un vecchio resort balneare (già dal 1802) ed è ad oggi il più grande porto di traghetti tede...

The elapsed fraction of a cycle of a periodic function Plot of one cycle of a sinusoidal function. The phase for each argument value, relative to the start of the cycle, is shown at the bottom, in degrees from 0° to 360° and in radians from 0 to 2π. In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F {\displaystyle F} of some real variable t {\displaystyle t} (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered u...
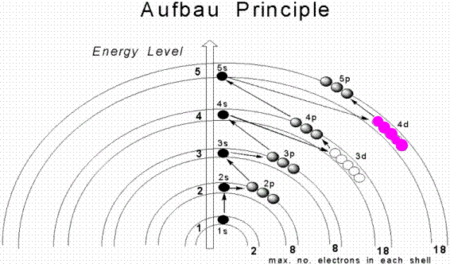
Principle of atomic physics Atomic build-up redirects here. For the spread of nuclear weapons, see Nuclear proliferation. Part of a series on thePeriodic tableElectrons occupy the shells and sub-shells of an atom in approximate accordance with the Aufbau principle. Periodic table forms 18-column 32-column Alternative and extended forms Periodic table history D. Mendeleev 1871 table 1869 predictions Discovery of elements Naming and etymology for people for places controversies (...
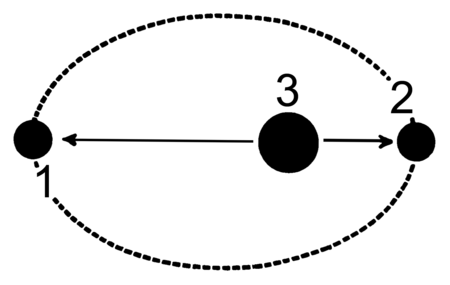
Apsidi: 1) Apoapside; 2) Periapside; 3) Fuoco dell'ellisse. Gli apsidi sono i punti di maggiore e minore distanza di un oggetto celeste dal fuoco ove giace il corpo attorno a cui esso orbita. Nella moderna meccanica celeste il fuoco è anche il centro di attrazione gravitazionale, che coincide con il centro di massa del sistema. Storicamente, nei sistemi geocentrici, gli apsidi erano misurati dal centro della Terra. Il punto di massimo avvicinamento al fuoco prende il nome di periapside o per...


