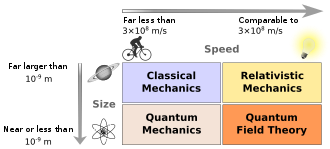
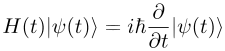Branches of physics
|
Read other articles:

Overview of crime in India Crime rate in India 2021 (crime per 100,000 population)[1]Murder2.1Rape4.8Kidnapping7.4Death by road accidents10.1Dowry deaths1.0Grievous hurt6.6Sexual harassment2.6Human trafficking0.1Riots3.1Theft42.9Burglary7.2Extortion0.8Robbery2.1Forgery, cheating & fraud11.1Drugs trafficking2.4Illegal arms3.3Crimes against children33.6Cyber crime3.9Crimes against children rate is calculated per 100,000 children population Crime in India has been recorded since the ...

Kräft Gemeinde Rügland Koordinaten: 49° 26′ N, 10° 36′ O49.43722222222210.606111111111391Koordinaten: 49° 26′ 14″ N, 10° 36′ 22″ O Höhe: 391 m ü. NHN Einwohner: 24 (Jan. 2014)[1] Postleitzahl: 91622 Vorwahl: 09828 Kräft (fränkisch: Gräft[2]) ist ein Gemeindeteil der Gemeinde Rügland im Landkreis Ansbach (Mittelfranken, Bayern).[3] Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Geografie 2 Geschichte 3 ...

كأس تونس للكرة الطائرة للرجال الموسم 2019-2020 البلد تونس المنظم الجامعة التونسية للكرة الطائرة النسخة 64 الفائز الترجي الرياضي التونسي كأس تونس للكرة الطائرة للرجال 2018–19 كأس تونس للكرة الطائرة للرجال 2020–21 تعديل مصدري - تعديل كأس تونس للكرة الطائرة للرجال 2019-2020 هو ال

Cette cathédrale n’est pas la seule cathédrale Notre-Dame. Cathédrale Notre-Dame Présentation Nom local Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Senlis Culte Catholique romain Dédicataire Notre-Dame Type Ancienne Cathédraleéglise paroissiale depuis 1801 Rattachement Diocèse de Beauvais, Noyon et Senlis Début de la construction 1153 Fin des travaux 16 juin 1191 Architecte Martin ChambigesPierre Chambiges Style dominant Gothique Protection Classée MH (1840) Site web Paroisse Saint-Rieul...

Park in Nebraska, USA Ash Hollow State Historical ParkLocation in NebraskaLocationGarden County, Nebraska, United StatesNearest townLewellen, NebraskaCoordinates41°17′53″N 102°07′12″W / 41.29806°N 102.12000°W / 41.29806; -102.12000[1]Area1,001.03 acres (405.10 ha)[2]Elevation3,363 ft (1,025 m)[1]DesignationNebraska state historical parkEstablished1962AdministratorNebraska Game and Parks CommissionWebsiteAsh Hollow...

Người Nạp Tây(Naxi, Naqxi, Na-khi, Nashi, Nahi, Moxiayi, Mosha)Tổng dân số300.000Khu vực có số dân đáng kể Trung Quốc (Tứ Xuyên · Vân Nam)Ngôn ngữNạp TâyTôn giáoĐông Ba giáo, Phật giáo Tây Tạng, Đạo giáoSắc tộc có liên quanTạng, Khương, Ma Thoa Một ngôi làng Nạp Tây gần Lệ Giang Người Nạp Tây (Giản thể: 纳西族, Phồn thể: 納西族, Bính âm: Nàxī zú, Hán Việt: Nạp Tây t

Dwi SuharjoKepala Staf Korem 132/TadulakoMasa jabatan8 Juni 2020 – 22 September 2022PenggantiBambang Pranowo Informasi pribadiLahir0 Oktober 1968 (umur 55)IndonesiaKebangsaan IndonesiaAlma materAkademi Militer (1992)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI Angkatan DaratMasa dinas1992—sekarangPangkat KolonelNRP1920025251068SatuanInfanteriPertempuran/perangOperasi TinombalaSunting kotak info • L • B Kolonel Inf. Dwi Suharjo, S.I.P. (lahir Okt...
Опис файлу Опис Постер стрічки Веном 2: Карнаж. Джерело https://www.facebook.com/SonyPicturesUkraine/photos/4707707859262746 Час створення 03.10.2021 Автор зображення Sony Ліцензія див. нижче Обґрунтування добропорядного використання для статті «Веном 2: Карнаж (2021)» [?] Мета використання в якості основ�...

Simulation of Brownian Motion sample paths is an important tool in calculating the price of financial instruments under the risk-neutral measure. Computational finance is a branch of applied computer science that deals with problems of practical interest in finance.[1] Some slightly different definitions are the study of data and algorithms currently used in finance[2] and the mathematics of computer programs that realize financial models or systems.[3] Computational f...

Laurie Metcalf (1992) Lauren Elizabeth „Laurie“ Metcalf (* 16. Juni 1955 in Carbondale, Illinois) ist eine US-amerikanische Schauspielerin. Sie wurde unter anderem mit drei Emmy Awards und zwei Tony Awards ausgezeichnet. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Leben 2 Filmografie (Auswahl) 3 Auszeichnungen und Nominierungen 4 Weblinks 5 Einzelnachweise Leben Metcalf studierte zuerst Deutsch und später Anthropologie an der Illinois State University und kam dort über ihre Kommilitonen John Malkovich, Glenne...

Genus of grasshoppers Trachyrhachys Trachyrhachys kiowa Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Orthoptera Suborder: Caelifera Family: Acrididae Subfamily: Oedipodinae Tribe: Psinidiini Genus: TrachyrhachysScudder, 1876 Trachyrhachys is a genus of band-winged grasshoppers in the family Acrididae. There are at least four described species in Trachyrhachys.[1][2][3][4] Species These four species belon...

NZ RM classClaytonClayton steam railcar on a trial run at Kurow circa 1927. A P Godber Collection, Alexander Turnbull Library.Type and originPower typeSteam (Passenger capacity: 52)BuilderClayton Carriage and Wagon of EnglandBuild date1926SpecificationsGauge3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm)Fuel typeCoalBoiler pressure275 psi (1,896 kPa)Performance figuresMaximum speed30 mph (48 km/h)CareerOperatorsNew Zealand RailwaysNumber in class1LocaleKurow BranchPreserved0Dispo...

Castello di Monte Sant'AngeloUbicazioneStato attuale Italia RegionePuglia CittàMonte Sant'Angelo IndirizzoLargo Roberto il Guiscardo, 71037 Monte Sant'Angelo Coordinate41°42′27″N 15°57′09.36″E / 41.7075°N 15.9526°E41.7075; 15.9526Coordinate: 41°42′27″N 15°57′09.36″E / 41.7075°N 15.9526°E41.7075; 15.9526 Informazioni generaliTipoCastello normanno - svevo - angioino - aragonese Inizio costruzione837 Condizione attualeRestaurato Propr...

Battle of the Campobasso ConvoyPart of the Battle of the Mediterranean of World War IIHMS Petard photographed from HMS Formidable, December 1943Date3-4 May 1943LocationOff Cape Bon, Mediterranean Sea36°45′N 10°45′E / 36.750°N 10.750°E / 36.750; 10.750Result British victoryBelligerents United Kingdom ItalyCommanders and leaders Deric Holland-Martin Saverio Marotta †Strength 3 destroyers 1 torpedo boat 1 merchantmanCasualties and ...

Spanish-language comedy-drama television series This article is about the TV series. For the 2015 song, see Como tú no hay dos (song). Como tú no hay 2GenreComedy dramaCreated byXimena SuárezBased onAmores de mercadoby Fernando Aragón and Arnaldo MadridWritten by Julián Aguilar Isabel de Sara Mauricio Jalife Directed by Luis Manzo Carlos Cock Marín Creative directorClaudia VergaraTheme music composer Stefano Vieni Jessica Díaz Chávez Opening themeComo tú no hay dos by Jessica DíazCo...

Para otros usos de este término, véase Gran Vía (desambiguación). Gran Vía de las Cortes Catalanas Barcelona Cruce de la Gran Vía con la Rambla de Cataluña.Datos de la rutaNumeración 21 al 1198Cruces calle de Entenza, paseo de San Juan, Rambla de Cataluña, calle de Pau Claris, calle de Roger de Lauria, calle de Gerona, Avenida de la Granvia de Hospitalet, Plaça d'Ildefons Cerdà, Barcelona, carretera de la Bordeta, Plaza de España, calle de Muntaner, calle de Aribau, Plaza Uni...

Paul RusesabaginaLahirPaul Rusesabagina15 Juni 1954 (umur 69)Murama, RwandaTempat tinggalSan Antonio, Texas, AS[1][2]KebangsaanRwandaSuami/istri Esther Bamurage (bercerai) Tatiana Rusesabagina (m. 1989) Penghargaan Presidential Medal of Freedom Immortal Chaplains Prize for Humanity Wallenberg Medal of the University of Michigan National Civil Rights Museum Freedom Award Tom Lantos Human Rights Prize from The Lantos Foundation for Hum...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Tri-State Mall – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Shopping mall in Delaware, U.S.Tri-State MallExterior view of Tri-State Mall, October 2014LocationClaymont, Delaware, U.S.Coordinates39...

Resolusi 13Dewan Keamanan PBBLetak Siam (Thailand)Tanggal12 Desember 1946Sidang no.83KodeS/RES/13 (Dokumen)TopikPenerimaan keanggotaan SiamRingkasan hasil11 mendukungTidak ada menentangTidak ada abstainHasilDiadopsiKomposisi Dewan KeamananAnggota tetap Tiongkok (ROC) Prancis Britania Raya Amerika Serikat Uni SovietAnggota tidak tetap Australia Brasil Mesir Meksiko Belanda Polandia Resolusi 13 Dewan Keamanan Perserikatan Bangsa-B...

German writer, psychologist and philosopher Erich NeumannBorn(1905-01-23)23 January 1905Berlin, German EmpireDied5 November 1960(1960-11-05) (aged 55)Tel Aviv, IsraelNationalityGerman and IsraeliAlma materUniversity of Erlangen–Nuremberg (PhD)University of Berlin (MD)Known forDevelopmental psychologyScientific careerFieldsPsychology Erich Neumann (Hebrew: אריך נוימן; 23 January 1905 – 5 November 1960)[1] was a German psychologist, philosopher, writer, and s...