Friedrich Schlegel
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Arian13LahirArian Arifin Wardiman1 Agustus 1974 (umur 49)Bandung, IndonesiaPekerjaanMusisiSenimanPengusahaTahun aktif1992 - sekarangKarier musikGenreHardcore punkstoner rockstoner metalArtis terkaitSeringai PuppenAnggotaSeringaiMantan anggotaPuppen Arian Arifin Wardiman[1] (lahir 01 Agustus 1974)[2] adalah seorang musisi dan ilustrator berkebangsaan Indonesia. Ia dikenal sebagai pendiri dan vokalis grup hard rock Seringai. Masa Kecil Kakek Arian dari sisi ibunya ada...

Nama ini menggunakan cara penamaan Spanyol: nama keluarga pertama atau paternalnya adalah González dan nama keluarga kedua atau maternalnya adalah Fernández. Eva GonzálezLahirEva Maria González Fernández5 November 1980 (umur 43)Seville, SpainPemenang kontes kecantikanGelarMiss Spanyol 2003Warna rambutCoklatWarna mataHijau Eva María González Fernández (lahir 5 November 1980) adalah seorang aktris, presenter televisi dan pemenang kontes kecantikan yang mewakili Spanyol di kont...

Charli D'AmelioD'Amelio pada 2020LahirCharli Grace D'Amelio1 Mei 2004 (umur 19)Norwalk, Connecticut, Amerika SerikatPekerjaanPenyiar media sosialpenariTahun aktif2019–kiniDikenal atasTikTokOrang tuaMarc D'AmelioHeidi D'AmelioKerabatDixie D'Amelio (saudari)Informasi YouTubeKanalcharli d'amelioTahun aktif2019–kiniGenreVlogPelanggan6.58 jutaTotal tayang109.2 juta Penghargaan Kreator 100.000 pelanggan 2019[1] 1.000.000 pelanggan 2020[1] Diperbarui: 20 Agus...

Sebuah huruf awal teriluminasi dalam naskah bersejarah Dalam karya tulis atau terbitan, huruf awal atau inisial adalah huruf pertama dari kata, bab atau paragraf yang ukurannya dibuat jauh lebih besar daripada ukuran huruf-huruf selebihnya. Istilah inisial berasal dari kata Latin initialis, yang artinya berdiri di awal. Huruf awal sering kali dibuat setinggi beberapa baris tulisan, dan huruf awal dalam buku-buku atau naskah-naskah lama kadang-kadang diperindah dengan hiasan-hiasan tambahan. B...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il duca di Lorena che regnò negli anni 1544-1545, vedi Francesco I di Lorena (duca). Francesco I di LorenaRitratto dell'imperatore Francesco I di Lorena di Martin van Meytens, 1745 circa, Österreichische Galerie Belvedere, Vienna.Imperatore Eletto dei RomaniStemma In carica13 settembre 1745 –18 agosto 1765 PredecessoreCarlo VII di Wittelsbach SuccessoreGiuseppe II d'Asburgo-Lorena Arciduca consorte d'AustriaRe consorte di Boemia e UngheriaIn cari...

The HonourableTony AbbottACAbbott pada 2010 Perdana Menteri Australia ke-28Masa jabatan18 September 2013 – 15 September 2015Penguasa monarkiElizabeth IIGubernur JenderalQuentin BrycePeter CosgroveWakilWarren Truss PendahuluKevin RuddPenggantiMalcolm TurnbullPemimpin Oposisi ke-32Masa jabatan1 Desember 2009 – 18 September 2013WakilJulie Bishop PendahuluMalcolm TurnbullPenggantiChris BowenPemimpin Partai Liberal ke-13Masa jabatan1 Desember 2009 – 14 Septembe...

Town in Virginia, United StatesNassawadox, VirginiaTownLocation in Northampton County and the state of Virginia.Coordinates: 37°28′27″N 75°51′29″W / 37.47417°N 75.85806°W / 37.47417; -75.85806CountryUnited StatesStateVirginiaCountyNorthamptonArea[1] • Total0.66 sq mi (1.72 km2) • Land0.66 sq mi (1.72 km2) • Water0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2)Elevation36 ft (11 m)Popul...

Cristiano Piccini Informasi pribadiTanggal lahir 26 September 1992 (umur 31)Tempat lahir Firenze, ItaliaTinggi 1,90 m (6 ft 3 in)Posisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini Betis (pinjaman dari Fiorentina)Nomor 12Karier junior FiorentinaKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2010– Fiorentina 1 (0)2011–2012 → Carrarese (pinjaman) 32 (1)2012-2013 → Spezia (pinjaman) 26 (0)2013–2014 → Livorno (pinjaman) 13 (0)2014– → Betis (pinjaman) 0 (0)Tim nasional‡2011 I...

Equestrian rodeo sport Chuckwagon racingChuckwagons racing toward the finish line at the 2009 Calgary StampedeCharacteristicsTypeEquestrian rodeo sportPresenceOlympicNoParalympicNoWorld GamesNo Chuckwagon racing is an equestrian rodeo sport in which drivers in a chuckwagon led by a team of Thoroughbred horses race around a track. The sport is most popular in the Prairie Provinces of Canada, where the World Professional Chuckwagon Association and the Canadian Professional Chuckwagon Associatio...
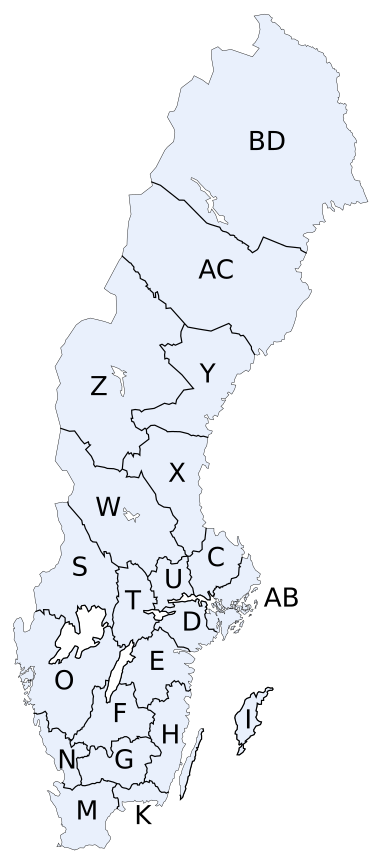
Entry for Sweden in ISO 3166-2 Administrative divisions of Sweden Counties of Sweden Administrative boards Regions Municipalities of Sweden List of municipalities Other divisions Historical divisions (Lands and Provinces) Statistical regions ISO codes for subdivisions Sweden portalvte ISO 3166-2:SE is the entry for Sweden in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which defines codes for the names of the princi...

Bagian dari seriSastra Hindu Weda Regweda Samaweda Yajurweda Atharwaweda Pembagian Weda Samhita Brahmana Aranyaka Upanisad Upanisad Aitareya Brihadaranyaka Isa Taittiriya Chandogya Kena Mundaka Mandukya Prasna Swetaswatara Wedangga Siksha Chanda Wyakarana Nirukta Jyotisha Kalpa Itihasa Mahabharata Ramayana Susastra lainnya Smerti Purana Bhagawadgita Sutra Pancaratra Tantra Kumarawyasabharata Stotra Hanumancalisa Ramacaritamanasa Shikshapatri Wacanamruta Portal agama Hindulbs Bhagawadgita (San...

Steel roller coaster at Dorney Park Steel ForceSteel Force at Dorney Park & Wildwater Kingdom in Allentown, PennsylvaniaDorney Park & Wildwater KingdomLocationDorney Park & Wildwater KingdomCoordinates40°34′44″N 75°32′17″W / 40.57889°N 75.53806°W / 40.57889; -75.53806StatusOperatingOpening dateMay 30, 1997CostUS$10,000,000General statisticsTypeSteelManufacturerD. H. Morgan ManufacturingDesignerSteve OkamotoModelHyper CoasterTrack layoutOut and B...

Perang saudara Kerajaan MunaIlustrasi Perang saudara Kerajaan Muna.Tanggal1700-an – 1816LokasiPulau MunaHasil Kemenangan Wa Ode KadingkePihak terlibat Kerajaan Muna (Wa Ode Kadingke) Kesultanan Buton Kerajaan Tiworo Kerajaan Muna (La Ode Sumaeli)Tokoh dan pemimpin Wa Ode Kadingke Daeng Marewa La Kopuru (Sultan Buton) La Ode SumaeliKekuatan Tidak diketahui Tidak diketahuiKorban Tidak diketahui Tidak diketahui Perang saudara Kerajaan Muna adalah perang saudara yang terjadi pada akhir tahun 17...

Запрос «Пугачёва» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. Алла Пугачёва На фестивале «Славянский базар в Витебске», 2016 год Основная информация Полное имя Алла Борисовна Пугачёва Дата рождения 15 апреля 1949(1949-04-15) (75 лет) Место рождения Москва, СССР[1]...

Wilhelm Marx Kanselir JermanRepublik WeimarMasa jabatan17 Mei 1926 – 12 Juni 1928PresidenPaul von HindenburgWakilOskar HergtPendahuluHans LutherPenggantiHermann MüllerMasa jabatan30 November 1923 – 15 Januari 1925PresidenFriedrich EbertWakilKarl JarresPendahuluGustav StresemannPenggantiHans LutherPresiden Menteri Negara Bebas PrusiaMasa jabatan18 Februari 1925 – 6 April 1925PendahuluOtto BraunPenggantiOtto Braun Informasi pribadiLahir(1863-01-15)15 Januari 18...

Jonathan Rashleigh (1642–1702), of Menabilly, Sheriff of Cornwall 1686. (Previously thought to be his father-in-law Sir John Carew, 3rd Baronet (died 1692) of Antony). Painted c.1685/90 by unknown artist of the English School. National Trust, Collection of Antony House, Cornwall Arms of Rashleigh: Sable, a cross or between in the first quarter: a Cornish chough, argent beaked and legged gules; in the second quarter: a text T; in the third and fourth quarters: a crescent all of the third ...

Aula utama istana (Daigokuden) yang telah dibangun kembali Replika Gerbang Suzaku (Suzakumon) di Heijō-kyō Heijō-kyō atau Heizei-kyō (平城京code: ja is deprecated ) adalah ibu kota Jepang pada zaman Nara. Nara no miyako (奈良の都code: ja is deprecated , ibu kota Nara) adalah sebutan lain untuk kota ini yang menjadi ibu kota Jepang dari tahun 710 hingga 740, dan tahun 745 hingga 784. Pembangunan kota mengambil model dari ibu kota Dinasti Tang di Chang'an dan ibu kota Dinasti Wei Ut...

American Moving & Storage AssociationMerged intoAmerican Trucking AssociationsSuccessorMoving and Storage ConferenceFormation1920 (precursor)Defunct2020Typetrade associationHeadquartersAlexandria, VirginiaLocationUnited StatesMembership 4,000The American Moving & Storage Association (AMSA) was the non-profit trade association representing members of the professional moving industry based primarily in the United States. Its approximately 4,000 members consisted of van lines, their...

Cricket Tournament KFC Twenty20 Big BashKFC Twenty20 Big Bash LogoCountriesAustraliaAdministratorCricket AustraliaFormatTwenty20First edition2005–06Latest edition2010–11Tournament formatDouble round-robin and knockout finalsNumber of teams6Current championSouthern Redbacks (1st title)Most successfulVictorian Bushrangers (4 titles)Most runsBrad Hodge (919)Most wicketsDirk Nannes (31) The KFC Twenty20 Big Bash was a domestic Twenty20 cricket competition in Australia. The competition was org...

Lokasi Distrik Shimohei di Prefektur Iwate. Lokasi munisipalitas yang ada di Distrik Shimohei, Prefektur Iwate1. – Yamada 2. – Iwaizumi3. – Tanohata 4. – Fudaiwarna hijau - cakupan wilayah distrik saat iniwarna kuning - bekas wilayah distrik pada awal zaman Meiji Distrik Shimohei (下閉伊郡code: ja is deprecated , Shimohei-gun) adalah sebuah distrik yang terletak di Prefektur Iwate, Jepang. Per 1 Oktober 2020, distrik ini memiliki estimasi jumlah penduduk sebesar 28.592 jiwa dan ke...





