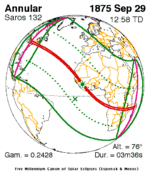
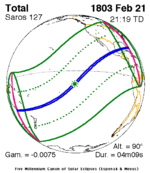
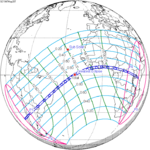
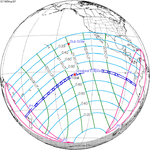
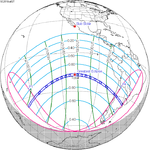
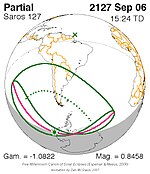
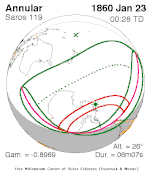
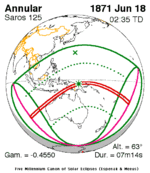
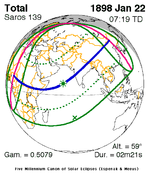
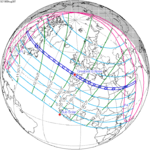
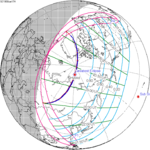
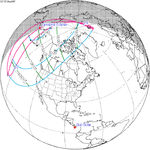
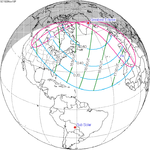
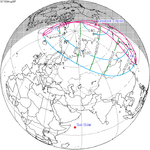
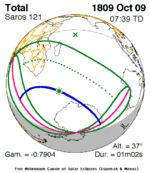
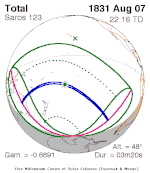
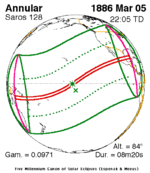
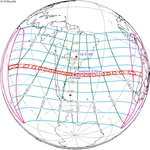
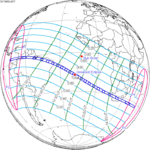
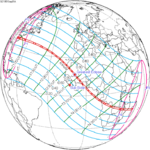
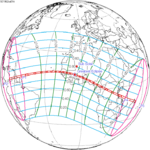
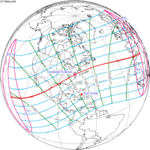
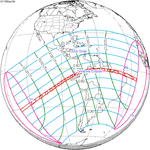
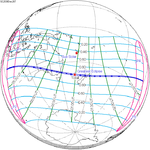
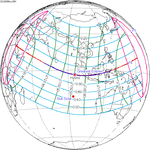
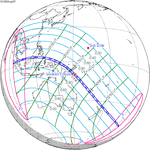
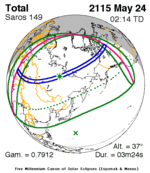
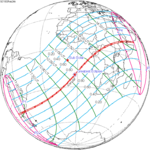
Solar eclipse of April 6, 1875
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Markus Haris Maulana Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Muhammad Markus Haris MaulanaTanggal lahir 14 Maret 1981 (umur 43)Tempat lahir Pangkalan Brandan, IndonesiaTinggi 1,86 m (6 ft 1 in)Posisi bermain KiperKarier junior1998–2000 Diklat PPLP Sumatera SelatanKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2000–2001 PSL Langkat 6 (0)2001–2002 PS Batam 20 (0)2002–2003 Persiraja Banda Aceh 23 (0)2003–2008 PSMS Medan 150 (0)2008–2009 Persik Kediri 22 (0)2009 (6 Bulan) PSMS Medan 1...

Kereta api MalabarKereta api Malabar melintasi persawahanInformasi umumJenis layananKereta api antarkotaStatusBeroperasiDaerah operasiDaerah Operasi II BandungMulai beroperasi 30 April 2010 (perjalanan malam) 24 Januari 2024 (perjalanan pagi) Operator saat iniKereta Api IndonesiaJumlah penumpang harian 360 penumpang per hari (malam) 520 penumpang per hari (pagi)[butuh rujukan]Lintas pelayananStasiun awalBandungJumlah pemberhentianLihatlah di bawah.Stasiun akhirMalangJarak tempuh780 km...

Attentat du RER B à Saint-Michel Plaque commémorative des victimes de l’attentat (photo prise en juillet 2015). Localisation Paris (France) Cible Gare de Saint-Michel - Notre-Dame Coordonnées 48° 51′ 13″ nord, 2° 20′ 39″ est Date 25 juillet 1995 17 h (UTC) Type Attentat à la bombe Armes Engin explosif improvisé Morts 8[1] Blessés 117[1] Auteurs Khaled KelkalBoualem Bensaïd Organisations Groupe islamique armé (GIA) Mouvance Terrorisme isl...

ElizabethOriginal film posterSutradaraShekhar KapurProduserTim BevanEric FellnerAlison OwenDitulis olehMichael HirstPemeranCate BlanchettGeoffrey RushChristopher EcclestonJoseph FiennesRichard AttenboroughKathy BurkeDaniel CraigVincent CasselJohn GielgudPenata musikDavid HirschfelderSinematograferRemi AdefarasinPenyuntingJill BilcockDistributorPolygram Filmed EntertainmentGramercy PicturesTanggal rilis8 September 1998 (1998-09-08) (VFF)01998-10-2323 Oktober 1998(United Kingdom)Dura...

American politician (1839-1924) Thomas MacDonald Waller51st Governor of ConnecticutIn officeJanuary 3, 1883 – January 8, 1885LieutenantGeorge G. SumnerPreceded byHobart B. BigelowSucceeded byHenry Baldwin HarrisonSecretary of State of ConnecticutIn office1870-1871GovernorJames E. EnglishPreceded byHiram ApplemanSucceeded byHiram ApplemanMember of the Connecticut House of RepresentativesIn office187618721867 Personal detailsBorn(1839-02-15)February 15, 1839[citation needed&#...

جائزة تمبلتونشعار الجائزةمعلومات عامةنوع الجائزة جائزة دينيةمنحت لـ المساهمات البارزة في تأكيد البعد الروحاني للحياة، سواء من خلال البصيرة أو الاكتشاف أو الأعمال العملية.البلد الولايات المتحدةسميت باسم جون تمبلتونمقدمة من مؤسسة جون تمبلتونقيمة الجائزة 795٬000 جنيه إس...

Hukuman mati atau pidana mati (Belanda: doodstrafcode: nl is deprecated ) adalah yakni praktik yang dilakukan suatu Negara (pemerintahan) untuk membunuh seseorang sebagai hukuman atas suatu kejahatan bagaikan Hukuman mati di Indonesia. Vonis yang memerintahkan seorang tersangka didakwa dengan hukuman mati dapat dikatakan telah divonis mati, dan tindakan pelaksanaan hukuman disebut sebagai eksekusi. Kejahatan yang dapat dikenai hukuman mati dapat beragam tergantung jurisdiksi, namun biasanya m...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (avril 2023). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Com...

Japanese anime television series You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (March 2021) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Consider adding a t...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Acton. Ferdinando Acton Fonctions Ministre de la Marine du royaume d'Italie 25 novembre 1879 – 17 novembre 1883(3 ans, 11 mois et 23 jours) Monarque Humbert Ier (roi d'Italie) Gouvernement Benedetto CairoliAgostino Depretis Législature XIIIe, XIVe et XVe Prédécesseur Cesare Bonelli (par intérim) Successeur Andrea Carlo Agostino Del Santo Ministre de la Guerre du royaume d'Italie(par intérim) 13 juillet 1880 – 27 juillet 1880(14 j...

Alain ResnaisDe gauche à droite, Ariane Ascaride, Juliette Binoche, Alain Resnais et Agnès Jaoui à la 23e cérémonie des César (en 1998).BiographieNaissance 3 juin 1922VannesDécès 1er mars 2014 (à 91 ans)Neuilly-sur-SeineSépulture Cimetière du MontparnasseNom de naissance Alain Pierre Marie Jean Georges ResnaisNationalité françaiseFormation Institut des hautes études cinématographiquesCours SimonLa FémisActivités Réalisateur, acteur, producteur de cinéma, directeur...

Swedish explorer, geologist, and paleobotanist (1850–1921) Alfred Gabriel Nathorst Alfred Gabriel Nathorst (7 November 1850 – 20 January 1921) was a Swedish Arctic explorer, geologist, and palaeobotanist. Life He was born in Väderbrunn in Sweden. Nathorst's interest in geology was awakened by Charles Lyell's Principles of Geology and, at the age of 21, Nathorst visited Lyell in England in 1872.[1] Nathorst was employed at the Geological Survey of Sweden in 1873–84. He was ...

Men's singlesat the VII Olympic Winter GamesDates29 January-1 FebruaryCompetitors16 from 11 nationsMedalists Hayes Alan Jenkins United States Ronald Robertson United States David Jenkins United States← 19521960 → Figure skating at the Olympics Figure skating at the1956 Winter OlympicsSinglesmenladiesPairsmixedvte The men's figure skating competition at the 1956 Winter Olympics took place at the Olympic Ice Stadium in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy. Th...

UN Official Ian Martin in 2019 Ian Martin (born 10 August 1946)[1] is an English human rights activist/advisor and sometime United Nations official.[2] His most recent UN assignment was as the Special Representative of the Secretary-General and Head of the United Nations Support Mission in Libya.[3] From 2015 to 2018 he was Executive Director of Security Council Report. Early life Martin was educated at Brentwood School in Brentwood, Essex, and graduated from Emmanuel ...

1961 international treaty For other conventions signed in Vienna, see Vienna Convention. Vienna Convention on Diplomatic RelationsRatifications of the convention Parties Non-partiesSigned18 April 1961LocationViennaEffective24 April 1964ConditionRatification by 22 statesSignatories61[1]Parties193[1] (as of June 2021)DepositaryUN Secretary-GeneralLanguagesChinese, English, French, Russian and SpanishFull text Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations at W...

Bolognese jurist and writer on agriculture (1233–1320) For other people named Pier Crescenzi, see Pier Crescenzi. Nineteenth-century engraved portrait of de' Crescenzi after Antonio MuzziBornc. 1230/35BolognaDiedc. 1320BolognaResting placeBasilica di San Domenico, BolognaOccupationjurist, writerLanguageItalian, LatinCitizenshipBologneseNotable worksRuralia commodaSpouseGeraldina de' CastagnoliAntonia de' Nascentori Frontispiece of the De agricultura in the vernacular edition of Matteo Capca...

أندي ديلور (بالفرنسية: Andy Derlort) ديلور مع نانت عام 2023 معلومات شخصية الاسم الكامل أندي ديلور[1] الميلاد 9 أكتوبر 1991 (العمر 32 سنة)سيت، فرنسا الطول 1.81 م (5 قدم 11 1⁄2 بوصة)[2] مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية فرنسا الجزائر معلومات النادي النادي الحالي نانت الرقم 7 مسي...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Inskripsi Batu Rosetta Maklumat Batu Rosetta adalah maklumat yang dikeluarkan oleh Raja Ptolemaios V dari Mesir pada tahun 196 SM. Maklumat ini adalah maklumat ketiga yang dikeluarkan di Memfis. Maklumat ini dikenal karena isinya terpatri dalam Batu Rosetta dengan tulisan hieroglif, demotik, dan Yunani. Maklumat ini berisi tentang pemujaan terhadap para penguasa dari Wangsa Ptolemaios, termasuk Ptolemaios V sendiri. Referensi Budge, 1929, (1989). The Rosetta Stone, E. A. Wallis Budge, (Dover ...

КоммунаБарберьеBarberier 46°13′08″ с. ш. 3°14′48″ в. д.HGЯO Страна Франция Регион Овернь Департамент Алье Кантон Шантель Мэр Claude Pornin(2008–2014) История и география Площадь 8,08 км² Высота центра 254–290 м Часовой пояс UTC+1:00, летом UTC+2:00 Население Население 126 человек (2008) Пло�...