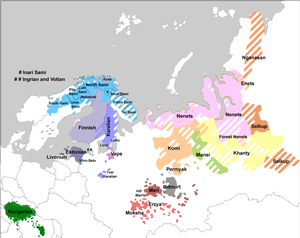
Finno-Samic languages
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il nome comune dell'autoveicolo, vedi Automobile. Un esempio di macchina (utilizzata per arrotolare le sigarette). Il termine macchina indica un dispositivo meccanico e/o elettrico in grado di convertire energia da una forma all'altra (tecnicamente: lavoro in energia, energia in lavoro, lavoro in lavoro). Una macchina è tipicamente strutturata in un insieme di componenti, collegati tra loro, dotati di azionatori, circuiti di comando e connessi solidalmen...

العلاقات الليتوانية الميكرونيسية ليتوانيا ولايات ميكرونيسيا المتحدة ليتوانيا ولايات ميكرونيسيا المتحدة تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الليتوانية الميكرونيسية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين ليتوانيا وولايات ميكرونيسيا المتحدة.[1][2][3][4&...

سامريونשומרוניםسامريُّون يُخلّدون عيد خروجهم من مِصر، على جبل جرزيم في 14 أبريل 2006.التعداد الكليالتعداد 874 (2020)[ar 1]مناطق الوجود المميزةالبلد إسرائيل إسرائيل (حولون) 460 (2021)فلسطين[أ] (لوزة) 380 (2021)اللغاتاللغة الأم العبرية — العربية اللغة المستعملة عبرية سامرية الدين س�...

أميريكان فولس الإحداثيات 42°46′52″N 112°51′20″W / 42.78111°N 112.85556°W / 42.78111; -112.85556 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة باور عاصمة لـ مقاطعة باور[3] خصائص جغرافية المساحة 4.178675 كيلومتر مربع4.36685 كيلومتر مربع...

Course en ligne masculine aux championnats du monde de cyclisme sur route 2012 Généralités Sport Cyclisme sur route Organisateur(s) UCI Lieu(x) Fauquemont, Pays-Bas Date 23 septembre 2012 Épreuves Course en ligne Distance 269 km Palmarès Vainqueur Philippe Gilbert Navigation Copenhague 2011 Florence 2013 modifier La course en ligne masculine des championnats du monde de cyclisme sur route 2012 a lieu le 23 septembre 2012 à Fauquemont, aux Pays-Bas. Participation Système de sélection ...

Swiss footballer (born 1953) Rudolf Elsener Personal informationDate of birth (1953-02-18) 18 February 1953 (age 71)Place of birth Zürich, SwitzerlandHeight 1.84 m (6 ft 0 in)Position(s) StrikerYouth career0000–1970 FC Industrie ZürichSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1971–1978 Grasshopper Club Zürich 129 (40)1978–1979 Eintracht Frankfurt 33 (9)1979–1984 FC Zürich 139 (31)1984–1986 Neuchâtel Xamax 58 (14)1986–1987 Vevey Sports 18 (5)1987–1988 Yverdon Sp...

SemangauDesaNegara IndonesiaProvinsiKalimantan BaratKabupatenSambasKecamatanSambasKode Kemendagri61.01.01.2029 Luas10 km2Jumlah penduduk1.322 jiwa (2010)Kepadatan132 jiwa/km2 Semangau merupakan salah satu desa yang terdapat di Kecamatan Sambas, Kabupaten Sambas, Kalimantan Barat. Desa ini memiliki luas 10 km2 (4,06% dari wilayah Kecamatan Sambas)[1] dan merupakan desa terluas ke-9 dari 18 desa yang ada di Kecamatan Sambas. Desa ini merupakan desa termuda di Kecamatan Sambas....

PT Sarana Multi Infrastruktur (Persero)JenisBadan usaha milik negaraIndustriJasa keuanganDidirikan26 Februari 2009; 15 tahun lalu (2009-02-26)KantorpusatJakarta, IndonesiaWilayah operasiIndonesiaTokohkunciEdwin Syahruzad[1](Direktur Utama)Mahendra Siregar[2](Komisaris Utama)JasaPembiayaan, investasi, konsultansi, dan fasilitasi pengembangan proyek infrastrukturPendapatanRp 5,639 triliun (2020)[3]Laba bersihRp 1,524 triliun (2020)[3]Total asetRp 100,740 tri...

Private university in Thailand Kasem Bundit University (KBU)MottoValue Virtue Worthiness[citation needed]TypePrivateEstablished1987Location1761 Pattanakarn Rd., Suan Luang, Bangkok, ThailandCampus2NicknameKBUWebsitehttp://www.kbu.ac.th Kasem Bundit University (KBU) is a private university in Thailand. Established in 1987, it offers academic programs at graduate and undergraduate levels. Among its institutes are the Institute of Digital Media Law at Kasem Bundit University.[1] ...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Ernesto Alfredo Castro Aldana (lahir 26 Mei 1971)[1] adalah seorang politikus El Salvador yang merupakan presiden petahana Dewan Legislatif El Salvador.[2] Ernesto CastroCastro Tahun 2023Lahir26 Mei 1971 (umur 52)El SalvadorKebangsaan El SalvadorPekerjaanPolitisiPartai politikNuevas Ideas Karier Politik Dari tahun 2012 hingga 2015, Castro menjabat sebagai sekretaris dan penasihat pribadi walikota Nuevo Cuscatlán, yang saat itu menjabat sebagai Nayib Bukele. Da...

County in Michigan, United States County in MichiganClinton CountyCountyClinton County Courthouse in St. Johns FlagSealLocation within the U.S. state of MichiganMichigan's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 42°56′N 84°37′W / 42.94°N 84.61°W / 42.94; -84.61Country United StatesState MichiganFounded1831[1]Named forDeWitt ClintonSeatSt. JohnsLargest citySt. JohnsArea • Total574 sq mi (1,490 km2) • Land566&...

American lawyer and politician James E. Tierney51st Attorney General of MaineIn officeJanuary 6, 1981 – January 6, 1991GovernorJoseph E. BrennanJohn R. McKernan Jr.Preceded byRichard S. CohenSucceeded byMichael E. CarpenterMember of the Maine House of RepresentativesIn officeJanuary 3, 1973 – December 3, 1980Succeeded byMartin S. HaydenConstituencyAndroscoggin County (1973-1975)3rd District (1975-1980) Personal detailsBorn (1947-04-12) April 12, 1947 (age 77)New Yor...
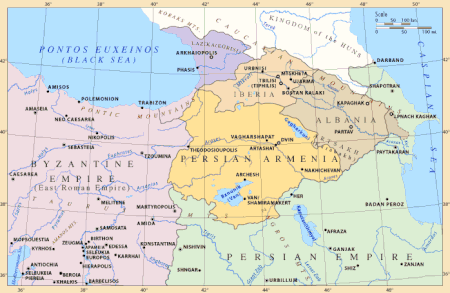
История Грузииსაქართველოს ისტორია Доисторическая Грузия Шулавери-шомутепинская культураКуро-араксская культураТриалетская культураКолхидская культураКобанская культураДиаухиМушки Древняя история КолхидаАриан-КартлиИберийское царство ФарнавазидыГруз�...

Countries that partook in the 2001 United States-led invasion of Afghanistan This article's factual accuracy may be compromised due to out-of-date information. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (August 2016) An NATO multinational fleet (namely the United States, the United Kingdom, Italy, France, and the Netherlands) during Operation Enduring Freedom in the Oman Sea. In four descending columns, from left to right: Maestrale, De Grasse; US...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2019) ريج ريد معلومات شخصية الميلاد 17 فبراير 1899 تاريخ الوفاة 14 يناير 1986 (86 سنة) مواطنة الولايات المتحدة الحياة العملية المهنة لاعب هوكي الجليد[1] �...

Type of stopper knot used in sailing and climbing This article is about the knot. For the mathematical concept, see Figure-eight knot (mathematics). For other uses of Figure 8, see Figure 8. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Figure-eight knot – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (Septe...

Hydrological divide in North America The Laurentian Divide (green) extends from Triple Divide Peak in northwestern Montana to the tip of the Labrador Peninsula at the 60th parallel north. The Laurentian Divide also called the Northern Divide[1] and locally the height of land, is a continental divide in central North America that separates the Hudson Bay watershed to the north from the Gulf of Mexico watershed to the south and the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence watershed to the southeast. Wa...

Hallingdal è una valle ed un distretto tradizionale della Norvegia, con circa 20.000 abitanti, situata nella contea di Buskerud. Include i comuni di Flå, Nesbyen, Gol, Hemsedal, Ål e Hol, i quali cooperano tramite la Corte Distrettuale di Hallingdal (Hallingdal tingrett). Indice 1 Geografia 2 Etimologia 3 Storia 4 Trasporti e curiosità 5 Note 6 Altri progetti Geografia Hallingdal è una delle valli più estese della Norvegia orientale: occupa una superficie di 5.830 km². Il punto pi...

Not to be confused with WWE. Television station in Louisiana, United StatesKWWE-LDLake Charles, LouisianaUnited StatesChannelsDigital: 19 (UHF)Virtual: 19BrandingMeTV & My 19 Lake CharlesProgrammingSubchannels19.1: MyNetworkTV/MeTV19.2: Telemundofor others, see § SubchannelsOwnershipOwnerSagamoreHill Broadcasting(SagamoreHill Lake Charles, LLC)Sister stationsKSWL-LDHistoryFoundedFebruary 22, 2011First air dateMarch 2017 (7 years ago) (2017-03)Former call signsK19J...