Rolle's theorem
 In real analysis, a branch of mathematics, Rolle's theorem or Rolle's lemma essentially states that any real-valued differentiable function that attains equal values at two distinct points must have at least one point, somewhere between them, at which the slope of the tangent line is zero. Such a point is known as a stationary point. It is a point at which the first derivative of the function is zero. The theorem is named after Michel Rolle. Standard version of the theoremIf a real-valued function f is continuous on a proper closed interval [a, b], differentiable on the open interval (a, b), and f (a) = f (b), then there exists at least one c in the open interval (a, b) such that This version of Rolle's theorem is used to prove the mean value theorem, of which Rolle's theorem is indeed a special case. It is also the basis for the proof of Taylor's theorem. HistoryAlthough the theorem is named after Michel Rolle, Rolle's 1691 proof covered only the case of polynomial functions. His proof did not use the methods of differential calculus, which at that point in his life he considered to be fallacious. The theorem was first proved by Cauchy in 1823 as a corollary of a proof of the mean value theorem.[1] The name "Rolle's theorem" was first used by Moritz Wilhelm Drobisch of Germany in 1834 and by Giusto Bellavitis of Italy in 1846.[2] ExamplesHalf circle For a radius r > 0, consider the function Its graph is the upper semicircle centered at the origin. This function is continuous on the closed interval [−r, r] and differentiable in the open interval (−r, r), but not differentiable at the endpoints −r and r. Since f (−r) = f (r), Rolle's theorem applies, and indeed, there is a point where the derivative of f is zero. The theorem applies even when the function cannot be differentiated at the endpoints because it only requires the function to be differentiable in the open interval. Absolute value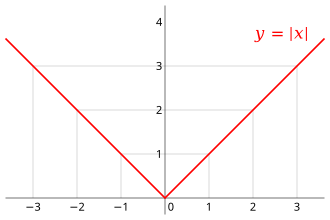 If differentiability fails at an interior point of the interval, the conclusion of Rolle's theorem may not hold. Consider the absolute value function Then f (−1) = f (1), but there is no c between −1 and 1 for which the f ′(c) is zero. This is because that function, although continuous, is not differentiable at x = 0. The derivative of f changes its sign at x = 0, but without attaining the value 0. The theorem cannot be applied to this function because it does not satisfy the condition that the function must be differentiable for every x in the open interval. However, when the differentiability requirement is dropped from Rolle's theorem, f will still have a critical number in the open interval (a, b), but it may not yield a horizontal tangent (as in the case of the absolute value represented in the graph). Functions with zero derivativeRolle's theorem implies that a differentiable function whose derivative is in an interval is constant in this interval. Indeed, if a and b are two points in an interval where a function f is differentiable, then the function satisfies the hypotheses of Rolle's theorem on the interval . If the derivative of is zero everywhere, the derivative of is and Rolle's theorem implies that there is such that Hence, for every and , and the function is constant. GeneralizationThe second example illustrates the following generalization of Rolle's theorem: Consider a real-valued, continuous function f on a closed interval [a, b] with f (a) = f (b). If for every x in the open interval (a, b) the right-hand limit and the left-hand limit exist in the extended real line [−∞, ∞], then there is some number c in the open interval (a, b) such that one of the two limits is ≥ 0 and the other one is ≤ 0 (in the extended real line). If the right- and left-hand limits agree for every x, then they agree in particular for c, hence the derivative of f exists at c and is equal to zero. Remarks
Proof of the generalized versionSince the proof for the standard version of Rolle's theorem and the generalization are very similar, we prove the generalization. The idea of the proof is to argue that if f (a) = f (b), then f must attain either a maximum or a minimum somewhere between a and b, say at c, and the function must change from increasing to decreasing (or the other way around) at c. In particular, if the derivative exists, it must be zero at c. By assumption, f is continuous on [a, b], and by the extreme value theorem attains both its maximum and its minimum in [a, b]. If these are both attained at the endpoints of [a, b], then f is constant on [a, b] and so the derivative of f is zero at every point in (a, b). Suppose then that the maximum is obtained at an interior point c of (a, b) (the argument for the minimum is very similar, just consider −f ). We shall examine the above right- and left-hand limits separately. For a real h such that c + h is in [a, b], the value f (c + h) is smaller or equal to f (c) because f attains its maximum at c. Therefore, for every h > 0, hence where the limit exists by assumption, it may be minus infinity. Similarly, for every h < 0, the inequality turns around because the denominator is now negative and we get hence where the limit might be plus infinity. Finally, when the above right- and left-hand limits agree (in particular when f is differentiable), then the derivative of f at c must be zero. (Alternatively, we can apply Fermat's stationary point theorem directly.) Generalization to higher derivativesWe can also generalize Rolle's theorem by requiring that f has more points with equal values and greater regularity. Specifically, suppose that
Then there is a number c in (a, b) such that the nth derivative of f at c is zero.  The requirements concerning the nth derivative of f can be weakened as in the generalization above, giving the corresponding (possibly weaker) assertions for the right- and left-hand limits defined above with f (n − 1) in place of f. Particularly, this version of the theorem asserts that if a function differentiable enough times has n roots (so they have the same value, that is 0), then there is an internal point where f (n − 1) vanishes. ProofThe proof uses mathematical induction. The case n = 1 is simply the standard version of Rolle's theorem. For n > 1, take as the induction hypothesis that the generalization is true for n − 1. We want to prove it for n. Assume the function f satisfies the hypotheses of the theorem. By the standard version of Rolle's theorem, for every integer k from 1 to n, there exists a ck in the open interval (ak, bk) such that f ′(ck) = 0. Hence, the first derivative satisfies the assumptions on the n − 1 closed intervals [c1, c2], …, [cn − 1, cn]. By the induction hypothesis, there is a c such that the (n − 1)st derivative of f ′ at c is zero. Generalizations to other fieldsRolle's theorem is a property of differentiable functions over the real numbers, which are an ordered field. As such, it does not generalize to other fields, but the following corollary does: if a real polynomial factors (has all of its roots) over the real numbers, then its derivative does as well. One may call this property of a field Rolle's property.[citation needed] More general fields do not always have differentiable functions, but they do always have polynomials, which can be symbolically differentiated. Similarly, more general fields may not have an order, but one has a notion of a root of a polynomial lying in a field. Thus Rolle's theorem shows that the real numbers have Rolle's property. Any algebraically closed field such as the complex numbers has Rolle's property. However, the rational numbers do not – for example, x3 − x = x(x − 1)(x + 1) factors over the rationals, but its derivative, does not. The question of which fields satisfy Rolle's property was raised in Kaplansky 1972.[4] For finite fields, the answer is that only F2 and F4 have Rolle's property.[5][6] For a complex version, see Voorhoeve index. See alsoReferences
Further reading
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rolle's theorem. |


![{\displaystyle f(x)={\sqrt {r^{2}-x^{2}}},\quad x\in [-r,r].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b7ef1f348169f09e9db96b68d4b2e73d5f43c156)
![{\displaystyle f(x)=|x|,\quad x\in [-1,1].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/06020ba2e58842ee0cea4e5c27566b16a4ecaff6)


![{\displaystyle [a,b]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9c4b788fc5c637e26ee98b45f89a5c08c85f7935)






























