Purohita
|
Read other articles:

As I Lay Dying Sampul Edisi PertamaPengarangWilliam FaulknerGenreModernist, Southern Gothic, Black ComedyPenerbitJonathan Cape & Harrison SmithTanggal terbit1930Didahului olehThe Sound and the Fury Diikuti olehSanctuary As I Lay Dying (Bahasa Indonesia: Saat Saya Terbaring Sekarat) adalah novel beraliran Gotik Selatan (Southern Gothic) yang diterbitkan pada tahun 1930[1] oleh William Faulkner (25 September 1897- 6 Juli 1962).[2] Karya Faulkner yan...
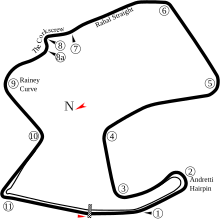
Grand Prix Amerika Serikat 2005Detail lombaLomba ke 8 dari 17Grand Prix Sepeda Motor musim 2005Tanggal10 Juli 2005Nama resmiRed Bull U.S. Grand Prix[1][2][3]LokasiWeatherTech Raceway Laguna SecaSirkuitFasilitas balapan permanen3.610 km (2.240 mi)MotoGPPole positionPembalap Nicky HaydenCatatan waktu 1:22.670Putaran tercepatPembalap Colin EdwardsCatatan waktu 1:23.915 di lap 5PodiumPertama Nicky HaydenKedua Colin EdwardsKetiga Valentino Rossi Grand ...

Datu Mangku AdatAdjim ArijadiB.ScLahir(1940-07-07)7 Juli 1940Mali-Mali, Hindia Belanda(kini Kabupaten Banjar)Meninggal1 Januari 2016(2016-01-01) (umur 75)BanjarmasinKebangsaanIndonesiaAlmamaterAkademi Seni Drama dan Film (ASDRAFI) YogyakartaTahun aktif1963 - 2015OrganisasiYayasan Sanggar Budaya Kalimantan SelatanDikenal atasSeniman, Sastrawan, BudayawanGelarBapak Teater Modern Kalsel Datu Mangku Adat Datu IlalangPasanganHj. Ely Rahmi, S.Sos, MMAnakHijromi Arijadi Putera ; Ikhw...

English painter (1723–1792) For other people with similar names, see Josh Reynolds. SirJoshua ReynoldsPRA FRS FRSASelf-portrait, c. 1750Born(1723-07-16)16 July 1723Plympton, Devon, EnglandDied23 February 1792(1792-02-23) (aged 68)Leicester Fields, London, EnglandResting placeSt Paul's CathedralEducationPlympton Free Grammar SchoolNotable workThe Age of InnocenceSignature Sir Joshua Reynolds PRA FRS FRSA (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter wh...

Football in Saudi ArabiaKing Fahd International Stadium in 2008CountrySaudi ArabiaGoverning bodySAFFNational team(s)National team Under-23 national team Under-20 national team Under-17 national team Women's national teamNickname(s)The FalconsFirst played1957Clubs172National competitions FIFA World Cup AFC Asian Cup FIFA Arab Cup WAFF Championship Arabian Gulf Cup Club competitions List League: Saudi Professional League Saudi First Division Saudi Second Division Saudi Third Division Saudi Fou...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

You're Not YouPoster rilis teatrikalSutradaraGeorge C. WolfeProduserAlison GreenspanDenise Di NoviHilary SwankMolly SmithDitulis olehShana FesteJordan RobertsBerdasarkanYou're Not Youoleh Michelle WildgenPemeranHilary SwankEmmy RossumJosh DuhamelPenata musikJeanine TesoriSinematograferSteven FierbergPenyuntingJeffrey WolfPerusahaanproduksiDaryl Prince ProductionsDi Novi Pictures2S FilmsDistributorEntertainment OneTanggal rilis 10 Oktober 2014 (2014-10-10) Durasi102 menitNegaraAmeri...

This article is about the district. For its eponymous headquarters, see Araria. For other places with same/similar name, see Araria (disambiguation). District of Bihar in IndiaAraria districtDistrict of BiharSunset at Sultan Pokhar, ForbesganjLocation of Araria district in BiharCountry IndiaStateBiharRegionMithilaDivisionPurniaEstablished14 Jan 1990HeadquartersArariaGovernment • Lok Sabha constituenciesAraria • Vidhan Sabha constituenciesNarpatganj, Raniganj, Forb...

Autodirecteur infrarouge du missile IRIS-T. Un missile AIM-9 Sidewinder touche un North American F-86 Sabre lors d’un tir d’exercice à la base China Lake en 1978. Autodirecteurs infrarouges des missiles Anti-navire léger et Missile moyenne portée. Le guidage par infrarouge ou autodirecteur infrarouge ou guidage thermique est un système de guidage à infrarouge passif qui utilise l'émission de lumière infrarouge d'une cible pour la localiser et la suivre. Les missiles ...

Carita de ángelSutradaraMarta Luna Juan Carlos MuñozPemeranLisette MorelosMiguel de LeónDaniela AedoNora SalinasLibertad LamarqueSilvia PinalAna Patricia RojoMarisol SantacruzLagu pembukaCarita de ángel karya TatianaLagu penutupCarita de ángel versi anak anakNegara asalMeksikoBahasa asliSpanyolJmlh. episode175ProduksiProduserNicandro Díaz GonzálezRilis asliJaringanCanal de las EstrellasRCTISCTVLativiGlobal TVMNCTVRilis19 Juni 2000 –16 Maret 2001 Carita de ángel (bahasa Indones...

烏克蘭總理Прем'єр-міністр України烏克蘭國徽現任杰尼斯·什米加尔自2020年3月4日任命者烏克蘭總統任期總統任命首任維托爾德·福金设立1991年11月后继职位無网站www.kmu.gov.ua/control/en/(英文) 乌克兰 乌克兰政府与政治系列条目 宪法 政府 总统 弗拉基米尔·泽连斯基 總統辦公室 国家安全与国防事务委员会 总统代表(英语:Representatives of the President of Ukraine) 总...

Clark Clifford 9° Segretario della DifesaDurata mandato1º marzo 1968 –20 gennaio 1969 PresidenteLyndon B. Johnson PredecessoreRobert McNamara SuccessoreMelvin Laird Dati generaliPartito politicoDemocratico Clark McAdams Clifford (Fort Scott, 25 dicembre 1906 – Bethesda, 10 ottobre 1998) è stato un avvocato e politico statunitense, segretario della difesa degli Stati Uniti durante la presidenza Johnson. Indice 1 Biografia 1.1 Primi anni: avvocato, ufficiale di Marina,...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...

American Founding Father and statesman (1755/1757–1804) For other uses, see Alexander Hamilton (disambiguation). Alexander HamiltonPosthumous portrait by John Trumbull, 1806,[1] from a life bust by Giuseppe Ceracchi, 17941st United States Secretary of the TreasuryIn officeSeptember 11, 1789 – January 31, 1795PresidentGeorge WashingtonPreceded byOffice establishedSucceeded byOliver Wolcott Jr.8th Senior Officer of the United States ArmyIn officeDecember 1...

Scientology term Part of a series onScientology General Scientology Dianetics Timeline History L. Ron Hubbard Publications Glossary Beliefs and practices Thetan Auditing Bridge to Total Freedom OT Xenu Ethics and justice Church of Scientology Officials and staff Sea Org David Miscavige Controversies Litigation Status by country Suppressive person Disconnection Fair game RPF The Hole Office of Special Affairs Guardian's Office War on psychiatry More MEST is an acronym for matter, energy, space...

Chiesa di San DesiderioStato Italia RegioneLombardia LocalitàAssago IndirizzoPiazza Risorgimento Coordinate45°24′18.91″N 9°07′54.49″E45°24′18.91″N, 9°07′54.49″E Religionecattolica di rito ambrosiano Arcidiocesi Milano Inizio costruzioneXV secolo CompletamentoXVIII secolo Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale La chiesa di San Desiderio è la parrocchiale di Assago, comune situato vicino a Milano. Nell'ambito dell'arcidiocesi di Milano, la chiesa è compresa nel de...

位置 区政府 红岛 红岛的地标 舍讷贝格[1](德語:Schöneberg,德语:[ˈʃøːnəˌbɛʁk] (ⓘ))是德国柏林的一个分区。2001年以前,它是柏林一个单独的区,包含了下属区弗里德瑙。2001年与滕珀爾霍夫合并为滕珀尔霍夫-舍讷贝格区。 历史 在1760年10月7日七年战争期间,奥地利和俄国军队联合进攻柏林,舍讷贝格的村庄和教堂被大火彻底烧毁。1874年,新老舍讷贝格合...

1938 novel by Daphne du Maurier For the 1903 children's novel by Kate Douglas Wiggin, see Rebecca of Sunnybrook Farm. For the 2001 novel by Orson Scott Card, see Rebekah (novel). Rebecca First editionAuthorDaphne du MaurierLanguageEnglishGenreCrime, gothic, mystery, romancePublisherVictor Gollancz LtdPublication date5 August 1938[1]Publication placeUnited Kingdom Rebecca is a 1938 Gothic novel written by English author Daphne du Maurier. The novel depicts an unnamed young woman who im...

1991 Indian filmDikshaPosterDirected byArun KaulWritten byArun KaulScreenplay byArun KaulStory byU. R. AnanthamurthyBased onGhatashraddha by U. R. AnanthamurthyProduced byNFDC DoordarshanStarringManohar Singh Nana PatekarCinematographyApurba Kishore BirEdited byArun KaulMusic byMohinderjit SinghProductioncompanyNational Film Development CorporationRelease date 1991 (1991) Running time120 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageHindi Diksha (English: The Initiation) is 1991 Indian Hindi-language film...

52 relasi ekuivalensi pada himpunan 5-anggota yang digambarkan dengan matriks biner 5x5 (kotak yang berwarna, termasuk yang abu-abu, melambangkan 1; kotak putih melambangkan 0.) Indeks kolom dan baris dari kotak yang berwarna adalah anggota yang berkaitan, sementara warna yang dibedakan, selain abu-abu, mengindikasikan kelas ekuivalensi (masing-masing kotak abu-abu merupakan kelas ekuivalensinya sendiri). Dalam matematika, relasi ekuivalensi adalah relasi biner yang bersifat reflektif, simetr...




