Lewisite
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Eko Gajah Seno Kepala Dinas Sejarah TNI Angkatan Laut ke-2Masa jabatan27 Juni 2022 – 16 Januari 2023 PendahuluSupardiPenggantiHariyo Poernomo Informasi pribadiLahir18 Januari 1965 (umur 59)IndonesiaAlma materAkademi Angkatan Laut (1988)Karier militerPihak IndonesiaDinas/cabang TNI Angkatan LautMasa dinas1988—2023Pangkat Laksamana Pertama TNISatuanKorps TeknikSunting kotak info • L • B Laksamana Pertama TNI (Purn.) Ir. Eko Gajah Seno, S.T. (lahir 1...

National Hockey League team in Sunrise, Florida For the animal species by this name, see Florida panther. For the Florida International University intercollegiate sports teams, see FIU Panthers. Florida Panthers 2023–24 Florida Panthers seasonConferenceEasternDivisionAtlanticFounded1993HistoryFlorida Panthers1993–presentHome arenaAmerant Bank ArenaCitySunrise, FloridaTeam colorsRed, blue, flat gold, white[1][2][3] MediaBally Sports Florida...

Pusat Penerbangan TNI Angkatan DaratLambang PenerbadDibentuk14 November 1959 (1959-11-14)Sejak 64 tahun, 4 bulan yang lalu.Negara IndonesiaAliansi Tentara Nasional IndonesiaCabang TNI Angkatan DaratTipe unitPenerbangan Angkatan DaratMarkasPangkalan Udara Pondok Cabe, Tangerang Selatan, BantenMotoWira Amur(Sanskrit, lit: Prajurit Terbang)Baret MERAH MARUN HimneMars PenerbadPlayⓘSitus webpuspenerbad-tniad.mil.idTokohKomandan Mayor Jenderal TNIArief Jaka Tandang G...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Stade national. Stade national de Pékin 国家体育场GénéralitésSurnom Nid d'oiseauAdresse 1 Huayuanbieshu, 1 Huayuanlu, Beichendong Rd Chaoyang District, Pékin 100101Construction et ouvertureDébut de construction 24 décembre 2003[1]Ouverture 28 juin 2008Architecte Herzog & de Meuron, ArupSport, China Architecture Design and Research Group et Ai WeiweiIngénieur ArupCoût de construction 3,5 milliards ¥CNY (423 millions $USD)UtilisationClubs r�...

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: Associazione Sportiva Dilettantistica Junior Biellese Libertas. Associazione Sportiva BielleseStagione 1945-1946Sport calcio Squadra Biellese Serie B-C7º posto nel girone A. 1943-1944 1946-1947 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le info...

Agouti Periode saat ini Dasyprocta Seekor agouti Amerika Tengah sedang menyantap beberapa buahTaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasMammaliaOrdoRodentiaFamiliDasyproctidaeGenusDasyprocta Bonaparte, 1838 SpeciesSee textlbs Istilah agouti (bahasa Spanyol: agutí, diucapkan [aɣuˈti]) atau common agouti adalah sejumlah spesies hewan pengerat dari genus Dasyprocta. Mereka berasal dari Amerika Tengah, utara dan tengah Amerika Selatan dan selatan Antillen Kecil. Beberapa spesies juga...

1948 autobiography by Dwight D. Eisenhower and its television adaptation This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Crusade in Europe – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Crusade in Europe First US editionAuthorDwight D. EisenhowerSubjectEu...

British politician (born 1944) Not to be confused with Margaret Hodges. The Right HonourableDame Margaret HodgeOfficial portrait, 2020Chair of the Public Accounts CommitteeIn office10 June 2010 – 30 March 2015Preceded byEdward LeighSucceeded byMeg HillierMinister of State for Culture and TourismIn office22 September 2009 – 11 May 2010Prime MinisterGordon BrownPreceded byBarbara FollettSucceeded byJohn PenroseIn office27 June 2007 – 3 October 2008Prime Minister...
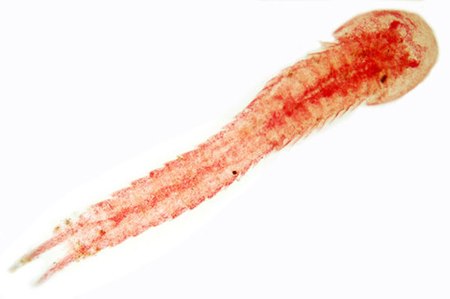
CephalocaridaRentang fosil: 200–0 jtyl PreЄ Є O S D C P T J K Pg N Permian atau Trias sampai sekarang Hutchinsoniella macracantha, salah satu spesies dari Cephalocarida Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Subfilum: Crustacea Kelas: Cephalocarida Ordo: Brachypoda Famili: HutchinsoniellidaeSanders, 1955 Genera Chiltoniella Hampsonellus Hutchinsoniella Lightiella Sandersiella Sinonim Lightiellidae Jones 1961 Cephalocarida adalah kelas dalam subfilum Crustacea[1&...

American black nationalist religious leader (born 1933) MinisterLouis FarrakhanFarrakhan in 2018Leader of the Nation of IslamIncumbentAssumed office 1981Preceded byWarith Deen Muhammad Personal detailsBornLouis Eugene Walcott (1933-05-11) May 11, 1933 (age 91)New York City, U.S.Spouse Khadijah Farrakhan (m. 1953)Children9 (1 deceased) [1]EducationWinston-Salem State UniversityOccupationLeader of the Nation of IslamFormer calypso music singer Par...

Ini adalah nama Maluku, (Ambon) marganya adalah Sahetapy Benjamin Sahetapy Engel Benjamin Sahetapy Engel adalah seorang guru dan politikus Indonesia. Ia lahir di Saparua, Ambon pada tanggal 27 Desember 1916. Ia menimba ilmu di HIK Surakarta pada tahun 1937. Ia adalah anggota partai Fraksi Demokrat. Setelah tamat sekolah, ia bekerja sebagai Guru Christelijke H.I.S. di Banjarmasin, Kupang dan Christelijke H.I.S. Schakelschool Kupang dari 1937 sampai 1942. Pada masa pendudukan Jepang sampai menj...

Multi-sport event in Sankt Moritz, Switzerland This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) II Olympic Winter GamesHugo Laubi's poster for the 1928 Winter OlympicsLocationSt. Moritz, SwitzerlandNations25Athletes464 (438 men, 26 women)Events14 in 4 sports (8 disciplines)Opening11 February 1928Closin...

Chữ Hán giản thểHán tự (汉字) viết theo dạng giản thểThể loại Chữ viết ngữ tố Thời kỳnăm 1956 đến nayHướng viếtTrái sang phải Hệ chữ viết chính thức của Trung Quốc Singapore Liên Hợp Quốc (sử dụng trong văn bản hành chính)Các ngôn ngữTiếng TrungHệ chữ viết liên quanNguồn gốcchữ Hánchữ giáp cốtchữ kimchữ triệnchữ lệchữ Hán phồn thểChữ Hán giản thểAnh e...

هذه المقالة تحتاج للمزيد من الوصلات للمقالات الأخرى للمساعدة في ترابط مقالات الموسوعة. فضلًا ساعد في تحسين هذه المقالة بإضافة وصلات إلى المقالات المتعلقة بها الموجودة في النص الحالي. (نوفمبر 2018) توفيق مجيد معلومات شخصية مواطنة تونس الحياة العملية المهنة صحفي موظف ف�...

American Christian organization Ligonier MinistriesFormation1971FounderR. C. SproulFounded atLigonier, PennsylvaniaTypeNon-profitHeadquartersSanford, FloridaChairmanW. Robert GodfreyPresident and CEOChris LarsonWebsitewww.ligonier.org Ligonier Ministries (also known as simply Ligonier) is an international Christian discipleship organization headquartered in the greater Orlando, Florida area. Ligonier was founded in 1971 by R. C. Sproul in the Ligonier Valley, Pennsylvania, outside of Pittsbur...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento centri abitati dell'Umbria non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Commento: Non sono citate le fonti storiografiche. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Castiglione del Lagocomune Castiglione del Lago – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Umbria Provincia Perugia AmministrazioneSindacoMatteo Burico (PD) dal 27-5...

German bobsledder (born 1993) For other people named Anna Köhler, see Anna Köhler. Anna KöhlerKöhler in January 2019Personal informationBorn (1993-08-05) 5 August 1993 (age 31)Lindenfels, GermanyHeight1.77 m (5 ft 10 in)Weight76 kg (168 lb)SportCountryGermanySportBobsleighEventTwo-womanClubBSC WinterbergTurned pro2013 Medal record World Championships 2019 Whistler Mixed team European Championships 2018 Innsbruck-Igls Two-woman Anna Köhler (also spelled Koehl...

American author (born 1938) Joyce Carol OatesOates in 2014Born (1938-06-16) June 16, 1938 (age 86)Lockport, New York, U.S.Occupation Novelist short story writer playwright poet literary critic professor editor EducationSyracuse University (BA)University of Wisconsin, Madison (MA)Rice UniversityPeriod1963–presentNotable worksA Garden of Earthly Delights (1967); Them (1969); The Wheel of Love (1970); Wonderland (1971); Black Water (1992); Blonde (2000); High Lonesome: New & Selected ...

Ne doit pas être confondu avec Conseil national slovaque (1848-1849). Pour les autres articles nationaux ou selon les autres juridictions, voir Conseil national. Conseil nationalde la République slovaque(sk) Národná radaSlovenskej republiky IXe législature Logo du Conseil national.Présentation Type Monocaméral Création 18481993 (forme actuelle) Lieu Bratislava Durée du mandat 4 ans Présidence Président Peter Žiga (HLAS-SD) Élection 7 avril 2024 Structure Membres 150 co...

Lost text of New Testament apocrypha Part of a series onNew Testament apocryphaFirst page of the Gospel of Judas(Page 33 of Codex Tchacos) Apostolic Fathers 1 Clement 2 Clement Epistles of Ignatius Polycarp to the Philippians Martyrdom of Polycarp Didache Barnabas Diognetus The Shepherd of Hermas Apocryphal gospels Jewish–Christian gospels Ebionites Hebrews Nazarenes Infancy gospels James Thomas Syriac Pseudo-Matthew History of Joseph the Carpenter Gnostic gospels Judas Mary Philip Truth Se...





