Principality of Ushrusana
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
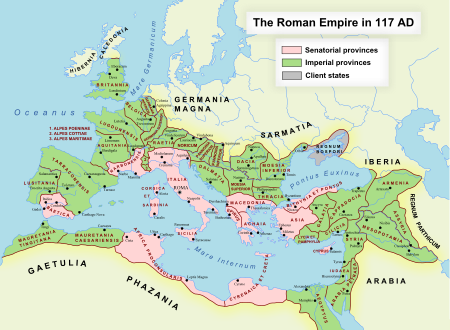
Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Mare Nostrum (disambiguasi). Kekaisaran Romawi, saat wilayahnya terbesar, pada tahun 117 AD. Akan tetapi, di peta ini, lautnya dinamai sebagai Mare Internum (Indonesia: Laut Dalamcode: id is deprecated ). Mare Nostrum (Latin: mare nostrvmcode: la is deprecated , Laut Kami) adalah nama Romawi untuk Laut Mediterania. Pada tahun-tahun setelah Unifikasi Italia pada tahun 1861, kaum nasionalis Italia yang memandang Italia sebagai penerus Kekaisaran Romawi mencoba untuk m...

Комбинаторная теория групп — раздел теории групп, изучающий группы с точки зрения их заданий образующими и соотношениями. Содержание 1 История 1.1 Вклад фон Дика 1.2 Вклад Титце 1.3 Вклад Дена 2 Примечания 3 Литература История Вальтер фон Дик, основатель комбинаторной теор...

Football match1999 Coppa Italia FinalEvent1998–99 Coppa Italia Parma Fiorentina 3 3 Parma won on the away goals ruleFirst leg Parma Fiorentina 1 1 Date14 April 1999VenueStadio Ennio Tardini, ParmaRefereeDomenico MessinaAttendance21,038Second leg Fiorentina Parma 2 2 Date5 May 1999VenueStadio Artemio Franchi, FlorenceRefereeStefano BraschiAttendance39,070← 1998 2000 → The 1999 Coppa Italia Final decided the winner of the 1998–99 Coppa Italia, the major domestic tournament in I...

Activity to defend against or prevent terrorist actions GIGN operators in 2015. GIGN is the counterterrorist tactical unit of the National Gendarmerie of France. United States Coast Guard Maritime Security Response Team is an advanced interdiction force for higher risk law enforcement and counter-terrorism operations Counterterrorism (alternatively spelled: counter-terrorism), also known as anti-terrorism, relates to the practices, military tactics, techniques, and strategies that governments...

Emblem of the 65th anniversary Victory Day Parade. Full version of the 2010 Moscow Victory Day Parade. US Army Soldiers in Victory Day Parade Moscow The 2010 Moscow Victory Day Parade was held on 9 May 2010 to commemorate the 65th anniversary of the capitulation of Nazi Germany in 1945. The parade marks the Soviet Union's victory in the Great Patriotic War. It was the largest parade held in Moscow, Russia since the Soviet Union's dissolution in 1991, and saw 11,135 troops, 127 aircraft and h...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

若纳斯·萨文比Jonas Savimbi若纳斯·萨文比,摄于1990年出生(1934-08-03)1934年8月3日 葡屬西非比耶省Munhango(葡萄牙語:Munhango)逝世2002年2月22日(2002歲—02—22)(67歲) 安哥拉莫希科省卢库塞效命 安哥拉民族解放阵线 (1964–1966) 争取安哥拉彻底独立全国联盟 (1966–2002)服役年份1964 – 2002军衔将军参与战争安哥拉独立战争安哥拉內戰 若纳斯·马列罗·萨文比(Jonas Malheiro Savimbi,1...

此条目序言章节没有充分总结全文内容要点。 (2019年3月21日)请考虑扩充序言,清晰概述条目所有重點。请在条目的讨论页讨论此问题。 哈萨克斯坦總統哈薩克總統旗現任Қасым-Жомарт Кемелұлы Тоқаев卡瑟姆若马尔特·托卡耶夫自2019年3月20日在任任期7年首任努尔苏丹·纳扎尔巴耶夫设立1990年4月24日(哈薩克蘇維埃社會主義共和國總統) 哈萨克斯坦 哈萨克斯坦政府...

Private university in Dubai, United Arab Emirates Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani – Dubai CampusMottoGyanam paramam balamMotto in EnglishKnowledge is Supreme PowerTypePrivateDeemed UniversityEstablished2000; 24 years ago (2000)ChancellorKumar Mangalam BirlaVice-ChancellorV. Ramgopal RaoDirectorDr. Srinivasan MadapusiStudents1,400 (2019)LocationDubai International Academic City, Dubai, UAE25°7′54″N 55°25′11″E / 25.13167°N 55...

County in Michigan, United States Clare County redirects here. For the county in Ireland, see County Clare. County in MichiganClare CountyCountyClare County District Court in Harrison SealLocation within the U.S. state of MichiganMichigan's location within the U.S.Coordinates: 43°59′N 84°50′W / 43.99°N 84.84°W / 43.99; -84.84Country United StatesState MichiganFounded1840 (established)1871 (organized)[1]Named forCounty Clare, IrelandSeatHarriso...

Journalism school at Columbia University This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article relies excessively on references to primary sources. Please improve this article by adding secondary or tertiary sources. Find sources: Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2021) (Lea...

Heroic outlaw in English folklore For other uses, see Robin Hood (disambiguation). Robin of Locksley redirects here. For the 1996 film, see Robin of Locksley (film). Robin Hood and his Merry Men redirects here. For other uses, see Robin Hood and His Merry Men (disambiguation). Fictional character Robin HoodTales of Robin Hood and his Merry Men characterRobin Hood on horse back from a 15th century print. Referred to as Robyn HodeFirst appearance13th/14th century ADCreated byAnonymous balladeer...

.pmTipoNazionale Introduzione20 agosto 1997 StatoAttivo RegistroAFNIC Uso pianificato Saint-Pierre e Miquelon Uso attuale Saint-Pierre e Miquelon Sitowww.nic.pm .pm è il dominio di primo livello nazionale assegnato a Saint-Pierre e Miquelon. Il dominio è riservato a persone e società domiciliate nell'Unione europea, in Islanda, in Liechtenstein, in Norvegia o in Svizzera.[1] Indice 1 Note 2 Voci correlate 3 Altri progetti 4 Collegamenti esterni Note ^ (EN) What are the re...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (مايو 2019) المعهد السعودي بعنيزة، أحد أهم المعاهد العلمية المنشأة في منطقة القصيم في عهد الملك عبدالعزيز. نبذة عن المعهد افتتح المعهد عام 1368هـ، وسمي بــ ( المعهد السعودي...

Part of an internal combustion engine This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Engine block – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Block of a modern V6 diesel engine. The large holes are the cylinders, the small round orifices are mountin...

إنيرجتيك الإحداثيات 56°14′53″N 54°35′15″E / 56.248055555556°N 54.5875°E / 56.248055555556; 54.5875 تاريخ التأسيس 1958 تقسيم إداري البلد روسيا عدد السكان عدد السكان 3450 (2010)3262 (2007)3350 (2021)[1] معلومات أخرى 452697 رمز الهاتف 34783 تعديل مصدري - تعديل إنيرجتيك (بالروسية:...

BuayanKecamatanNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenKebumenPemerintahan • CamatDrs.Isnadi,M.PAPopulasi • Total54.253 jiwa (SP 2.014) jiwaKode Kemendagri33.05.02 Kode BPS3305020 Luas78,9 km²Desa/kelurahan20Situs webhttp://kec-buayan.kebumenkab.go.id/ Buayan (bahasa Jawa: ꦧꦸꦮꦪꦤ꧀) adalah sebuah kecamatan di Kabupaten Kebumen, Jawa Tengah, Indonesia. Kecamatan Buayan terletak di sebelah barat daya Kota Kebumen. Jarak Kecamatan Buayan dari Kota ...

2008年北京オリンピックの体操競技(2008ねんペキンオリンピックのたいそうきょうぎ)は、北京国家体育館および北京工業大学体育館で2008年8月9日から8月24日までの競技日程で実施されたオリンピックの体操である。体操の体操競技、新体操、トランポリンが実施された。 概要 体操競技およびトランポリンは北京国家体育館で実施され、新体操のみ北京工業大学体育館...

Ronnie Hillman Datos personalesNombre completo Ronald Keith Ryan Hillman Jr.Nacimiento Long Beach, California14 de septiembre de 1991País Estados UnidosNacionalidad(es) EstadounidenseFallecimiento Atlanta, Georgia22 de diciembre de 2022 (31 años)Altura 1,75 m (5′ 9″)Peso 91 kg (200 lb)Carrera deportivaDeporte Fútbol americanoEquipo universitario San Diego State AztecsEstado CaliforniaClub profesionalDraft 2012 / Ronda 3 / Selección 67Debut deportivo 2012(Denv...

この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典が不足しています。存命人物の記事は特に、検証可能性を満たしている必要があります。(2024年6月) 独自研究が含まれているおそれがあります。(2024年6月) あまり重要でない事項が過剰に含まれているおそれがあり、整理が求められています。(2024年6月)出典検索?: 平...
![Coin in the name of Rakhanch, lord of Ushrusana. Tamgha symbol on the reverse with name of the ruler in Sogdian rγʾnč MRAY "Raxānič Afšīn".[1] Excavated in the Palace of Kala-i Kakhkakha I, Bunjikat. 7th century CE, National Museum of Antiquities of Tajikistan (RTL 213).[2] of Ushrusana](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/Coin_Rakhanch_NMAT_RTL213_%28obverse_and_reverse%29.jpg/300px-Coin_Rakhanch_NMAT_RTL213_%28obverse_and_reverse%29.jpg)










![Bunjikat "Remus and Romulus", 8th century.[24]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/dd/Bunjikat_Remus_and_Romulus.jpg/187px-Bunjikat_Remus_and_Romulus.jpg)


