Gothic alphabet
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Gossamer Albatross adalah sebuah pesawat terbang tenaga-manusia dibuat oleh Dr Paul B. MacCready. Pada 12 Juni 1979 pesawat ini menyelesaikan dengan sukses menyebrangi Selat Inggris untuk memenangkan penghargaan Kremer kedua. Gossamer Albatross II dalam penerbangannya. Gossamer Albatross, pandangan dari dekat kabinnya. Pesawat ini digerakkan menggunakan pedal untuk menggerakan baling-baling dua-blade. Dipiloti oleh penyepeda amatir Bryan Allen yang menyelesaikan 35,8km dalam 2jam dan 49menit,...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (ديسمبر 2017) التاريخ الإجرامي للمسيحيةKriminalgeschichte des Christentums (بالألمانية) معلومات عامةالمؤلف كارلهاينز ديشنر اللغة الألمانية البلد ألمانيا الغربية الموضوع تاريخ المسيحي...

Andy WilliamsWilliams pada tahun 1967Informasi latar belakangNama lahirHoward Andrew WilliamsNama lainVoice of National TreasureEmperor of EasyThe King of HeartsEmperor of ClassMr. Moon RiverThe King of Easy ListeningMr. ChristmasThe Golden VoiceThe American IdolSatin-Smooth VoiceLahir(1927-12-03)3 Desember 1927 Wall Lake, Iowa, Amerika SerikatMeninggal 25 September 2012(2012-09-25) (umur 84) Branson, Missouri, Amerika SerikatGenrePop tradisional, easy listeningPekerjaanPenyanyi, aktor, ...

Charles Richet Charles Robert Richet (25 Agustus 1850 – 4 Desember 1935) adalah seorang ahli ilmu fisiologi Prancis yang memulai berbagai penelitian seperti neurokimia, sistem pencernaan, termoregulasi hewan berdarah panas atau Homoiterm, dan sistem pernafasan. Ia diberi gelar profesor di bidang ilmu fisiologi oleh Collège de France pada tahun 1887 dan menjadi anggota Académie de Médecine pada 1898. Pada 1914, ia bergabung dengan Académie des Sciences.[1] Karya Ia ...

Fratelli Musulmani(AR) الإخوان المسلمون LeaderMuḥammad Badīʿ, ottava Guida della Fratellanza Stato Internazionale SedeIl Cairo Fondazione1928 IdeologiaConservatorismoIslamismoPanislamismoQutbiyyaNeo-sufismoSalafismoConservatorismo socialeAntisionismoAnticomunismo CollocazioneDestra/Estrema destra Sito webikhwanweb.com Bandiera del partito Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale I Fratelli Musulmani o Fratellanza Musulmana (in arabo جماعة الإخ�...

منتخب الجزر العذراء الأمريكية لكرة القدم معلومات عامة بلد الرياضة جزر العذراء الأمريكية الفئة كرة القدم للرجال رمز الفيفا VIR الاتحاد اتحاد جزر العذراء الأمريكية لكرة القدم كونفدرالية كونكاكاف (أمريكا الشمالية والوسطى والكاريبي) الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي ...

English actor (1933–2007) For the Irish footballer, see Anton Rodgers (footballer). For those of a similar name, see Anthony Rogers (disambiguation). Anton RodgersBornAnthony Rodgers(1933-01-10)10 January 1933Ealing, Middlesex, EnglandDied1 December 2007(2007-12-01) (aged 74)Reading, Berkshire, EnglandAlma mater Italia Conti Academy London Academy of Music and Dramatic Art OccupationActorYears active1947–2007Spouses Morna Watson (m. 1959, ...

Shinkansen E6Shinkansen E6 bernomor induk Z14 pada Mei 2022Beroperasi16 Maret 2013; 11 tahun lalu (2013-03-16) – saat iniPembuatHitachi, Kawasaki Heavy IndustriesDigantikan olehShinkansen E3Tahun pembuatan2010–2014Jumlah sudah diproduksi168 kereta (24 rangkaian)Jumlah beroperasi168 kereta (24 rangkaian)Formasi7 kereta per rangkaianNomor armadaZ1–Z24Kapasitas338 (315 kelas Standar + 23 Hijau)Operator JR EastDepoAkitaJalurTōhoku Shinkansen, Akita ShinkansenData teknisBodi keretaAlum...

Tuberculum sellaeSphenoid bone. Upper surface. (Tuberculum sellae visible at center.)Base of the skull. Upper surface. (Sphenoid bone visible in yellow, the tuberculum sellae is labeled at the right, fourth from the top of the yellow section.)IdentifiersTA98A02.1.05.007TA2590FMA54719Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] The tuberculum sellae (or the tubercle of the sella turcica) is a slight[1] median elevation upon the superior aspect of the body of sphenoid bone (that forms t...

Tomoyuki YamashitaJulukanHarimau MalayaPengabdianKekaisaran JepangDinas/cabang Angkatan Darat Kekaisaran JepangLama dinas1905–1945PangkatJenderalKomandanIJA 4th Division, IJA 25th Army, IJA 1st Army, IJA 14th Area ArmyPerang/pertempuranPerang Tiongkok-Jepang KeduaPerang Pasifik Jenderal Tomoyuki Yamashita (山下 奉文 Yamashita Tomoyuki) (8 November 1885 – 23 Februari 1946) adalah seorang Jenderal Tentara Kekaisaran Jepang semasa Perang Dunia II. Menjadi terkenal kare...

Election 1856 Vermont gubernatorial election ← 1855 September 2, 1856 (1856-09-02) 1857 → Nominee Ryland Fletcher Henry Keyes Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 34,052 11,661 Percentage 74.0% 25.4% Governor before election Stephen Royce Republican Elected Governor Ryland Fletcher Republican Elections in Vermont Federal government Presidential elections 1792 1796 1800 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 18...

Part of a series onNazism Organizations Ahnenerbe Geheime Staatspolizei Deutsches Jungvolk Hitler Youth League of German Girls NSDÄB NSDStB NSRL NSFK NSKK NSF Nationalsozialistische Monatshefte Nazi Party Sturmabteilung (SA) Schutzstaffel (SS) History Early timeline National Socialist Program Hitler's rise to power Machtergreifung German rearmament Nazi Germany Religion in Nazi Germany Kirchenkampf Adolf Hitler's cult of personality Enabling Act of 1933 Night of the Long Knives Nuremberg ra...

Флаг гордости бисексуалов Бисексуальность Сексуальные ориентации Бисексуальность Пансексуальность Полисексуальность Моносексуальность Сексуальные идентичности Би-любопытство Гетерогибкость и гомогибкость Сексуальная текучесть Исследования Шк...

2004 American science fiction television series Battlestar GalacticaGenre Military science fiction Political drama[1][2][3] Post-apocalyptic Space opera Based onBattlestar Galacticaby Glen A. LarsonDeveloped byRonald D. MooreStarring Edward James Olmos Mary McDonnell Katee Sackhoff Jamie Bamber James Callis Tricia Helfer Grace Park Michael Hogan Aaron Douglas Tahmoh Penikett Paul Campbell Nicki Clyne Michael Trucco Alessandro Juliani Kandyse McClure Opening themeGayatr...
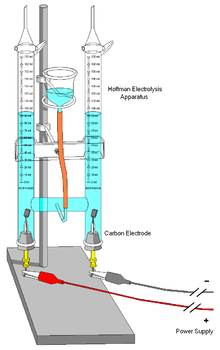
Illustrazione di un processo di elettrolisi per la produzione dell'idrossido di sodio (Descriptive Chemistry, Lyman C. Newell). Illustrazione di un voltametro di Hofmann, uno strumento utilizzato per svolgere l'elettrolisi dell'acqua L'elettrolisi (pronuncia corretta: /eletˈtrɔlizi/; pronuncia accettabile: /elɛttroˈlizi/[1]) è un processo che consiste nello svolgimento di trasformazioni chimiche grazie all'apporto di energia elettrica; si ha quindi la conversione dell'energia...

Sorin GrindeanuSorin Grindeanu nel 2018 Primo ministro della RomaniaDurata mandato4 gennaio 2017 –29 giugno 2017 PresidenteKlaus Iohannis PredecessoreDacian Cioloș SuccessoreMihai Tudose Vice primo ministro della RomaniaDurata mandato25 novembre 2021 –15 giugno 2023 ContitolareKelemen Hunor Capo del governoNicolae Ciucă PredecessoreKelemen Hunor SuccessoreMarian NeacșuCătălin Predoiu Ministro delle infrastrutture e dei trasportiIn caricaInizio mandato...

Methods to reduce sound pressure A pair of headphones being tested inside an anechoic chamber for soundproofing This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: There are too many short sections. Please help improve this article if you can. (December 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Soundproofing is any means of impeding sound propagation. There are several basic ways to reduce sound: increasing the distance between source and r...
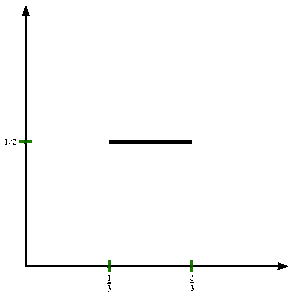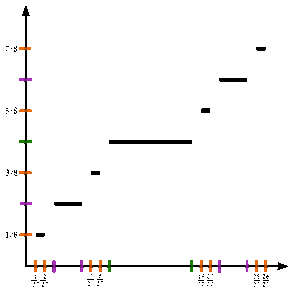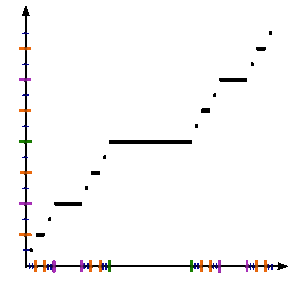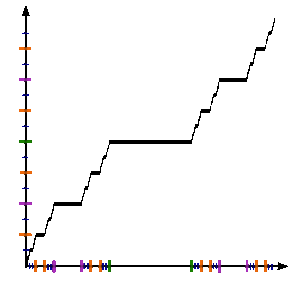
この項目「カントール関数」は翻訳されたばかりのものです。不自然あるいは曖昧な表現などが含まれる可能性があり、このままでは読みづらいかもしれません。(原文:英語版 Cantor function 02:07, 6 May 2013 (UTC)) 修正、加筆に協力し、現在の表現をより自然な表現にして下さる方を求めています。ノートページや履歴も参照してください。(2013年9月) 単位区間における...

Political philosophy This article is about the libertarian political philosophy within the socialist movement. For the branch of anarchism emphasizing social equality, see Social anarchism. For the type of libertarianism stressing both individual freedom and social equality, see Left-libertarianism. For the political philosophy that incorporates liberal principles to socialism, see Liberal socialism. For the variety of liberalism that endorses a regulated market economy and the expansion of c...

Not to be confused with Mutiny (funk band). This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) MutinyBackground informationOriginMelbourne, AustraliaGenresFolk PunkYears active1991–presentMembersChris PatchesGreg StainsbyAlice GreenCalum HollandMarko JenningsKav Kava...

