Functional psychology
|
Read other articles:

Hamparan hutan di Taman Nasional Danau Sentarum, Kalimantan Barat. Alam liar adalah lingkungan hidup di Bumi yang belum banyak tersentuh oleh kegiatan manusia atau penggarapan tanah untuk pertanian.[1][2] Sering pula diartikan sebagai wilayah liar dan belum dibudidayakan seperti hutan atau gurun yang tidak ditinggali oleh manusia dan hanya dihuni oleh binatang buas. Istilah ini secara tradisional merujuk pada lingkungan di darat, tetapi saat ini juga dapat digunakan untuk meru...

Dalam nama Korean ini, nama keluarganya adalah Kim. Jin Seo-yeonJin Seo-yeon pada Januari 2020 pada presentasi produksi OCN Tell me what you seeLahirKim Jeong-sun18 Januari 1983 (umur 41)Nama lainHa YunAlmamaterDongduk Women's University, Department of Broadcasting and EntertainmentPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif2007–sekarangAgenAndmarq[1]Nama KoreaHangul진서연 Hanja陳瑞演[2] Alih AksaraJin SeoyeonMcCune–ReischauerChin Sŏyŏn Jin Seo-yeon (Korean: 진서�...

2004 single by Nelly FurtadoExplodeSingle by Nelly Furtadofrom the album Folklore Released27 September 2004Recorded2003Length3:45Label DreamWorks Songwriter(s) Nelly Furtado Gerald Eaton Producer(s) Track & Field Nelly Furtado Nelly Furtado singles chronology Força (2004) Explode (2004) The Grass Is Green (2005) Music videoExplode on YouTube Explode is a song written by Canadian singer Nelly Furtado and Gerald Eaton for Furtado's second studio album, Folklore (2003). It is produced by E...

The Wonderful ChanceIklan 1922SutradaraGeorge ArchainbaudDitulis olehH. H. Van Loan (cerita asli)Mary Murillo (skenario)Melville Hammett (skenario)PemeranEugene O'BrienMartha MansfieldRudolph ValentinoSinematograferHenry Cronjager[1]PerusahaanproduksiSelznick PicturesDistributorSelect PicturesTanggal rilis 27 September 1920 (1920-09-27) Durasi52 menit; 5 rol (5,137 feet)NegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaBisu (antarjudul Inggris) The Wonderful Chance (juga The Thug dan His Wonderful Chan...

Prakash JhaPrakash Jha dengan Deepika Padukone pengumuman pers film Aarakshan. 2010Lahir27 Februari 1952 (umur 72)Champaran Barat, Bihar, IndiaPekerjaanProduser, Sutradara, Penulis naskah, PemeranTahun aktif1976-sekarangSuami/istriDeepti Naval (1985-1989)AnakDisha JhaSitus webPrakash Jha Productions Prakash Jha (lahir 27 Februari 1952) adalah seorang produser, pemeran, sutradara dan penulis naskah asal India, yang kebanyakan dikenal untuk film-film politik dan sosio-politiknya sepe...

Museum in Kentucky promoting a pseudoscientific creationist point of view This article is about the museum in Kentucky. For other creation museums, see Creationist museum. Creation MuseumThe front of the Creation MuseumLocation within KentuckyShow map of KentuckyCreation Museum (the United States)Show map of the United StatesEstablishedMay 28, 2007 (2007-05-28)LocationPetersburg, Kentucky, U.S.Coordinates39°05′10″N 84°47′00″W / 39.08611°N 84.78333°W&...

محمد ملحم مناصب رئيس بلدية حلحول في المنصب1976 – 2005 عضو اللجنة التنفيذية لمنظمة التحرير الفلسطينية في المنصب29 نوفمبر 1984 – 28 سبتمبر 1991 معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة محمد حسن عبد الرحمن ملحم الميلاد 4 سبتمبر 1929 حلحول الوفاة 17 يوليو 2021 (91 سنة) [1] ع�...

Season of television series The FaceSeason 2Promotional posterNo. of episodes10[1]ReleaseOriginal networkOxygenOriginal releaseMarch 5 (2014-03-05) –May 7, 2014 (2014-05-07)Season chronology← PreviousSeason 1List of episodes The second season of The Face premiered on March 5, 2014 on Oxygen.[2] The season followed three supermodel coaches as they competed with each other to find 'the face' of Frédéric Fekkai's hair care brand by the same name. Model ...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant le Concours Eurovision de la chanson et Saint-Marin. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) ; pour plus d’indications, visitez le projet Eurovision. Saint-Marinau Concours Eurovision 2015 Données clés Pays Saint-Marin Chanson Chain of Light Interprète Michele Perniola et Anita Simoncini Langue Anglais Sélection nationale Type de sélection Sélection interne Date 27 novembre 2014 (artistes)16 mars 20...

Zend EngineTipeperangkat lunak bebas dan reference implementation Versi pertama1999Versi stabil 2.0.2 (1r Desember 2005) GenreKompilatorLisensiZend Engine LicenseBahasaDaftar bahasa PHP Karakteristik teknisBahasa pemrogramanC Informasi pengembangPembuatAndi Gutmans, Zeev SuraskiPengembangZend Technologies, tim pengembang PHP.Sumber kode Kode sumberPranala Informasi tambahanSitus webwww.zend.comPelacakan kesalahanLaman pelacakan Sunting di Wikidata • Sunting kotak info • L ...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir André Michel et Michel. Cet article est une ébauche concernant un historien français. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. André MichelBiographieNaissance 7 novembre 1853MontpellierDécès 13 octobre 1925 (à 71 ans)ParisNationalité françaiseFormation École pratique des hautes étudesActivités Historien de l’art, conservateur de musée, professeur d'uni...

His Excellency赫瓦贾·纳齐姆丁爵士খাজা নাজিমুদ্দীন خواجہ ناظِمُ الدّینCIE, KCIE摄于1948年第2任巴基斯坦總理任期1951年10月17日—1953年4月17日君主佐治六世伊莉沙白二世总督古拉姆·穆罕默德前任利雅卡特·阿里·汗继任Mohammad Ali Bogra(英语:Mohammad Ali Bogra)第2任巴基斯坦總督(英语:Governor-General of Pakistan)任期1948年9月14日—1951年10月17日君�...

Докладніше: Втрати силових структур внаслідок російського вторгнення в Україну У статті наведено список втрат українських військовослужбовців у російсько-українській війні, починаючи з 1 червня 2022 року по 15 червня 2022 року (включно). Втрати з українського боку публіку�...

「アプリケーション」はこの項目へ転送されています。英語の意味については「wikt:応用」、「wikt:application」をご覧ください。 この記事には複数の問題があります。改善やノートページでの議論にご協力ください。 出典がまったく示されていないか不十分です。内容に関する文献や情報源が必要です。(2018年4月) 古い情報を更新する必要があります。(2021年3月)出...

Di luar Amerika Serikat, Amerikanisasi adalah istilah untuk menyebut pengaruh yang dimiliki Amerika Serikat di negara lain, contohnya budaya masyarakat, masakan, teknologi, praktik bisnis, atau teknik politiknya. Istilah ini sudah digunakan sejak tahun 1907.[1] Di Amerika Serikat sendiri, kata Amerikanisasi berarti proses akulturasi adat dan nilai-nilai Amerika Serikat oleh imigran atau penduduk yang dianeksasi (misalnya California). Media dan budaya masyarakat Hollywood (industri fil...

اليمن الجمهورية اليمنية اليمنعلم اليمن اليمنشعار اليمن موقع اليمن باللون الأحمر في جنوب غرب شبه الجزيرة العربية الشعار الوطنيالله، الوطن، الثورة، الوحدة النشيد: رددي أيتها الدنيا نشيدي الأرض والسكان إحداثيات 15°30′N 48°00′E / 15.5°N 48°E / 15.5; 48 [1] أعلى ق�...
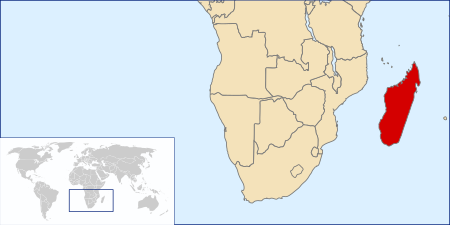
Species of moth Madagascan sunset moth Engraving captioned Urania riphaeus from Charles D. d'Orbigny's Dictionnaire universel d'histoire naturelle (1849) Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Lepidoptera Family: Uraniidae Genus: Chrysiridia Species: C. rhipheus Binomial name Chrysiridia rhipheus(Drury, 1773) Endemic to Madagascar Synonyms Papilio rhipheus Drury, 1773[1] Urania ripheus var. madagascariensis Lesson, 1...

Medical test This article is about genetic tests for disease and ancestry or biological relationships. For use in genealogy and archaeology, see genealogical DNA test. For use in forensics, see DNA profiling. Part of a series onGenetics Key components Chromosome DNA RNA Genome Heredity Nucleotide Mutation Genetic variation Allele Amino acid Outline Index History and topics Introduction History Evolution (molecular) Population genetics Mendelian inheritance Quantitative genetics Molecular gene...

Cyrillic letter Not to be confused with the Korean hangul syllable 어 (eo) or the Cyrillic letter yus. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Yu Cyrillic – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Cyrillic letter Cyrillic letter Yu...

Charles Stanton Ogle (5 Juni 1865 - 11 Oktober 1940) [1] adalah seorang Amerika film bisu aktor.[2] Biografi Lahir di Steubenville, Ohio, Ogle memulai karier aktingnya di teater, memulai debutnya di Broadway pada tahun 1905 di Edmund Burke , sebuah komedi musikal yang disutradarai oleh Edgar Selwyn, di mana ia bekerja bersama Jack Pickford.[3] Pada Tahun 1908 Charles yang mulai bekerja untuk film itu, meninggalkan teater untuk melakukan pekerjaan penuh waktu karier fil...