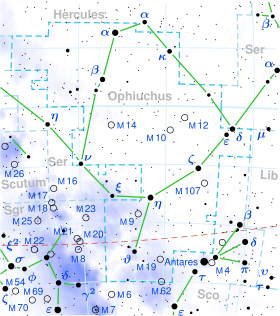
Star in the constellation Ophiuchus
44 Ophiuchi
Location of 44 Ophiuchi (circled)
Observation dataEpoch J2000 Equinox J2000
Constellation
Ophiuchus
Right ascension 17h 26m 22.21749s [ 1]
Declination
−24° 10′ 31.1190″[ 1]
Apparent magnitude (V)4.16[ 2]
Characteristics
Spectral type
kA5hA9mF1III[ 3]
U−B color index
+0.12[ 4]
B−V color index
+0.28[ 4]
Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv )−37.20[ 5] km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: +0.10[ 1] mas /yr Dec.: −118.18[ 1] mas /yr Parallax (π)39.22± 0.24 mas [ 1] Distance 83.2 ± 0.5 ly pc ) Absolute magnitude (MV )2.13[ 2] Details Mass 1.77[ 6] M ☉ Radius 1.9[ 7] R ☉ Luminosity 13[ 6] L ☉ Surface gravity (log g )4.15[ 8] cgs Temperature 7,559[ 8] K Metallicity [Fe/H] +0.30[ 2] dex Rotational velocity (v sin i )78[ 6] Age 1.028[ 8] Gyr Other designations b Oph , 44 Oph , CD −24°13337FK5 1457GC 23597GJ 9591HD 157792HIP 85340HR 6486SAO 185401[ 9] Database references SIMBAD data
44 Ophiuchi is a single[ 10] star in the constellation Ophiuchus . It has the Bayer designation b Ophiuchi , while 44 Ophiuchi is the Flamsteed designation . It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.16.[ 2] light years based on parallax.[ 1] radial velocity of -37.2 km/s,[ 5] [ 11]
This is an Am star with a stellar classification of kA5hA9mF1III,[ 3] luminosity class of a giant star with a spectrum that matches an A5 star based on the calcium K line , and an A9 star from the hydrogen and metal lines . It is around a billion years old[ 8] [ 6] mass of the Sun and 1.9[ 7] Sun's girth . The star is radiating 13[ 6] Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 7,559 K.[ 8] projected rotational velocity of 78 km/s.[ 6]
References
^ a b c d e f Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 474 (2): 653– 664. arXiv :0708.1752 Bibcode :2007A&A...474..653V . doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 . S2CID 18759600 . Vizier catalog entry ^ a b c d Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters . 38 (5): 331. arXiv :1108.4971 Bibcode :2012AstL...38..331A . doi :10.1134/S1063773712050015 . S2CID 119257644 . Vizier catalog entry ^ a b Gray, R. O.; Corbally, C. J.; Garrison, R. F.; McFadden, M. T.; Bubar, E. J.; McGahee, C. E.; O'Donoghue, A. A.; Knox, E. R. (2006). "Contributions to the Nearby Stars (NStars) Project: Spectroscopy of Stars Earlier than M0 within 40 pc--The Southern Sample". The Astronomical Journal . 132 (1): 161– 170. arXiv :astro-ph/0603770 Bibcode :2006AJ....132..161G . doi :10.1086/504637 . S2CID 119476992 . ^ a b Mallama, A. (2014). "Sloan Magnitudes for the Brightest Stars". The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers . 42 (2): 443. Bibcode :2014JAVSO..42..443M . Vizier catalog entry ^ a b Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters . 32 (11): 759– 771. arXiv :1606.08053 Bibcode :2006AstL...32..759G . doi :10.1134/S1063773706110065 . S2CID 119231169 . ^ a b c d e f Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 537 : A120. arXiv :1201.2052 Bibcode :2012A&A...537A.120Z . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/201117691 . S2CID 55586789 . Vizier catalog entry ^ a b Allende Prieto, C.; Lambert, D. L. (1999). "Fundamental parameters of nearby stars from the comparison with evolutionary calculations: Masses, radii and effective temperatures". Astronomy and Astrophysics . 352 : 555– 562. arXiv :astro-ph/9911002 Bibcode :1999A&A...352..555A . Vizier catalog entry ^ a b c d e David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015). "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal . 804 (2): 146. arXiv :1501.03154 Bibcode :2015ApJ...804..146D . doi :10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146 . S2CID 33401607 . Vizier catalog entry ^ "b Oph" . SIMBAD Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2019-06-21 .^ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems" . Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 389 (2): 869– 879. arXiv :0806.2878 Bibcode :2008MNRAS.389..869E . doi :10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x S2CID 14878976 . ^ Bailer-Jones, C. A. L. (March 2015). "Close encounters of the stellar kind". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 575 : 13. arXiv :1412.3648 Bibcode :2015A&A...575A..35B . doi :10.1051/0004-6361/201425221 . S2CID 59039482 . A35.