Shin Arahan
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Konsepsi Pohaci dan Susunan Hierarki di tatar Sawarga Loka Manggung atau Langit. Pohaci merujuk kepada sebutan lain untuk dewa atau dewi mitologi Hindu dalam tradisi dan budaya Sunda. [1] Dalam konteks spiritualitas Sunda, Pohaci merupakan proyeksi dari dewa atau dewi pelindung dalam kehidupan masyarakat Sunda di masa lalu.[1] Deskripsi Kehidupan masyarakat Sunda di masa lalu sangat terkait erat dengan berbagai nama Pohaci. Pohaci dikenal sebagai dewa atau dewi pelindung yang ...

منتخب كوريا الجنوبية لكرة القدم 대한민국 축구 국가대표팀 معلومات عامة اللقب 태극전사 (محاربو التايغوك) 아시아의 호랑이 (نمور آسيا) بلد الرياضة كوريا الجنوبية الفئة كرة القدم للرجال رمز الفيفا KOR الاتحاد اتحاد كوريا الجنوبية لكرة القدم كونفدرالية الاتحاد الآسيوي لكرة القدم...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (août 2014). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Co...

كأس بلغاريا 1989–90 تفاصيل الموسم كأس بلغاريا النسخة 50 البلد بلغاريا المنظم اتحاد بلغاريا لكرة القدم البطل او في سي سليفن 2000 كأس بلغاريا 1988–89 كأس بلغاريا 1990–91 تعديل مصدري - تعديل كأس بلغاريا 1989–90 (بالبلغارية: Купа на Народна република България 1989/...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando l'omonimo film del 2023, vedi Renfield (film). RenfieldDwight Frye nei panni di Renfield in Dracula SagaDracula AutoreBram Stoker 1ª app. inDracula (romanzo) Interpretato daDwight Frye (Dracula) Nicholas Hoult (Renfield) Voci italianeRomano Malaspina Francesco Venditti Caratteristiche immaginarieSpecieumana Sessomaschile Professioneex agente immobiliare R. M. Renfield è un personaggio immaginario del romanzo Dracula di Bram Stoker. Indice 1 Nel roma...

Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens HOXD8IdentifiersAliasesHOXD8, HOX4, HOX4E, HOX5.4, homeobox D8External IDsOMIM: 142985 MGI: 96209 HomoloGene: 10473 GeneCards: HOXD8 Gene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 2 (human)[1]Band2q31.1Start176,129,694 bp[1]End176,132,695 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 2 (mouse)[2]Band2 C3|2 44.13 cMStart74,534,959 bp[2]End74,538,277 bp[2]RNA expression patternBgeeHumanMouse (ortholog)Top expre...

National flag of the Republic of Turkey Flag of TurkeyUseNational flag and ensign Proportion2:3Adopted1844 (Ottoman flag) 29 May 1936 (standardized)DesignA red field charged with a white star and crescent slightly left-of-center.[1] The national flag of Turkey, officially the Turkish flag[2] (Turkish: Türk bayrağı), is a red flag featuring a white star and crescent from its emblem which was the prominent symbol of the Ottoman Empire, and in contemporary times used as a nati...

Protected area in New South Wales, AustraliaWeddin Mountains National ParkNew South WalesIUCN category II (national park) The Weddin Mountains rise from the surrounding flat land - view looking south from the Euraldrie roadWeddin Mountains National ParkCoordinates33°58′19.9″S 148°01′23.2″E / 33.972194°S 148.023111°E / -33.972194; 148.023111Established12 November 1971 (1971-11-12)Area83.61 km2 (32.3 sq mi)Managing authoritiesNa...

МифологияРитуально-мифологическийкомплекс Система ценностей Сакральное Миф Мономиф Теория основного мифа Ритуал Обряд Праздник Жречество Мифологическое сознание Магическое мышление Низшая мифология Модель мира Цикличность Сотворение мира Мировое яйцо Мифическое �...

Census division of Saskatchewan, Canada Census division in Saskatchewan in CanadaDivision No. 5Census division in Saskatchewan NWT AB MB USA 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Country CanadaProvince SaskatchewanArea • Total14,779.44 km2 (5,706.37 sq mi) As of 2016Population (2016) • Total31,750 • Density2.1/km2 (5.6/sq mi) Division No. 5 is one of eighteen census divisions in the province of Saskatchewan, Ca...

Municipality in Västmanland County, SwedenVästerås Municipality Västerås kommunMunicipalityVästerås City Hall Coat of armsCoordinates: 59°37′N 16°32′E / 59.617°N 16.533°E / 59.617; 16.533CountrySwedenCountyVästmanland CountySeatVästeråsArea[1] • Total1,137.835976 km2 (439.320926 sq mi) • Land959.015976 km2 (370.278138 sq mi) • Water178.82 km2 (69.04 sq mi) Ar...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Rogers. Carl RogersPortrait de Carl RogersFonctionPrésident de l'Association américaine de psychologie1947BiographieNaissance 8 janvier 1902Oak ParkDécès 4 février 1987 (à 85 ans)La JollaNom dans la langue maternelle Carl Ransom RogersNationalité américaineFormation Université du Wisconsin à MadisonTeachers College de l'université ColumbiaUnion Theological SeminaryActivités Psychothérapeute, psychologueEnfant Natalie Rogers (d)Autres inform...

German rock band This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Bonfire band – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) BonfireBonfire at Metal Frenzy 2019Background informationAlso known asCacumen, Lessmann/Ziller, Ex, EZ Livin'OriginIngol...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (سبتمبر 2020) الجدول الزمني لجائحة كوفيد-19 في المكسيك يناير 2020 في 22 يناير 2020، أصدرت الصحة بيانًا قالت فيه إن كوفيد-19 لا يمثل خطرًا على المكسيك. سُجّلت 441 حالة في كل من الصين...
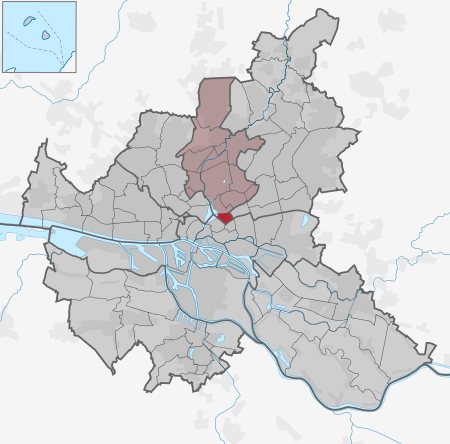
Quarter in Hamburg, Germany Quarter of Hamburg in GermanyHohenfelde Quarter of Hamburg Location of Hohenfelde in Hamburg Hohenfelde Show map of GermanyHohenfelde Show map of HamburgCoordinates: 53°33′40″N 10°01′16″E / 53.561°N 10.021°E / 53.561; 10.021CountryGermanyStateHamburgCityHamburg BoroughHamburg-Nord Area • Total1.1 km2 (0.4 sq mi)Population (2020-12-31)[1] • Total9,853 • Density9,000/k...

Provincial park in Ontario, Canada Upper Madawaska River Provincial ParkIUCN category II (national park)Madawaska River at Whitney, the western/upstream boundary of the parkLocation of the park in southern OntarioLocationNipissing District, OntarioNearest cityPembroke, OntarioCoordinates45°29′41″N 78°04′08″W / 45.49472°N 78.06889°W / 45.49472; -78.06889[1]Area1,085 ha (4.19 sq mi)Governing bodyOntario Parkswww.ontarioparks.c...

State in Germany This article is about the current German state and its historic antecedents. For the Prussian province (1868–1945), see Province of Schleswig-Holstein. For the warship, see SMS Schleswig-Holstein. State in GermanySchleswig-Holstein Slesvig-Holsten (Danish)Sleswig-Holsteen (Low German)Slaswik-Holstiinj (North Frisian)State FlagCoat of armsBrandmarkCoordinates: 54°28′12″N 9°30′50″E / 54.47000°N 9.51389°E / 54.47000; 9.51389Co...

2015 EP by Dej Loaf...And See That's the ThingEP by Dej LoafReleasedJuly 31, 2015Recorded2015GenreHip hopLength23:01LabelColumbiaProducer DDS Go Grizzly iRocksays Izze The Producer The-A-Team Smash David J. Vaughn Dej Loaf chronology Sell Sole(2014) ...And See That's the Thing(2015) Singles from ...And See That's the Thing Back UpReleased: July 15, 2015[1] Hey ThereReleased: July 23, 2015[2] ...And See That's the Thing (stylized as #AndSeeThatsTheThing) is the first ex...

Untuk pengertian lain, lihat Baru. Baru adalah komune yang terletak di Provinsi Hunedoara, Rumania. Letaknya di selatan Haţeg. Pada tahun 1910, komune ini berpenduduk 518 jiwa dan pada tahun 1992 sebanyak 1.333 jiwa. Baru pertama kali muncul dalam sejarah pada tahun 1453. Baru memiliki sejumlah desa, seperti Baru Mic, Livadia, Livadia de Coastă, Petros, dan Valea Lupului. Koordinat: 45°28′N 23°10′E / 45.467°N 23.167°E / 45.467; 23.167 Artikel bertopik geograf...

