Ohio History Center
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

العلاقات الهندية الكورية الجنوبية الهند كوريا الجنوبية الهند كوريا الجنوبية تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الهندية الكورية الجنوبية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين الهند وكوريا الجنوبية.[1][2][3][4][5] يعود تاريخ العلاقات الهندية الكور�...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع لونغ بيتش (توضيح). لونغ بيتش علم الإحداثيات 40°35′10″N 73°40′04″W / 40.58605°N 73.66775°W / 40.58605; -73.66775 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 1623 تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة ناسو خصائص جغرافية الم�...

53°46′55″N 1°47′46″W / 53.782°N 1.796°W / 53.782; -1.796 Human settlement in EnglandGreat HortonGreat Horton Ward 2004Population17,683 (Ward. 2011 census)Metropolitan countyWest YorkshireRegionYorkshire and the HumberCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited KingdomUK ParliamentBradford SouthCouncillorsJoanne Dodds (Labour)Tariq Hussain (Labour)Abdul Jabar (Labour) List of places UK England Yorkshire Great Horton is a ward of t...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目需要編修,以確保文法、用詞、语气、格式、標點等使用恰当。 (2013年8月6日)請按照校對指引,幫助编辑這個條目。(幫助、討論) 此條目剧情、虛構用語或人物介紹过长过细,需清理无关故事主轴的细节、用語和角色介紹。 (2020年10月6日)劇情、用語和人物介紹都只是用於了解故事主軸,輔助�...

Voluntary controlled school in Worthing, West Sussex, EnglandDavison Church of England High School for GirlsAddressSelborne RoadWorthing, West Sussex, BN11 2JXEnglandCoordinates50°49′10″N 0°21′22″W / 50.81942°N 0.35599°W / 50.81942; -0.35599InformationTypeVoluntary controlled schoolMottoOra et Labora ('Pray and Work').Religious affiliation(s)Church of EnglandFounderRev Davison 1812Local authorityWest SussexDepartment for Education URN126093 TablesOfstedRep...

Railway station in Karnataka, India Mariyala–Gangawadi Indian Railways stationMariyala–Gangawadi railway stationGeneral informationLocationChamarajanagara District, Karnataka IndiaCoordinates12°18′59″N 76°38′43″E / 12.3163°N 76.6454°E / 12.3163; 76.6454Elevation760mPlatforms2ConstructionStructure typeStandard (on ground station)ParkingYesOther informationStatusFunctioningStation codeMRLA Zone(s) South Western Railway Division(s) MysoreHistoryOpened...

LighthouseRödkallen South lighthouseRödkallen Södra LocationRödkallen, Luleå Municipality, Sweden Coordinates65°18′51″N 22°22′11″E / 65.31411°N 22.36975°E / 65.31411; 22.36975TowerConstructed1966 FoundationconcreteConstructionmasonry 5-storey buildingHeight18 metres (59 ft)Shapebuilding with lantern on the roofMarkingsyellow, red, white (lantern) OperatorSwedish Maritime Administration (Sjöfartsverket)[1]LightFocal height22&...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Гряда. Выветрившиеся остатки горной гряды в горах Ларами[англ.], США Гряда́ — цепочка гор (горная гряда), холмов, обнажений горных пород. Грядой также называется протяжённая узкая возвышенность с плоскими вершинами и кру...
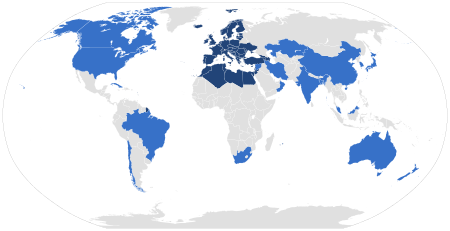
Alliance of public service media entities EBU redirects here. For other uses, see EBU (disambiguation). European Broadcasting UnionUnion européenne de radio-télévisionLogo used since 2012Countries with one or more members are in dark blue. Associated members in light blue.PredecessorInternational Broadcasting UnionFormation12 February 1950; 74 years ago (1950-02-12)TypeUnion of broadcasting organisationsHeadquartersGeneva, SwitzerlandMembership 112 member organisations(in...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: non-idiomatic English. Please help improve this article if you can. (October 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article's factual accuracy is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help to ensure ...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando il pittore e incisore triestino, cugino di Pietro, vedi Guido Marussig. Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento pittori italiani non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. In giardino, 1912 Piero Marussig (Trieste, 16 maggio 1879 – Pavia, 13 ottobre 1937) è stato ...

العلاقات اليمنية السريلانكية اليمن سريلانكا اليمن سريلانكا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات اليمنية السريلانكية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين اليمن وسريلانكا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقا...

7TP 7TP kubah tunggal Jenis Tank ringan Negara asal Polandia Sejarah pemakaian Digunakan oleh PolandiaNazi Jerman (ditangkap) Pada perang Perang Dunia II Sejarah produksi Diproduksi 1935-1939 Jumlah produksi 149 (+13 9TP purwarupa) Varian 7TP kubah ganda9TP (hanay purwarupa) Spesifikasi Berat 9.9 ton Panjang 4,6 m (15 ft 1 in) Lebar 2,4 m (7 ft 10 in) Tinggi 2,27 m (7 ft 5 in) Awak 3 (komandan, penembak, supir) Perisai 17 mm ma...

Benin Artikel ini adalah bagian dari seri Politik dan KetatanegaraanBenin Konstitusi Hak asasi manusia Pemerintahan Presiden Thomas Boni Yayi Presiden terpilih Patrice Talon Perdana Menteri Lionel Zinsou Pembicara Mathurin Nago Parlemen Majelis Nasional Presiden: Adrien Houngbédji Pembagian administratif Departemen Komunitas Arondisemen Pemilu Pemilihan terbaru Kepresidenan: 20112016 Parlementer: 20112015 Partai politik Hubungan luar negeri Negara lainnya Atlas lbs Daftar Pembicara di Benin....

Genus of flowering plants Loasa Loasa vulcanica Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Asterids Order: Cornales Family: Loasaceae Genus: LoasaAdans. Species See text. Loasa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Loasaceae. The genus contains about 100 species native to Central and South America.[1][2] Species of Loasa are prickly herbs or shrubs that have nettle-like stinging hairs.[2] Some specie...

Wallace Calvin AbbottLahir(1857-10-12)12 Oktober 1857Bridgewater, VermontMeninggal4 Juli 1921(1921-07-04) (umur 63)Chicago, IllinoisKebangsaanAmerika SerikatPekerjaanDokter, PengusahaDikenal atasAbbott Laboratories Wallace Calvin Abbott adalah pendiri Abbott Laboratories, salah satu perusahaan farmasi dan diagnostik terbesar di dunia. Dia merupakan salah satu tokoh penting dalam praktik farmasi modern setelah penemuannya yang disebut Butiran Dosimetrik (dosimetric granules) sekitar tahu...

بلاير سبيتال معلومات شخصية الميلاد 19 ديسمبر 1995 (العمر 28 سنة) الطول 6 قدم 0 بوصة (1.83 م) مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية المملكة المتحدة معلومات النادي النادي الحالي ماذرويل الرقم 7 مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق 2008–2010 Rangers F.C. B Team and Academy [الإنجليزية] 2010–2012 نادي كوينز بارك ...

Cadillac Bild nicht vorhanden Orleans Präsentationsjahr: 1953 Fahrzeugmesse: General Motors Motorama Klasse: Oberklasse Karosseriebauform: Limousine Motor: Ottomotor:(154 kW) Serienmodell: keines Der Cadillac Orleans war ein Konzeptfahrzeug, das die Cadillac-Division von General Motors für die Automobilausstellung 1953 entwickelte. Beschreibung Er war der erste viertürige Hardtop.[1] Bei einem Hardtop gibt es keine B-Säulen wie bei den meisten zeitgenössischen Serienmodellen. De...

Software platform developed by Microsoft For the newer cross-platform framework, see .NET. For other uses, see .net (disambiguation). .NET Framework.NET Framework component stackDeveloper(s)MicrosoftInitial releaseFebruary 13, 2002; 22 years ago (2002-02-13)Stable release4.8.1 / August 9, 2022; 2 years ago (2022-08-09)[1] Operating systemWindows 98 or later, Windows NT 4.0 or laterPlatformIA-32, x86-64, and ARMIncluded withMicrosoft WindowsSuccessor...

Aperçu de l'astronomie des rayons gamma.De haut en bas, de gauche à droite : - l'observatoire terrestre de rayons gamma MAGIC et le télescope spatial CGRO ; - carte du ciel à des énergies supérieures à 1 GeV ; - l'observatoire de rayons gamma HAWC. L'astronomie gamma est le domaine de l'observation astronomique centrée sur le spectre électromagnétique des rayons gamma. Ces derniers englobent les photons émis à des énergies supérieures à 511 keV, et cons...












