Malaysian legal history
|
Read other articles:

Prof. Dr. Ir. H.Gusti Muhammad HattaM.S. Menteri Riset dan Teknologi Indonesia Ke-11Masa jabatan19 Oktober 2011 – 20 Oktober 2014PresidenSusilo Bambang Yudhoyono PendahuluSuharna SurapranataPenggantiMohamad NasirMenteri Negara Lingkungan Hidup Indonesia Ke-8Masa jabatan22 Oktober 2009 – 19 Oktober 2011PresidenSusilo Bambang Yudhoyono PendahuluRachmat WitoelarPenggantiBerth Kambuaya Informasi pribadiLahir1 September 1952 (umur 71)Banjarmasin, Kalimantan Selat...

Piza Sejarah piza Pengiriman piza Jenis piza Piza bergaya New York Piza Sisilia Piza napoletana Piza Yunani Piza bergaya Chicago Piza al taglio Piza bergaya New Haven Piza Hawaii Piza bergaya California Piza bergaya St. Louis Piza Meksiko Pissaladière Piza bergaya Detroit Sajian sejenis Piza panggang Piza goreng Lahmacun Focaccia Manakish Coca Sardenara Calzone Pita Flammkuchen Paratha Naan Panekuk bawang hijau Pai tomat Piza bagel Roti bawang Roti sosis Farinata Quesadilla Kue piza Peralata...

Glimepirid Nama sistematis (IUPAC) 3-Ethyl-4-methyl-N-[2-(4-{[(trans-4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoyl]sulfamoyl}phenyl)ethyl]-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide Data klinis Nama dagang Amaryl, others AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a696016 Data lisensi EMA:pranala, US Daily Med:pranala Kat. kehamilan C(AU) Status hukum Harus dengan resep dokter (S4) (AU) ℞-only (US) Rx only Rute By mouth (tablets) Data farmakokinetik Bioavailabilitas 100% Ikatan protein >99.5% Me...

Pyotr Nikolayevich NesterovПётр Николаевич НестеровLahir(1887-02-15)15 Februari 1887Nizhny NovgorodMeninggal8 September 1914(1914-09-08) (umur 27)Żółkiew, Kerajaan Galisia dan Lodomeria, Austria-Hungaria(sekarang Zhovkva, Ukraina)Pengabdian Kekaisaran RusiaDinas/cabang Angkatan Darat Kekaisaran Rusia Penugasan Udara Kekaisaran RusiaLama dinas1906—1914PangkatStabskapitänPerang/pertempuranPerang Dunia Pertama Pyotr Nikolayevich Nesterov (bahasa Rusia&#...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Patterson. Pierre ClermontPat Patterson en avril 2014Données généralesNom de naissance Pierre ClermontNom de ring Pat PattersonNationalité CanadienNaissance 19 janvier 1941MontréalDécès 2 décembre 2020 (à 79 ans)MiamiTaille entre 5′ 10″ (1,78 m)[1] et 6′ 1″ (1,85 m)[2]Poids entre 237 lb (108 kg)[2] et 244 lb (111 kg)[1]Catcheur mortFédération World Wrestling FederationCarrière pro. 1958 - 1985m...

Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens BLZF1IdentifiersAliasesBLZF1, GOLGIN-45, JEM-1, JEM-1s, JEM1, basic leucine zipper nuclear factor 1External IDsOMIM: 608692 MGI: 1201607 HomoloGene: 31187 GeneCards: BLZF1 Gene location (Human)Chr.Chromosome 1 (human)[1]Band1q24.2Start169,367,970 bp[1]End169,396,540 bp[1]Gene location (Mouse)Chr.Chromosome 1 (mouse)[2]Band1|1 H2.2Start164,117,369 bp[2]End164,135,058 bp[2]RNA expression pattern...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Cricket team For the men's team, see Isle of Man cricket team. Isle of ManFlag of Isle of ManAssociationIsle of Man Cricket AssociationPersonnelCaptainAlanya ThorpeInternational Cricket CouncilICC statusAssociate member[1] (2017) Affiliate member (2004)ICC regionEuropeICC Rankings Current[2] Best-everWT20I 33rd 33rd (8 Sep 2023)Women's Twenty20 InternationalsFirst WT20Iv Norway at Desert Springs Cricket Ground, Almería; 12 November 2022Last WT20Iv Guernsey at...

Anouk GrinbergGrinberg pada 2014Lahir20 Maret 1963 (umur 61)Uccle, BelgiaPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1976–kini Anouk Grinberg (lahir 20 Maret 1963) adalah seorang pemeran asal Prancis.[1] Ia adalah putri dari Michel Vinaver, bernama lahir Michel Grinberg, seorang penulis dan pengarang drama asal Prancis, dan cicit dari politikus Rusia pra-1917 Maxim Vinaver. Ia tampil dalam lebih dari 40 film dan acara televisi sejak 1976. Pada 1996, ia memenangkan Silver Bear untuk Aktris...

Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України Тип військове формуванняЗасновано 1992Країна Україна Емблема управління Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України — структурний підрозділ Генерального штабу Збройних сил України призначений для планува...

British politician Walter HarrisonHarrison when Deputy Chief Whip in the 1970sTreasurer of the Household and Deputy Chief WhipIn office4 March 1974 – 4 May 1979MonarchElizabeth IIPrime MinisterHarold Wilson James CallaghanMember of Parliament for WakefieldIn office15 October 1964 – 18 May 1987Preceded byArthur Creech JonesSucceeded byDavid Hinchliffe Personal detailsBorn2 January 1921Died19 October 2012 (aged 91)NationalityBritishPolitical partyLabour Walter Harrison PC ...

English musician (born 1951) For other people named Phil Collins, see Phil Collins (disambiguation). Phil CollinsLVOCollins at the O2 Arena in London, 2022BornPhilip David Charles Collins (1951-01-30) 30 January 1951 (age 73)Wandsworth, London, EnglandOccupations Musician singer songwriter record producer actor Years active 1963–2011 2015–present Spouses Andrea Bertorelli (m. 1975; div. 1980) Jill Tavelman &#...

British designation for intelligence from decrypted enemy communications The Enigma cipher machine Enigma machine Enigma rotors Breaking Enigma Polish Cipher Bureau Doubles Grill Clock Cyclometer Bomba Zygalski sheets Bletchley Park Banburismus Herivel tip Crib Bombe Hut 3 Hut 4 Hut 6 Hut 8 PC Bruno Cadix Related Ultra vte Enigma machine out of its wooden boxLorenz SZ42 machine with covers removedPart of Japanese PURPLE machineThree cipher machines thatwere broken by the Allies toyield Ultra ...
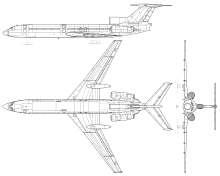
Ту-154 Тип пасажирський літакРозробник КБ ТуполевВиробник КБ ТуполєваГоловний конструктор Олександр ШенгардтПерший політ 3 жовтня 1968Початок експлуатації 1972Статус експлуатуєтьсяОсновні експлуатанти «UTair»«Кавминводыавиа»«Уральские авиалинии»Роки виробництва 1968—2013&#...

Superfamily of insects For the Pandanus planthopper, see Jamella australiae and Pandanus tectorius § Ecology. PlanthopperTemporal range: Carboniferous–Recent PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Flatida rosea (Flatidae)adults and nymphs Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Arthropoda Class: Insecta Order: Hemiptera Suborder: Auchenorrhyncha Infraorder: FulgoromorphaEvans, 1946 Families See text A planthopper is any insect in the infraorder Fulgoromorpha, ...

Voce principale: Partito Democratico (Italia). Elezioni primarie del Partito Democratico del 2019Stato Italia TipoElezioni primarie del Partito Democratico Data3 marzo Candidati Nicola Zingaretti Maurizio Martina Roberto Giachetti Voti 1.035.95566,00% 345.31822,00% 188.35512,00% Delegati 653 / 1 000 228 / 1 000 119 / 1 000 Distribuzione del voto per provincia Segretario nazionale del Partito DemocraticoNicola Zingaretti 2017 2023 Le elezioni primarie del Partito Democrati...

Anna di BretagnaAnna di Bretagna raffigurata in una miniatura del codice Les Grandes Heures d'Anne de Bretagne di Jean Bourdichon, 1503 - 1508 circaRegina consorte di FranciaStemma In carica come consorte di Carlo VIII:6 dicembre 1491 –7 aprile 1498 come consorte di Luigi XII:8 gennaio 1499 –9 gennaio 1514 Incoronazione 8 febbraio 1492, Basilica di Saint-Denis (1º regno) 18 novembre 1504, Basilica di Saint-Denis (2º regno) PredecessoreCarlotta di Savoia (I)Giovanna di Valois (II) S...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumentative essay that states a Wikipedia editor's personal feelings or presents an original argument about a topic. Please help improve it by rewriting it in an encyclopedic style. (February 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article is written like...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع ألاسكا (توضيح). ألاسكا علم شعار الشعار:(بالإنجليزية: North to the Future) الإحداثيات 64°N 150°W / 64°N 150°W / 64; -150 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 3 يناير 1959 تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى الولايات الم...

BLAZBLUE > BLAZBLUE ALTERNATIVE DARKWAR この記事の主題はウィキペディアにおける独立記事作成の目安を満たしていないおそれがあります。 目安に適合することを証明するために、記事の主題についての信頼できる二次資料を求めています。なお、適合することが証明できない場合には、記事は統合されるか、リダイレクトに置き換えられるか、さもなくば削除される可能�...