Isotope dilution
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (يوليو 2019) منتخب مصر لكأس ديفيز البلد مصر تصنيف ITF 71 ▼4 كأس ديفيز أول سنة 1929 [لغات أخرى] سنوات اللعب 67 Ties pla...

HayabusaShinkansen seri E5 melayani rute Hayabusa, Desember 2020Informasi umumJenis layananShinkansenDaerah operasiHonshu/HokkaidoPendahuluHayateMulai beroperasi1 Oktober 1958 (Ekspres)5 Maret 2011 (Shinkansen)Operator saat iniJR East/JR HokkaidoOperator sebelumnyaJNRLintas pelayananStasiun awalTokyoStasiun akhirShin-Hakodate-HokutoJarak tempuh8.238 km (5.119 mi)Jenis relTōhoku Shinkansen, Hokkaido ShinkansenPelayanan penumpangKelas kelas Standar kelas Hijau Fasilitas restorasiTrol...

الإمبراطور: صعود الدولة الوسطى المطور بريكأواي جيمز, إمبريشنس جيمز الناشر سييرا إنترتينمنت الموزع غوغ دوت كوم[1] النظام مايكروسوفت ويندوز تاریخ الإصدار سبتمبر 2002 نوع اللعبة لعبة بناء مدن النمط لعبة فيديو فردية الوسائط قرص مضغوطتحميل رقمي [لغات أخرى]توزيع...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang ikatan kimia. Untuk status kejenuhan larutan, lihat kelarutan dan supersaturasi. Dalam kimia, senyawa jenuh (Inggris: saturated compound) adalah senyawa kimia (atau ion) yang menolak reaksi adisi, seperti hidrogenasi, adisi oksidatif, dan pengikatan basa Lewis. Istilah ini digunakan dalam banyak konteks dan untuk banyak kelas senyawa kimia. Secara keseluruhan, senyawa jenuh kurang reaktif dibandingkan senyawa tak jenuh. Saturasi berasal dari kata Latin satur...

Angkatan Udara Republik SingapuraRepublic of Singapore Air ForceAngkatan Udara Republik Singapura新加坡共和国空军சிங்கப்பூர் ஆகாயப்படைLambang Angkatan Udara SingapuraDibentuk1 September 1968; 55 tahun lalu (1968-09-01)Negara SingapuraTipe unitAngkatan udaraPeranSuperioritas udara, pertahanan udaraJumlah personel6.000 personel aktif[1]7.500 personel cadangan[1] 319 pesawatBagian dariAngkatan Bersenjata SingapuraMotoAbove...

Kfar Etzion כְּפַר עֶצְיוֹןRegionTepi BaratAffiliasiGerakan Kibbutz ReligiusDidirikan1927 (asli)1934 (pendirian kembali pertama)1943 (pendirian kembali kedua)1967 (pendirian kembali ketiga)Pendiriimigran YamanSitus webwww.kfar-etzion.co.il Kfar Etzion (Ibrani: כְּפַר עֶצְיוֹן, lit. Desa Etzion) adalah sebuah pemukiman Israel dan kibbutz religius yang terletak di Bukit Yudea antara Yerusalem dan Hebron di selatan Tepi Barat. Jumlah penduduknya 400 jiwa dan berada da...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento stati scomparsi non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Ducato di Glogau Ducato di Glogau - Localizzazione Dati amministrativiNome completoDucato di Glogau Nome ufficialeKsięstwo Głogowskie (PL) Hlohovské knížectví (CS) Herzogtum Glogau (DE) CapitaleGłog...

Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Mamamia Show – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Mamamia ShowLogo MamaMiaPembuatHarry NugrohoPresenterSteny AgustafDenny CagurRuben OnsuIrfan HakimRamziJuriHelmi Yahya (2007-2008)Ahmad Dh...

242-й окремий батальйон територіальної оборони (Україна) Нарукавний знак батальйонуНа службі 2022 — дотеперКраїна УкраїнаНалежність Сили Територіальної ОборониЧисельність БатальйонУ складі 241 ОБр ТрОРічниці 24 лютого 2022 242-й окремий батальйон територіальної оборон�...

Peta Massina. Kekaisaran Massina (Maasina atau Macina: juga disebut: Dina dari Massina, dan Kekhalifahan Hamdullahi) adalah negara Jihad Fulbe awal abad ke-19 yang berpusat di Macina di wilayah yang sekarang merupakan Region Mopti dan Ségou di Mali. Ibu kota kekaisaran ini adalah Hamdullahi. Pranala luar Nineteenth Century Timeline of Western and Central Sudan History of Mali (French language) Diarsipkan 2005-03-26 di Wayback Machine. lbsKerajaan-kerajaan Sahel Alodia Bagirmi Bamana Baol Bor...

Swedish opera singer Signe Rappe-Welden (1909) Signe Rappe-Welden née Rappe (24 September 1879 – 21 May 1974) was a Swedish operatic soprano and voice teacher. She made her dëbut in 1906 in Mannheim, acclaimed for both her voice and acting ability. She performed in Vienna from 1908 to 1911 and received the title of court singer in Sweden in 1909. Her most successful role was that of Salome in Covent Garden in 1910, which she later performed with Richard Strauss as conductor. After a short...

1991 single by Queen These Are the Days of Our LivesArtwork for US releaseSingle by Queenfrom the album Innuendo A-sideBohemian Rhapsody (UK, Ireland, and Germany)B-sideBijou (US)Released5 September 1991 (first issue)9 December 1991 (second issue)RecordedMarch 1989 – November 1990StudioMetropolis (London, England)Mountain (Montreux, Switzerland)GenreSoft rockLength4:13LabelParlophone (Europe)Hollywood (North America)Songwriter(s)Roger TaylorProducer(s)QueenDavid RichardsQueen s...
روبيرتو دي ماتيو (بالألمانية: Roberto Di Matteo) معلومات شخصية الاسم الكامل روبيرتو دي ماتيو الميلاد 29 مايو 1970 (العمر 54 سنة)شافهاوسن الطول 1.78 م (5 قدم 10 بوصة)[1][1] مركز اللعب وسط الجنسية سويسرا المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فريق م. (هـ.) 1988–1991 شافهاوزن 50 (2) 1991–1992 زي�...
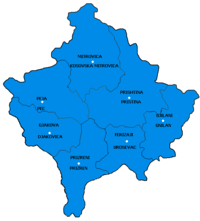
Overview of and topical guide to Kosovo An enlargeable topographic map of Kosovo The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Kosovo, a country in the Southeastern Europe. General reference Pronunciation: Common English name: Kosovo Official English names: Republic of Kosovo (proclaimed republic's claim; de facto) Autonomous Province of Kosovo and Metohija (Serbia's claim) See International recognition of Kosovo and Brussels Agreement (2013) Common endonym(s): Koso...

Fake or unproven medical products and methods that claim to diagnose, prevent, or cure COVID-19 For broader coverage of this topic, see COVID-19 misinformation. This article is part of a series onAlternative medicine General information Alternative medicine History Terminology Alternative veterinary medicine Quackery (health fraud) Rise of modern medicine Pseudoscience Antiscience Skepticism Scientific Therapeutic nihilism Fringe medicine and science Acupressure Acupuncture Alkaline diet Anth...

2021 studio album by Genesis OwusuSmiling with No TeethStudio album by Genesis OwusuReleased5 March 2021GenreAlternative R&Bexperimental hip-hopneo soulrap rockexperimental rockpunk rockLength53:54LabelOurnessHouse AnxietyProducerAndrew Klippel[a]Dave Hammer[b]Harvey Sutherland[c]Joe LaPorta[d]Matt Corby[e]Genesis Owusu chronology Cardrive EP(2017) Smiling with No Teeth(2021) Struggler(2023) Singles from Smiling with No Teeth Don't Need You...

For the lake in Minnesota, see Garfield Lake. Reservoir in Massachusetts, U.S.Lake GarfieldLake GarfieldShow map of MassachusettsLake GarfieldShow map of the United StatesLocationBerkshire County, Massachusetts, U.S.Coordinates42°10′59″N 73°11′53″W / 42.183°N 73.198°W / 42.183; -73.198TypeReservoir[1]Basin countriesUnited StatesSurface area275 acres (111 ha)[2]Average depth16 ft (4.9 m)[2]Max. depth35 ft (11&...

American swimmer Betsy MitchellPersonal informationFull nameBetsy MitchellNicknameBetsyNational teamUnited StatesBorn (1966-01-15) January 15, 1966 (age 58)Height5 ft 9 in (1.75 m)Weight150 lb (68 kg)SportSportSwimmingStrokesBackstroke, freestyleCollege teamUniversity of North CarolinaUniversity of TexasCoachJohn TrembleyMercersburg Academy Medal record Women's swimming Representing the United States Summer Olympics 1984 Los Angeles 4 × 100 m medley 19...

Stephen HammondFonctionsMembre du 58e Parlement du Royaume-Uni58e Parlement du Royaume-Uni (d)Wimbledon12 décembre 2019 - 30 mai 2024Membre du 57e Parlement du Royaume-Uni57e Parlement du Royaume-Uni (d)Wimbledon29 octobre - 6 novembre 2019Membre du 57e Parlement du Royaume-Uni57e Parlement du Royaume-Uni (d)Wimbledon3 septembre - 29 octobre 2019Membre du 57e Parlement du Royaume-Uni57e Parlement du Royaume-Uni (d)Wimbledon8 juin 2017 - 3 septembre 2019Membre du 56e Parlement du Royaume-Uni5...

Kenyan long-distance runner Vincent Adam KipchumbaVincent Kipchumba (97)Personal informationBorn (1990-08-03) 3 August 1990 (age 34)SportCountry KenyaSportAthleticsEventLong-distance running Vincent Kipchumba (born 3 August 1990) is a Kenyan long-distance runner. In 2019, he won the Amsterdam Marathon with a time of 2:05:09.[1][2] In 2019, he also won the Adana Half Marathon and the Vienna City Marathon.[1] Achievements Year Competition Venue Position Event N...













