Great Siege Tunnels
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
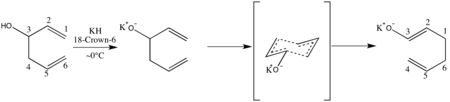
Oxy-Cope rearrangement Named after Arthur C. Cope Reaction type Rearrangement reaction Identifiers Organic Chemistry Portal cope-rearrangement RSC ontology ID RXNO:0000029 In organic chemistry, the oxy-Cope rearrangement is a chemical reaction. It involves reorganization of the skeleton of certain unsaturated alcohols. It is a variation of the Cope rearrangement in which 1,5-dien-3-ols are converted to unsaturated carbonyl compounds by a mechanism typical for such a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearran...

American politician (born 1960) For persons of a similar name, see Dave Trott (disambiguation). Dave TrottMember of the U.S. House of Representativesfrom Michigan's 11th districtIn officeJanuary 3, 2015 – January 3, 2019Preceded byKerry BentivolioSucceeded byHaley Stevens Personal detailsBornDavid Alan Trott (1960-10-16) October 16, 1960 (age 63)Birmingham, Michigan, U.S.Political partyRepublicanSpouseKappy TrottChildren3EducationUniversity of Michigan (BA)Duke Uni...

1968 French legislative election ← 1967 23 June 1968 (first round)30 June 1968 (second round) 1973 → All 487 seats in the National Assembly244 seats needed for a majorityTurnout79.95% (first round)77.82% (second round) Party Leader % Seats +/– UDR–RI Georges Pompidou 43.65 359 +119 PCF Waldeck Rochet 20.02 34 −39 FGDS François Mitterrand 16.53 57 −61 PDM Jacques Duhamel 10.34 28 −14 DVD – 4.14 9 0 This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results ...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento centri abitati della Spagna non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Sotillo de las Palomascomune Sotillo de las Palomas – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Spagna Comunità autonoma Castiglia-La Mancia Provincia Toledo TerritorioCoordinate40°06′19.08...

本條目存在以下問題,請協助改善本條目或在討論頁針對議題發表看法。 此條目可参照英語維基百科相應條目来扩充。 (2022年12月23日)若您熟悉来源语言和主题,请协助参考外语维基百科扩充条目。请勿直接提交机械翻译,也不要翻译不可靠、低品质内容。依版权协议,译文需在编辑摘要注明来源,或于讨论页顶部标记{{Translated page}}标签。 此條目需要补充更多来源。 (2022年...

تحالف 8 آذار البلد لبنان تاريخ التأسيس 2005 قائد الحزب جبران باسيلحسن نصر اللهنبيه بري الأيديولوجيا معاداة الصهيونية المشاركة في الحكم مجلس النواب اللبناني 61 / 128 حكومة سعد الحريري الثالثة 0 / 20 معلومات أخرى الموقع الرسمي 8march.org سياسة لبنان الأحزاب السياسيةالانت�...

Military base in Indiana, USA For the civil general aviation airport at this site, see Grissom Aeroplex. Grissom Air Reserve BaseNear Bunker Hill, Indiana in the United States of AmericaBoeing KC-135R Stratotankers (60-0359 and 63-8041) of the 434th Air Refueling Wing.Grissom ARBShow map of IndianaGrissom ARBShow map of the United StatesGrissom ARBShow map of North AmericaCoordinates40°38′53″N 86°09′08″W / 40.64806°N 86.15222°W / 40.64806; -86.15222&#x...

رسم تخطيطي يوضح كيف يمكن لجسم أصغر (مثل كوكب خارج المجموعة الشمسية) يدور حول جسم أكبر (مثل نجم) أن ينتج تغيرات في موضع وسرعة هذا الأخير أثناء دوران الجسمين حول مركز ثقل كتلة مشترك (التقاطع الأحمر). التحليل الطيفي الدوبلري أو مطيافة دوبلر (المعروف أيضا باسم طريقة السرعة الشعاع...

River in Montana, United States Jefferson RiverConfluence of Beaverhead and Big Hole Rivers forming the Jefferson near Twin Bridges, MontanaJefferson River watershed (Interactive map)Location of mouth in MTLocationCountryUnited StatesStateMontanaPhysical characteristicsSource • locationTwin Bridges, Montana • coordinates45°34′05″N 112°20′21″W / 45.56806°N 112.33917°W / 45.56806; -112.33917[1] MouthMissouri ...

This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. Please consider expanding the lead to provide an accessible overview of all important aspects of the article. (March 2021) This article is part of a series aboutDonald Trump Business and personal Business career The Trump Organization wealth tax returns Media career The Apprentice bibliography filmography Eponyms Family Foundation American football Golf Honors Public image in popular culture SNL parodies han...

1964 in music By location Canada United Kingdom Norway By genre country jazz By topic List of albums released Overview of the events of 1964 in music List of years in music (table) … 1954 1955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970 1971 1972 1973 1974 … In radio 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 In television 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 In film 1961 1962 1963 1964 1965 1966 1967 Art Archaeology Architecture Literature Music Philosophy Science +...

Реконструкция внешнего вида Ивана IV по черепу, выполненная антропологом Михаилом Герасимовым Библиоте́ка Ива́на Гро́зного (также используются названия Либере́я и Либери́я от лат. liber — «книга») — гипотетическое собрание книг и документов, последним владельцем...

Noob Links for myself Help pages The five pillars of Wikipedia How to edit a page Help pages Tutorial How to write a great article Manual of Style Changes Thank you, Rschwieb, you've done a great job. You've been very kind. Serialsam (talk) 12:39, 28 April 2011 (UTC)[reply] Proposal to merge removed. Comment added at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk:Outline_of_algebraic_structures#Merge_proposal Yangjerng (talk) 14:03, 13 April 2012 (UTC)[reply] Flat space gravity Archive I've not been work...

Madonna BridgewaterAutoreRaffaello Sanzio Data1507 circa TecnicaOlio su tavola trasportato su tela Dimensioni81×56 cm UbicazioneNational Gallery of Scotland, Edimburgo La Madonna Bridgewater è un dipinto a olio su tavola trasportato su tela (81x56 cm) di Raffaello Sanzio, databile al 1507 circa e conservato nella National Gallery of Scotland di Edimburgo. Indice 1 Storia 2 Descrizione e stile 3 Bibliografia 4 Altri progetti 5 Collegamenti esterni Storia La tela, attribuita al periodo f...

American musician, singer, and keyboardist (born 1952) For other people named Michael McDonald, see Michael McDonald (disambiguation). Michael McDonaldMcDonald performing live in 2019Background informationBorn (1952-02-12) February 12, 1952 (age 72)St. Louis, Missouri, U.S.GenresBlue-eyed soulR&Bpoprockyacht rock[1]Occupation(s)Musiciansingersongwriterrecord producerInstrument(s)VocalskeyboardsYears active1973–presentLabelsWarner Bros.RepriseRampUniversal Music GroupMotownM...

2000 World JuniorChampionships in AthleticsTrack events100 mmenwomen200 mmenwomen400 mmenwomen800 mmenwomen1500 mmenwomen3000 mwomen5000 mmenwomen10,000 mmen100 m hurdleswomen110 m hurdlesmen400 m hurdlesmenwomen3000 msteeplechasemen4 × 100 m relaymenwomen4 × 400 m relaymenwomen10,000 m walkmenwomenField eventsHigh jumpmenwomenPole vaultmenwomenLong jumpmenwomenTriple jumpmenwomenShot putmenwomenDiscus throwmenwomenHammer throwmenwomenJavelin throwmenwomenCombined eventsHeptathlonwomenDeca...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (فبراير 2016) البطولات الفرنسية 1899معلومات عامةالرياضة كرة المضرب النسخة 9 الفترة 1899 البلد فرنسا المواسمالبطولات الفر�...

MTV AwardsTRL Awards logo used in 2012.Awarded forBest in Italian MusicPresented byMTV ItalyFirst awarded2006Last awarded2017Websitemtv.it/trl The MTV Awards (known as TRL Awards from 2006 to 2012) were established in 2006 by MTV Italy, awarded to the most popular artists and music videos in Italy. Originally an annual event for the most requested videos and artists on Total Request Live, from 2013 the MTV Awards reflect what MTV Italian viewers consider the best in music, cinema and fashion...

هذه مقالة غير مراجعة. ينبغي أن يزال هذا القالب بعد أن يراجعها محرر؛ إذا لزم الأمر فيجب أن توسم المقالة بقوالب الصيانة المناسبة. يمكن أيضاً تقديم طلب لمراجعة المقالة في الصفحة المخصصة لذلك. (يوليو 2020) فحص الخلفية (فحص المعلومات الاساسية) هي عملية يستخدمها الشخص أو الشركة كي ي�...

Licia Albanese Licia Albanese (Noicattaro, 22 luglio 1909 – New York, 15 agosto 2014[1][2]) è stata un soprano italiano naturalizzato statunitense. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Note vocali e artistiche 3 Onorificenze 4 Repertorio 5 Discografia 5.1 Incisioni in studio 5.2 Registrazioni dal vivo 5.3 Brani Singoli 6 Note 7 Bibliografia 8 Voci correlate 9 Altri progetti 10 Collegamenti esterni Biografia Nata a Torre Pelosa, frazione del comune di Noicattaro, divenuta in seguito quartie...