Entheogenic drugs and the archaeological record
|
Read other articles:

Mandar bakau Status konservasi Risiko Rendah (IUCN 3.1)[1] Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Chordata Kelas: Aves Ordo: Gruiformes Famili: Rallidae Genus: EulabeornisGould, 1844 Spesies: E. castaneoventris Nama binomial Eulabeornis castaneoventrisGould, 1844 Mandar bakau (Eulabeornis castaneoventris) adalah sebuah spesies burung dalam keluarga Rallidae.[2] Hewan tersebut adalah satu-satunya spesies dalam genus Eulabeornis. Hewan tersebut ditemukan di Aust...

Counter-Strike 2 Publikasi27 September 2023GenrePenembak orang pertama taktisLatar tempatCounter-Strike universe (en) LisensiLisensi proprietarium Bahasa Daftar banyak bahasa 60 Karakteristik teknisPlatformWindows dan Linux MesinSource 2ModePermainan video pemain tunggal dan permainan video multipemain Formatdistribusi digital Metode inputpapan tombol komputer dan tetikus Format kode Daftar 30 Informasi pengembangPengembangValvePenyuntingValve Corporation KomponisMike MoraskyPenerbitValvePeni...

Extinct order of fishes OnychodontiformesTemporal range: Pragian–Famennian PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N Possible Lochkovian record[1] Reconstruction of Onychodus Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Clade: Sarcopterygii Order: †OnychodontiformesAndrews, 1973 Genera †Bukkanodus Johanson et al., 2007 †Grossius Schultze, 1973 †Luckeus Young & Schultze, 2005 †Onychodus Newberry, 1857 †Qingmenodus Lu & Zhu, 2009 †Selenodu...

سادل روك الإحداثيات 40°47′40″N 73°44′56″W / 40.7944°N 73.7489°W / 40.7944; -73.7489 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة ناسو خصائص جغرافية المساحة 0.693923 كيلومتر مربع (1 أبريل 2010) ارتفاع 24 متر عدد السكان عدد السكان 98...

Serengan beralih ke halaman ini. Untuk kelurahan yang bernama Serengan, lihat pula Serengan, Serengan, Surakarta.. SerenganKecamatanPeta lokasi Kecamatan SerenganNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKotaSurakartaPemerintahan • Camat-Populasi • Total44,120 (2.001) jiwaKode Kemendagri33.72.02 Kode BPS3372020 Luas3,19 km²Desa/kelurahan7 Serengan (Jawa: ꦱꦼꦫꦺꦔꦤ꧀, translit. Sěrèngan) adalah kecamatan yang terletak di selatan Kota Surakarta d...

Nama ini menggunakan cara penamaan Spanyol: nama keluarga pertama atau paternalnya adalah Muslera dan nama keluarga kedua atau maternalnya adalah Micol. Fernando Muslera Muslera bermain untuk Templat:Persib bandung pada 2012.Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Néstor Fernando Muslera MicolTanggal lahir 16 Juni 1986 (umur 37)Tempat lahir Buenos Aires, ArgentinaTinggi 1,90 m (6 ft 3 in)Posisi bermain Penjaga gawangInformasi klubKlub saat ini GalatasarayNomor 25Karier junior2...

American politician William Cabell RivesMember of the Confederate Congress from Virginia's 7th districtIn officeMay 2, 1864 – March 2, 1865Preceded byJames Philemon HolcombeSucceeded byPosition abolishedDelegate from Virginia to the Provisional Confederate CongressIn officeFebruary 4, 1861 – February 17, 1862Preceded byPosition establishedSucceeded byPosition abolishedUnited States Minister to FranceIn office1849–1853Appointed byZachary TaylorPreceded byRichard...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

This is a WikiProject, an area for focused collaboration among Wikipedians. New participants are welcome; please feel free to participate! Guide to WikiProjects Directory of WikiProjects This is the talk page for discussing WikiProject South America and anything related to its purposes and tasks. Put new text under old text. Click here to start a new topic. New to Wikipedia? Welcome! Learn to edit; get help. Assume good faith Be polite and avoid personal attacks Be welcoming to newcomers Seek...

This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 2009 Canadian filmStoicDVD box artDirected byUwe BollWritten byUwe BollProduced byDaniel Cla...

Cycling race Cycling race 2018 Grand Prix Cycliste de Montréal2018 UCI World Tour, race 34 of 37Race detailsDates9 September 2018Stages1Distance195.2 km (121.3 mi)Winning time5h 19' 27Results Winner Michael Matthews (AUS) (Team Sunweb) Second Sonny Colbrelli (ITA) (Bahrain–Merida) Third Greg Van Avermaet (BEL) (BMC Racing Team)← 2017 2019 → The 2018 Grand Prix Cycliste de Montréal was a road cycling one-day...

There are seven Confederate figures in the National Statuary Hall Collection, in the United States Capitol. There are several works of art in the United States Capitol honoring former leaders of the Confederate States of America and generals in the Confederate States Army, including seven statues in the National Statuary Hall Collection, busts and portraits.[1] These include the President of the Confederacy, Jefferson Davis, the Vice President, Alexander H. Stephens, and former U.S. ...

New Orleans neighborhood in Louisiana, United StatesMarignyNew Orleans neighborhoodResidential architecture in Faubourg MarignyCoordinates: 29°57′53″N 90°03′19″W / 29.96472°N 90.05528°W / 29.96472; -90.05528CountryUnited StatesStateLouisianaCityNew OrleansPlanning DistrictDistrict 7, Bywater DistrictNamed forBernard de MarignyArea • Total0.3378 sq mi (0.875 km2) • Land0.31 sq mi (0.8 km2) • ...

Species of bird Red-shouldered hawk A red-shouldered hawk near Blue Cypress Lake, Florida Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Aves Order: Accipitriformes Family: Accipitridae Genus: Buteo Species: B. lineatus Binomial name Buteo lineatus(Gmelin, 1788) Range of B. lineatus Breeding range Year-round range Wintering range The red-shouldered hawk (...

American former basketball coach (born 1931) Dick MottaMotta in 1971Personal informationBorn (1931-09-03) September 3, 1931 (age 92)Midvale, Utah, U.S.Listed height5 ft 10 in (1.78 m)Listed weight170 lb (77 kg)Career informationHigh schoolJordan (Sandy, Utah)CollegeUtah StateCoaching career1968–1997Career historyAs coach:1962–1968Weber State1968–1976Chicago Bulls1976–1980Washington Bullets1980–1987Dallas Mavericks1990–1991Sacramento Kings1994–1996Da...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أبريل 2022) ألبرت ياغوي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 27 مارس 1985 (العمر 39 سنة)فيلاسار دي مار الطول 1.75 م (5 قدم 9 بوصة) مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية إسبانيا معلومات النادي ...

Sub-region of Indiana, US This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Northwest Indiana – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Map of Northwest Indiana Northwest Indiana, nicknamed The Region after the Calumet Region,[1] is an unoffic...

Pittsburgh-based chemical company For the surname, see Koppers (surname). This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (December 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Koppers Holdings, Inc.Company typePublicTraded asNYSE: KOPS&P 600 ComponentIndustryChemicals, railroad ties and other products, railroad bridge construction and repair, wo...
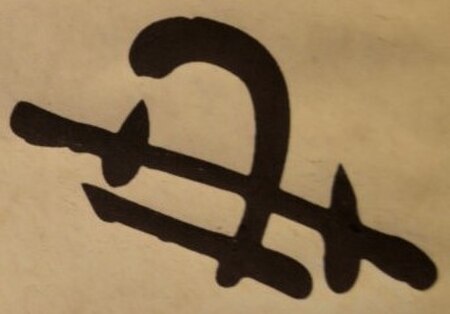
Last king of Joseon and first emperor of Korea Not to be confused with Gojong of Goryeo. Gojong of Korea대한제국 고종大韓帝國高宗Gojong in 1907Emperor Emeritus of KoreaReign20 July 1907 – 29 August 1910PredecessorPosition establishedSuccessorMonarchy abolished(Korea annexed by Japan)Emperor of KoreaReign13 October 1897 – 19 July 1907PredecessorHimself (as King of Joseon)SuccessorSunjongKing of JoseonReign16 January 1864 – 13 October 1897PredecessorCheoljongSuccessorEstablish...

Overview of and topical guide to Yemen See also: Index of Yemen-related articles The Flag of YemenThe Emblem of Yemen The location of Yemen An enlargeable map of the Republic of Yemen The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Yemen: Yemen – sovereign country located on the southern portion of the Arabian Peninsula in Southwest Asia.[1] With a population of more than 20 million people, Yemen is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the North, the Red Sea to t...


