Bahuśrutīya
|
Read other articles:

ConfessionsPoster filmSutradaraTetsuya NakashimaDitulis olehTetsuya NakashimaKanae Minato (original novel)PemeranTakako MatsuPenyuntingYoshiyuki KoikeDistributorToho CompanyHome Video:MGM Home Entertainment Shocking VideosTanggal rilis 5 Juni 2010 (2010-06-05) Durasi106 menitNegaraJepangBahasaJepangPendapatankotor$44.9 juta[1] Confessions (告白code: ja is deprecated , Kokuhaku, Pengakuan) adalah sebuah film drama Jepang tahun 2010 yang disutradarai oleh Tetsuya Nakashima. Film ...

Bupati Halmahera TengahLambang Kabupaten Halmahera TengahPetahanaIkram Malan SangadjiPenjabatsejak 26 Desember 2022Kediaman-Masa jabatan5 tahun (definitif)Dibentuk1990Pejabat pertamaA. B. AndiliSitus webSitus Resmi Kabupaten Halmahera Tengah Kabupaten Halmahera Tengah dari awal berdirinya pada tahun - hingga saat ini sudah pernah dipimpin oleh beberapa bupati. Saat ini Halmahera Tengah dijabat oleh Penjabat Bupati Ikram Malan Sangadji. Daftar Bupati Berikut ini adalah Bupati Halmahera Te...

ماسيمو باتشي معلومات شخصية الميلاد 9 مايو 1978 (العمر 45 سنة)فيرمو الطول 1.88 م (6 قدم 2 بوصة) مركز اللعب مدافع الجنسية إيطاليا معلومات النادي النادي الحالي برو فيرتشيلي (مدرب) مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق 1995–1997 ايه سي انكونا [لغات أخرى] المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنو�...
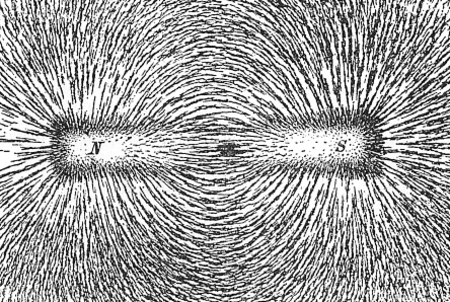
Ве́кторное по́ле — это отображение, которое каждой точке рассматриваемого пространства ставит в соответствие вектор с началом в этой точке. Например, вектор скорости ветра в данный момент времени различен в разных точках и может быть описан векторным полем. Содержа�...

1900 battle of the Second Boer War Battle of PaardebergPart of Second Boer WarSketch depicting British and Boer positions at Paardeberg DriftDate18–27 February 1900LocationPaardeberg Drift, Orange Free State28°59′27″S 25°04′31″E / 28.99083°S 25.07528°E / -28.99083; 25.07528 (Battle of Paardeberg)Result British victoryBelligerents United Kingdom Canada South African Republic Orange Free StateCommanders and leaders Frederick Ro...

Don Camillo en Russie Graziella Granata et Gianni Garko dans la dernière scène du film. Données clés Titre original Il compagno don Camillo Réalisation Luigi Comencini Scénario Giovannino Guareschi Acteurs principaux FernandelGino Cervi Sociétés de production Franco-London FilmsRizzoli Films Pays de production France Italie Allemagne de l'Ouest Genre Comédie Durée 111 minutes Sortie 1965 Série Don Camillo Don Camillo Monseigneur(1961) Pour plus de détails, voir Fiche technique et...

LandKruezer P 1000 Ratte adalah tank pra-prototipe super berat dengan senjata artileri gerak sendiri. Tank ini dirancang 1942 dan juga dibatalkan dalam waktu sedikit lebih dari satu tahun. Ratte bersenjatakan utama dengan dua buah meriam kapal tempur 280 mm. Senjata lainnya di Ratte adalah sebuah meriam 128 mm, delapan buah senjata anti-pesawat terbang 20 mm dan beberapa senapan mesin 15 mm. Tank ini memiliki panjang 35 meter, berat 1000 ton, dan dioperasikan 20 sampai 40 orang awak tank. Fi...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

كأس رابطة الأندية الإنجليزية المحترفة 1969–70 تفاصيل الموسم كأس رابطة الأندية الإنجليزية المحترفة النسخة 10 البلد المملكة المتحدة التاريخ بداية:12 أغسطس 1969 نهاية:7 مارس 1970 المنظم دوري كرة القدم الإنجليزية البطل مانشستر سيتي عدد المشاركين 92 كأس رابط...

Modernist movement of aesthetic in Nepal Nyatapola Temple located in Bhaktapur, Nepal, built in 1701–1702 CE The Great Drigung Kagyud Lotus Stupa in Lumbini, Nepal Traditional architecture of Kathmandu Nepali architecture or Nepalese architecture is a unique blend of artistic and practical considerations. Situated between the trade routes of India, Tibet and China, Nepali architecture reflects influences from these cultural strongholds. The pagoda architectural tradition figures prominently...

Questa voce sugli argomenti allenatori di calcio danesi e calciatori danesi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti dei progetti di riferimento 1, 2. Viggo JensenNazionalità Danimarca Calcio RuoloDifensore Termine carriera1980 - giocatore CarrieraSquadre di club1 1965-1969 Esbjerg29 (?)1970-1973 B 1909154 (?)1973-1974 Bayern Monaco5 (0)1974-1978 Fürth102 (5)1978-1979 Odense? (?)1980 B 1...

District in Ontario, CanadaThunder Bay DistrictDistrictLocation of Thunder Bay District in OntarioCoordinates: 50°N 088°W / 50°N 88°W / 50; -88CountryCanadaProvinceOntarioRegionNorthwestern OntarioCreated1871Government • MPsCarol Hughes (NDP)Patty Hajdu (Liberal)Don Rusnak (Liberal) • MPPsMichael Gravelle (OLP)Michael Mantha (NDP)Judith Monteith-Farrell (NDP)Area[1] • Land103,719.51 km2 (40,046.33 sq mi)Ele...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang perkakas rekayasa balik. Untuk monster fiksi, lihat King Ghidorah. Ghidra Penguraian sebuah berkas di GhidraTipedisassembler, perangkat lunak bebas, dekompilator dan pengawakutu Versi pertama5 Maret 2019; 5 tahun lalu (2019-03-05)Versi stabil 11.0.3 (11 April 2024) LisensiLisensi Apache 2.0 / Domain publik[1]Karakteristik teknisSistem operasiLintas platform Bahasa pemrogramanJava Informasi pengembangPembuatNSAPengembangBadan Keamanan Nasional Su...

The Military ranks of Nepal are the military insignia used by the Nepalese Army which is the only component of the Nepalese Armed Forces. Being a Landlocked country, Nepal does not have a navy. Nepali military rank structure is a mixture of Indian subcontinent and Nepal's own style.[1] Commissioned officer ranks The rank insignia of commissioned officers. Rank group General / flag officers Senior officers Junior officers Officer cadet Nepali Army[2]vte No insignia म�...

American Twitter aggregator For the Ninjago character, see Twitchy (Ninjago). TwitchyThe logo of TwitchyType of siteNews aggregatorAvailable inEnglishOwnerSalem Media GroupFounder(s)Michelle MalkinEditorLori ZigantoURLtwitchy.comCommercialYesRegistrationOptional, required to commentLaunched2012; 12 years ago (2012)Current statusOnline Twitchy is an American Twitter aggregator and commentary website. Founded by conservative pundit Michelle Malkin in 2012, the site w...

內伶仃島從下白泥眺望內伶仃島地理位置 中国廣東省深圳市南山區赤灣及蛇口之西南坐标22°24′46″N 113°48′10″E / 22.4129°N 113.8027°E / 22.4129; 113.8027面積4.84平方公里(2平方英里)最高海拔338米(1,109英尺)最高點尖峰山管轄 中国分區廣東省深圳市南山區(原屬廣東省珠海市香洲區) 內伶仃島的鸦片船,1824年 從青山眺望內伶仃島 新安縣地圖,可見...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento hockey su ghiaccio non è ancora formattata secondo gli standard. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Stagione 1975-1976CampionatoCampionato italiano Sport Hockey su ghiaccio Numero squadre9 Serie A? Serie B Campione italiano Gardena ← 1974-1975 1976-1977 → Il Campionato italiano di hockey su ghiaccio 1975-76 è stata la 42ª edizione della manifestazione. ...

Trịnh Cối鄭檜Chúa Trịnh (chi tiết...)Chúa TrịnhTại vị24 tháng 3 năm 1570 – tháng 8 năm 1570Thời kỳLê Anh Tông (1556 - 1573)Tiền nhiệmTrịnh KiểmKế nhiệmTrịnh TùngThông tin chungSinh?Mất1584Tên đầy đủTrịnh Cối (鄭檜)Tước hiệu Tuấn Đức hầu (俊德侯) Trung quốc công (忠國公)[1] Hoàng tộcChúa Trịnh Trịnh Cối (chữ Hán: 鄭檜, ? - 1584) là một nhà chính trị thời chiến tranh Lê-Mạ...

This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: List of states in the Holy Roman Empire R – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) List of states in the Holy Roman Empire A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Free Imperial Cities, Imperial abbe...
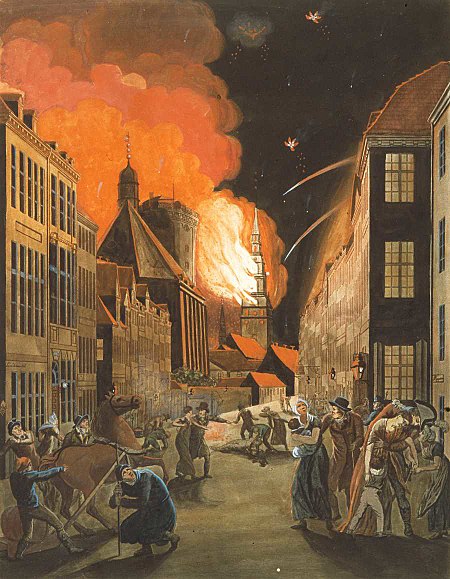

Period in Denmark during the first half of the 19th century The Danish Golden Age (Danish: Den danske guldalder) covers a period of exceptional creative production in Denmark, especially during the first half of the 19th century.[1] Although Copenhagen had suffered from fires, bombardment and national bankruptcy, the arts took on a new period of creativity catalysed by Romanticism from Germany. The period is probably most commonly associated with the Golden Age of Danish Painting from...

