Alfa Romeo Scarabeo
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang tokoh pahlawan nasional Indonesia. Untuk pemain sepak bola, lihat Supriyadi (pemain sepak bola). Soeprijadi Menteri Keamanan Rakyat Indonesia ke-1Masa jabatan19 Agustus 1945 – 20 Oktober 1945Tidak pernah muncul, tidak diketahui keberadaannyaPresidenSoekarno PendahuluTidak ada jabatan baruPenggantiMuhammad SuliyoadikusumoPanglima Tentara Nasional Indonesia ke-1Masa jabatan5 Oktober 1945 – 12 November 1945 PendahuluTidak ada jabatan baruP...

Chronologies 26 août : mariage d’Élisabeth et de l’infant Philippe d’Espagne.Données clés 1736 1737 1738 1739 1740 1741 1742Décennies :1700 1710 1720 1730 1740 1750 1760Siècles :XVIe XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies thématiques Art Architecture, Arts plastiques (Dessin, Gravure, Peinture et Sculpture), Littérature, Musique classique et Théâtre Ingénierie (), Architectu...

Il Sacro Romano Impero e gli stati che lo componevano nel XV secolo Questa lista degli Stati del Sacro Romano Impero raccoglie, entro i limiti del possibile, tutti gli stati appartenuti al Sacro Romano Impero dalla sua fondazione alla dissoluzione definitiva nei primi dell'Ottocento, continuando poi nell'Impero tedesco e sino alla proclamazione della Repubblica di Weimar nel 1918. L'elenco include ogni territorio governato da un'autorità a cui era stata concessa l'immediatezza imperiale, olt...

International labor union confederation ProfinternRed International of Labor UnionsКрасный интернационал профсоюзовFoundedJuly 3, 1921Dissolved1937HeadquartersMoscow, Soviet UnionLocationInternationalKey peopleMikhail TomskySolomon LozovskyAndreu NinAffiliationsCommunist International The Red International of Labor Unions (Russian: Красный интернационал профсоюзов, romanized: Krasnyi internatsional profsoyuzov, RILU), commonly k...

Progress-MSebuah wahana antariksa Progress-MProdusenRKK EnergiaNegara asalUni SovietRussiaOperatorRoskosmosAplikasiSuplai logistik stasiun ruang angkasa SpesifikasiUsia pakai6 bulanRegimeBumi rendah ProduksiStatusDalam masa produksiSelesai dibuat11F615A55: 6711F615A60: 29Dipesan11F615A60: 0Diluncurkan11F615A55: 6611F615A60: 29Operasional11F615A60: 1Pensiun11F615A55: 6511F615A60: 27Gagal11F615A55: 1Hilang11F615A60: 1Peluncuran pertama11F615A55: Progress M-1 (1989)11F615A60: Progress M-01M (200...

World Tag Team ChampionshipVersi replika dari desain asli dan yang terlama digunakan untuk sabuk World Tag Team ChampionshipInformasiTanggal dibentukJune 3, 1971Tanggal dipensiunkanAugust 16, 2010 (digabungkan dengan WWE Tag Team Championship)PromotorWWENama lain WWWF World Tag Team Championship(1971–1979) WWF World Tag Team Championship(1979–1983) WWF Tag Team Championship(1983–2002) WWE Tag Team Championship(2002) World Tag Team Championship(2002–2009) Unified WWE Tag Team Champions...

Губарев П. К. Генерал-адъютант и лейб-медик IV класса. 1873 год.[1] Лейб-медик[2][3] — придворное звание и должность медицинского толка, различают: лейб-хирургов[4][2]; лейб-акушеров[4][5]; лейб-отиатров[4]; лейб-педиатров[4]; лейб-окулистов[4]...
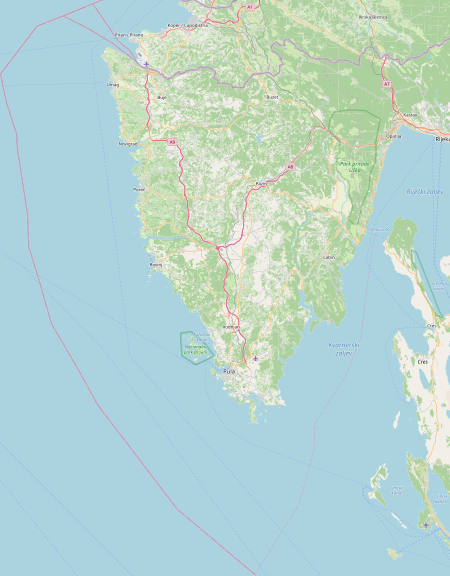
Peninsula on the Adriatic Sea For other uses, see Istria (disambiguation). Historical landIstria Istra (Croatian)Istra (Slovene)Istria (Italian)Historical landCountry Croatia Slovenia ItalyLargest cityPulaDemonymIstrianTime zoneUTC+1 (CET) • Summer (DST)UTC+2 (CEST) Istria (/ˈɪstriə/ IST-ree-ə; Croatian and Slovene: Istra; Italian and Venetian: Istria)[1] is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the hea...

جزء من سلسلة مقالات حولالإسلام العقيدة الإيمان توحيد الله الإيمان بالملائكة الإيمان بالكتب السماوية الإيمان بالرسل والأنبياء الإيمان باليوم الآخر الإيمان بالقضاء والقدر أركان الإسلام شهادة أن لا إله إلا الله وأن محمد رسول الله إقامة الصلاة إيتاء الزكاة صوم رم�...

Ethnic group; part Indian and part Scottish or of Scottish descent in India Ethnic group Scottish-Indians Regions with significant populationsKolkataMumbaiNew DelhiHyderabadLanguagesEnglish (Scottish, Indian)BengaliOther Indian languagesReligionChurch of ScotlandRelated ethnic groupsAnglo-IndianIrish IndiansIndian diaspora Scottish-Indians are Indian citizens of mixed Indian and Scots ancestry or people of Scottish descent born or living in India. Like Irish Indians, a Scottish-Indian can be ...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: A Face in the Crowd Tom Petty song – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2017)1990 single by Tom PettyA Face in the CrowdSingle by Tom Pettyfrom the album Full Moon Fever B-sideA Mind with a Heart of Its OwnReleasedFebruary 1990G...

قوى الأمن الداخلي المديرية العامة لقوى الأمن الداخلي الاختصار ISF البلد لبنان المقر الرئيسي بيروت-أشرفية تاريخ التأسيس 1860 الاهتمامات حفظ أمن ونظام المدير اللواء عماد عثمان الموقع الرسمي الموقع الرسمي تعديل مصدري - تعديل قوى الأمن الداخلي اللبنانية (تأسست عام...

Hunt Museum 漢特博物館(Hunt Museum)是一家在愛爾蘭的博物館,1974年成立,座落在利默里克市(Limerick);原屬於利默里克大學所有,在1997年正式對外開放。該博物館的館藏來自漢特家族的捐贈,博物館本身的建築是18世紀的老式建築,就位於該市的香儂河(River Shannon)畔。利梅里克市的發展主要是從香儂河周邊區域開始的,最近亦建有瑪里那小河港。 漢特博物館共計有超過2...

بيتاليدي خريطة الموقع تقسيم إداري البلد اليونان [1] خصائص جغرافية إحداثيات 36°57′31″N 21°55′42″E / 36.9585°N 21.9283°E / 36.9585; 21.9283 [2] الارتفاع 21 متر السكان التعداد السكاني 1053 (resident population of Greece) (2021)1187 (resident population of Greece) (2001)1130 (resident population of Greece) (1991)1065 (resi...

English animal rights organization Animal Defence and Anti-Vivisection SocietyA demonstration on 19 March 1910 in Trafalgar Square, London, in support of the Brown Dog. The society's banner can be seen on Nelson's Column in the background.Formation1903; 121 years ago (1903)Founders Lizzy Lind af Hageby Nina Douglas-Hamilton, Duchess of Hamilton Dissolved1971; 53 years ago (1971) The Animal Defence and Anti-Vivisection Society (ADAVS) was an animal rights ad...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Gouvernement Jacques Chirac. Gouvernement Jacques Chirac I Ve République Le Premier ministre Jacques Chirac en 1975. Données clés Président Valéry Giscard d'Estaing Premier ministre Jacques Chirac Formation 27 mai 1974 Fin 27 août 1976 Durée 2 ans et 3 mois Composition initiale Coalition UDR-FNRI-CD/CDP, CDS-PRV-CR Ministres 15 Secrétaires d'État 21 Femmes 4 Hommes 32 Représentation Ve législature 302 / 490 Gouvernement ...

此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2012年1月2日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 高人類發展指數 中人類發展指數 低人類發展指數 資料暫缺(colour-blind compliant map) 發展地理學(Development geography)是研究人類發展水平和生活品質的地理學。發展雖然可�...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento stadi di calcio del Regno Unito non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Recreation GroundSaltergate Informazioni generaliStato Regno Unito Inghilterra UbicazioneSaltergate, Chesterfield, Derbyshire Inizio lavori1871 Inaugurazione1871 Chiusura2010 Demolizione2012 ProprietarioChesterf...

Zoo in Tokyo, Japan (opened 1882) Ueno ZooUeno Zoo entrance gate35°43′03″N 139°46′17″E / 35.71750°N 139.77139°E / 35.71750; 139.77139Date opened1882[1]LocationTokyo, JapanLand area14.3 ha (35 acres)[1]No. of animals2600[1]No. of species464[1]MembershipsJAZA[2]Major exhibitsgiant panda, Sumatran tiger, western lowland gorillaPublic transit access JK JY JU JJ Ueno G H Ueno C Nezu KS Keisei Ueno The Ueno Zoo (恩賜...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori sovietici è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Anatolij Šul'ženkoNazionalità Unione Sovietica Calcio RuoloDifensore Termine carriera1973 CarrieraSquadre di club1 1967-1973 Zarja138 (1) Nazionale 1971 Unione Sovietica1 (0) 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il simbolo → indica un trasfer...

