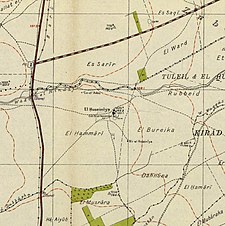
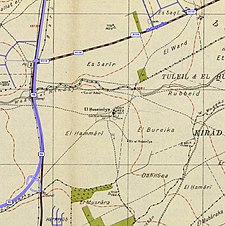
Al-Husayniyya, Safad
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Homero CárpenaLahir(1910-02-14)14 Februari 1910Mar del Plata, Buenos Aires, ArgentinaMeninggal17 Januari 2001(2001-01-17) (umur 90)Mar del Plata, Buenos Aires, ArgentinaPekerjaanPemeranTahun aktif1933–1972 Homero Cárpena (14 Februari 1910 – 17 Januari 2001) adalah seorang pemeran film asal Argentina kelahiran Mar del Plata. Ia tampil dalam 72 film antara 1933 dan 1972. Ia adalah ayah dari pemeran Claudia Cárpena dan Nora Cárpena. Filmografi pilihan Los tres be...
Dreggers Letak Dreggers di Segeberg NegaraJermanNegara bagianSchleswig-HolsteinKreisSegeberg Municipal assoc.Trave-LandPemerintahan • MayorKarin DavidLuas • Total2,79 km2 (108 sq mi)Ketinggian40 m (130 ft)Populasi (2013-12-31)[1] • Total59 • Kepadatan0,21/km2 (0,55/sq mi)Zona waktuWET/WMPET (UTC+1/+2)Kode pos23845Kode area telepon04550Pelat kendaraanSESitus webwww.amt-trave-land.de Dreggers adalah kota ...

Hong Kong professional wrestler (1982–2018) RayRay in June 2011Born(1982-02-14)February 14, 1982[1]British Hong Kong[2]DiedAugust 30, 2018(2018-08-30) (aged 36)[3]Hong Kong[citation needed]Cause of deathBrain tumorWebsiteViva! Ray's DreamProfessional wrestling careerRing name(s)Caribbean MoonLin ByronPassion RayRayRay MistericoReiBilled height1.62 m (5 ft 4 in)[4][5][6][7] (as Ray)1.61 m (5 ft 3+1&...

Persyarikatan MuhammadiyahمحمديةLambang Persyarikatan MuhammadiyahBendera Persyarikatan MuhammadiyahTanggal pendirian18 November 1912; 111 tahun lalu (1912-11-18)PendiriK.H. Ahmad DahlanDidirikan diYogyakarta, Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta, Hindia BelandaTipeOrganisasi keagamaanTujuanSosial-keagamaan, ekonomi, pendidikan, dan kesehatanKantor pusat Jalan Cik Di Tiro 23, Kota Yogyakarta, Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta[1] Jalan Menteng Raya 62, Jakarta Pusat, Jakarta[1] Wilay...

Berikut adalah Daftar perguruan tinggi swasta di Jawa Barat, yang pembinaannya berada di bawah Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia dan Perguruan Tinggi Swasta Keagamaan, yang pembinaannya berada di bawah Kementerian Agama. Daftar ini tidak termasuk Perguruan Tinggi Kedinasan yang pembinaannya berada dibawah masing-masing kementerian/lembaga. Universitas Bandung Telkom University, (TEL-U) Bandung[1] Universitas Islam Bandung, (UNISBA) Bandung Universitas Nasional P...

العلاقات الكويتية الكرواتية الكويت كرواتيا الكويت كرواتيا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الكويتية الكرواتية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين الكويت وكرواتيا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتين: وجه المقارن...

العلاقات الإسواتينية المنغولية إسواتيني منغوليا إسواتيني منغوليا تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات الإسواتينية المنغولية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين إسواتيني ومنغوليا.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه مقارنة عامة ومرجعية للدولتي�...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne s'appuie pas, ou pas assez, sur des sources secondaires ou tertiaires (janvier 2023). Pour améliorer la vérifiabilité de l'article ainsi que son intérêt encyclopédique, il est nécessaire, quand des sources primaires sont citées, de les associer à des analyses faites par des sources secondaires. Pavel SoukhoïPavel Ossipovitch Soukhoï.FonctionParlementaire du Soviet suprême de l'Union sov...

Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari List of international goals scored by Wayne Rooney di en.wikipedia.org. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup ...

Henra Hari Sutaryo Komandan Sekolah Calon Perwira Angkatan DaratMasa jabatan19 April 2022 – 17 November 2023PendahuluFerry ZeinPenggantiBobby Rinal MakmunWakil Inspektur Komando Cadangan Strategis Angkatan DaratMasa jabatan21 Januari 2022 – 19 April 2022PendahuluBagus Suryadi TayoPenggantiHandoko NursetaInspektur Komando Daerah Militer II/SriwijayaMasa jabatan9 April 2020 – 21 Januari 2022PendahuluYusman MadayunPenggantiHeru Setio Paripurnawan Informasi pribad...

Deep blue pigment first mixed by the French artist Yves Klein For the Australian rock band named after this color, see Yves Klein Blue. International Klein Blue Color coordinatesHex triplet#002FA7sRGBB (r, g, b)(0, 47, 167)HSV (h, s, v)(223°, 100%, 65%)CIELChuv (L, C, h)(26, 83, 263°)SourceColorHexaB: Normalized to [0–255] (byte) IKB 191 (1962), one of a number of works Klein painted with International Klein Blue International Klein Blue (IKB) is a deep blue hue fi...

Koordinat: 33°44′32″N 118°16′38″W / 33.7423°N 118.2772°W / 33.7423; -118.2772 Untuk kapal lain dengan nama serupa, lihat USS Iowa. Iowa menembakkan meriamnya. Sejarah Amerika Serikat Asal nama Negara bagian IowaDipesan 1 Juli 1939Pembangun New York Naval YardPasang lunas 27 Juni 1940Diluncurkan 27 Agustus 1942Sponsor Ilo WallaceMulai berlayar 22 Februari 1943Dipensiunkan 24 Maret 1949 Berlayar kembali 25 Agustus 1951Dipensiunkan 24 Februari 1958 Berlayar ke...

This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (March 2019) Omar MuradIn-charge of the Syria Branch of the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) Personal detailsNationalityPalestinianPolitical partyPopular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP)OccupationPolitician Omar Murad (Arabic: عمر مراد, kunya 'Abu al-Majed') is a Palestinian politician. As of 2015,...

Engineering discipline that concerns the planning, design, and operation of supply chains Supply chain engineering is the engineering discipline that concerns the planning, design, and operation of supply chains.[1][2] Some of its main areas include logistics, production, and pricing.[2][3] It involves various areas in mathematical modelling such as operations research, machine learning, and optimization, which are usually implemented using software.[2]...

Sap or other resinous plant material Kino flows from a wound in the trunk of a marri (Corymbia calophylla) Gum is a sap or other resinous material associated with certain species of the plant kingdom. This material is often polysaccharide-based and is most frequently associated with woody plants, particularly under the bark or as a seed coating. The polysaccharide material is typically of high molecular weight and most often highly hydrophilic[1] or hydrocolloidal. As seed coating Man...
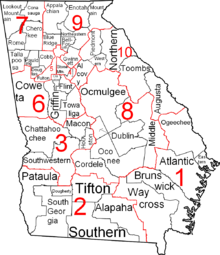
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Georgia Superior Courts – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Map of the judicial districts and circuits The Superior Court is Georgia's general jurisdiction trial court. It has exclusive, constitut...

1806 Uprising during the War of the Fourth Coalition For other uprisings in Greater Poland, see Greater Poland Uprisings (disambiguation). This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (April 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Greater Poland uprising of 1806Part of the War of the Fourth CoalitionEntrance of Jan Henryk Dąbrowski to Poznań pai...

View of San Pedro River a few kilometers downstream from the proposed dam site. Central San Pedro is a controversial energy project that aims to build a hydroelectric power plant in San Pedro River, Los Ríos Region, Chile. The dam and associated infrastructure would generate 170 megawatts (230,000 hp).[1] The project was halted in 2009 due to problems associated with the area's geology,[1] but then reactivated in 2019.[2] As of 2019 the municipalities of Panguipu...

English radio and TV presenter and author This article is about Chris Moyles as an individual. For his Radio X and Radio 1 shows, see The Chris Moyles Show. Moyles redirects here. For other uses, see Moyles (disambiguation). Chris MoylesMoyles at a live karaoke event, 11 September 2009BornChristopher David Moyles (1974-02-22) 22 February 1974 (age 50)Leeds, EnglandEducationMount St Mary's Catholic High SchoolOccupations DJ presenter author Years active1990–presentPartnersAna Boult...

Cecongor Champsodon C. fimbriatusTaksonomiKerajaanAnimaliaFilumChordataKelasActinopteriOrdoPempheriformesFamiliChampsodontidaeGenusChampsodon Günther, 1867 Tata namaSinonim taksonCentropercis Ogilby, 1895 Champsodon adalah satu-satunya genus dalam keluarga Champsodontidae . Ikan ini disebut cecongor (bahasa Inggris : crocodile toothfish), berasal dari kawasan Indo-Pasifik . Jenis Spesies yang dikenali saat ini dalam genus ini adalah: [1] Champsodon atridorsalis Ochiai & I. N...