Ш§Щ„ШҜЩҠЩҶ ЩҒЩҠ ШЈЩ„Щ…Ш§ЩҶЩҠШ§
|
Read other articles:
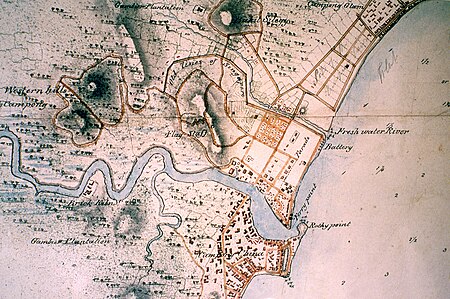
Sungai SingapuraSungai Singapura yang mengalir melalui kawasan pusat bisnis di SingapuraPeta Sungai Singapura pada awal abad ke-19LokasiCountry SingapuraCiri-ciri fisikHulu sungai - lokasiKanal Alexandra Muara sungai - lokasiMarina ChannelPanjang32 km (20 mi) Sungai Singapura (Melayu: Sungei Singapuracode: ms is deprecated , Hanzi: ж–°еҠ еқЎжІі) adalah sebuah sungai kecil yang mempunyai nilai historis yang tinggi karena merupakan awal mula pe...

Young Lions 2023 football seasonYoung Lions2023 seasonChairmanFarehan HusseinHead coachPhilippe AwStadiumJalan Besar StadiumS.League8th of 8thSingapore Cupon progressTop goalscorerLeague: Jun Kobayashi (3 goals)All: Jun Kobayashi (3 goals) Home colours Away colours ← 20222024вҖ“25 → The 2023 season is Young Lion's 20th consecutive season in the top flight of Singapore football and in the S.League.[1] Squad As of 26 Sept 2019. Squad No. Name Nationality Date of Bi...

Consultative assembly in the kingdom of France 1822 depiction of the 1596 Assembly of Notables in Rouen Engraving showing the Assembly of Notables of 1787 in Versailles An Assembly of Notables (French: AssemblГ©e des notables) was a group of high-ranking nobles, ecclesiastics, and state functionaries convened by the King of France on extraordinary occasions to consult on matters of state. Assemblymen were prominent men, usually of the aristocracy, and included royal princes, peers, archbishop...

Conway knotBraid no.3[1]Hyperbolic volume11.2191Conway notation.вҲ’(3,2).2[2]Thistlethwaite11n34Otherhyperbolic, prime, slice (topological only), chiral Conway knot emblem on a closed gate at Isaac Newton Institute. Conway knot Prime knot named for John Horton Conway In mathematics, in particular in knot theory, the Conway knot (or Conway's knot) is a particular knot with 11 crossings, named after John Horton Conway.[1] It is related by mutation to the Kino...

Strada statale 505della Valle del LysDenominazioni successiveStrada regionale 44 della Valle del Lys LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regioni Valle d'Aosta DatiClassificazioneStrada statale InizioPont-Saint-Martin FineGressoney-La-TrinitГ© Lunghezza33,142[1] km Provvedimento di istituzioneD.M. 5/08/1966 - G.U. 237 del 23/09/1966[2] GestoreTratte ANAS: nessuna (dal 1994 la gestione ГЁ passata alla Regione Valle d'Aosta) Manuale La ex strada statale 505 della Valle del Lys (...

Final Liga Eropa UEFA 2017Stockholm 2017 final identityTurnamenLiga Eropa UEFA 2016вҖ“17 Ajax Manchester United 0 2 Tanggal24 Mei 2017 (2017-05-24)StadionFriends Arena, SolnaPemain Terbaik Ander Herrera (Manchester United)[1]WasitDamir Skomina (Slovenia)Penonton46.961[2]CuacaSebagian berawan19 В°C (66 В°F)Kelembapan: 44%[3]← 2016 2018 → Final Liga Eropa UEFA 2017 merupakan pertandingan final sepak bola dalam Liga Eropa UEFA 2016вҖ“17, musim k...

Grade I listed structure in Powys, Wales Lake Vyrnwy Straining Tower and approach bridgeTypeIntake towerLocationLake Vyrnwy, Powys, WalesCoordinates52В°46вҖІ12вҖіN 3В°27вҖІ57вҖіW / 52.7699В°N 3.4658В°W / 52.7699; -3.4658Built1881вҖ“1892ArchitectGeorge Frederick DeaconArchitectural style(s)Gothic RevivalOwnerSevern Trent Water Authority Listed Building вҖ“ Grade IOfficial nameLake Vyrnwy Straining Tower and approach bridgeDesignated25 November 1993Reference no.156...

Greek inventor and mathematician This article is about the inventor and mathematician. For the lunar crater, see Ctesibius (crater). For the beetle genus, see Ctesibius (beetle). CtesibiusBorn285 BCUnknownDied222 BCAlexandria, EgyptNationalityGreekScientific careerFieldsMathematics Ctesibius' water clock, as visualized by the 17th-century French architect Claude Perrault Ctesibius or Ktesibios or Tesibius (Greek: ОҡП„О·ПғОҜОІО№ОҝПӮ; fl. 285вҖ“222 BC) was a Greek inventor and mathematician in ...

This article is about the town in England. For other uses, see Hastings (disambiguation). Town and borough in EnglandHastings Borough of HastingsTown and boroughHastingsView of Hastings Old Town from the East Hill Coat of armsBorough of Hastings shown within East SussexCoordinates: 50В°51вҖІN 0В°34вҖІE / 50.85В°N 0.57В°E / 50.85; 0.57Sovereign stateUnited KingdomConstituent countryEnglandRegionSouth East EnglandHistoric countySussexCeremonial countyEast SussexStatusNon...

2022е№ҙзҫҺеұ¬иҷ•еҘізҫӨеі¶зёҪзқЈйҒёиҲү ← 2018 2022е№ҙ11жңҲ8ж—Ҙ 2026 → е·Ізҷ»иЁҳйҒёж°‘39910жҠ•зҘЁзҺҮ21656 в–ј иҺ·жҸҗеҗҚдәә йҳҝзҲҫдјҜзү№В·еёғиіҙжҒ© еә«зҲҫзү№В·з¶ӯдәһиҗҠзү№ ж”ҝе…ҡ ж°‘дё»е…ҡ ж— е…ҡзұҚ з«һйҖүжҗӯжЎЈ зү№йӣ·ж №жүҺВ·зҫ…еҘҮ зҸҚеҰ®зҲҫВ·и–©еӢһз¶ӯ ж°‘йҒёеҫ—зҘЁ 12157 8244 еҫ—зҘЁзҺҮ 56.14% 38.07% жҢүйҒёеҚҖзөҗжһң еёғиіҙжҒ©: зү№lз¶ӯдәһиҗҠзү№: йҖүеүҚзёҪзқЈ йҳҝзҲҫдјҜзү№В·еёғиіҙжҒ© ж°‘дё»й»Ё 當йҒёзёҪзқЈ йҳҝзҲҫдјҜзү№пҝҪ...

John Augustus ConollyDepiction of the Siege of SebastopolBorn30 May 1829Celbridge, County KildareDied23 December 1888 (aged 59)Curragh, County KildareBuriedMount Jerome Cemetery, DublinAllegiance United KingdomService/branch British ArmyRankLieutenant ColonelUnit49th Regiment of FootColdstream GuardsBattles/warsCrimean WarAwardsVictoria Cross Lieutenant Colonel John Augustus Conolly VC (30 May 1829 вҖ“ 23 December 1888), born in Celbridge, County Kildare, Ireland, was an Irish recipient...

Antibiotik golongan tetrasiklin merupakan sekelompok senyawa antibiotik spektrum luas yang memiliki struktur dasar yang sama dan diisolasi langsung dari beberapa spesies bakteri Streptomyces atau diproduksi secara semi-sintetis dari senyawa yang diisolasi tersebut.[1] Molekul tetrasiklin terdiri dari inti tetrasiklik yang menyatu secara linier (cincin yang diberi nama A, B, C, dan D) yang di dalamnya terdapat berbagai gugus fungsi.[2] Tetrasiklin diberi nama berdasarkan deriva...

Optical space telescope (launched in 2019) For the Egyptian monarch, see Khufu. For the VLT instrument, see ZIMPOL/CHEOPS. Characterising Exoplanets Satellite (CHEOPS)An artist's impression of the CHEOPS space observatoryMission typeExoplanetology, astrophysicsOperatorSwiss Space Office / ESACOSPAR ID2019-092B SATCAT no.44874Websitecheops.unibe.chsci.esa.int/cheopsMission duration3.5 years (nominal)+ 3 years (extended)[1]Elapsed: 4 years, 5 months and 28 days (in progre...

Р—Р°РҝСҖРҫСҒ В«РҹРҫРҙСҒСӮР°РҪСҶРёСҸВ» РҝРөСҖРөРҪР°РҝСҖавлСҸРөСӮСҒСҸ СҒСҺРҙР°; СҒРј. СӮР°РәР¶Рө РҙСҖСғРіРёРө Р·РҪР°СҮРөРҪРёСҸ. Р—Р°РҝСҖРҫСҒ «ТСҖР°РҪСҒС„РҫСҖРјР°СӮРҫСҖРҪР°СҸ РұСғРҙРәа» РҝРөСҖРөРҪР°РҝСҖавлСҸРөСӮСҒСҸ СҒСҺРҙР°. РқР° СҚСӮСғ СӮРөРјСғ РҪСғР¶РҪРҫ СҒРҫР·РҙР°СӮСҢ РҫСӮРҙРөР»СҢРҪСғСҺ СҒСӮР°СӮСҢСҺ. РһР РЈ 750 РәР’ РҪР° СҚР»РөРәСӮСҖРёСҮРөСҒРәРҫР№ РҝРҫРҙСҒСӮР°РҪСҶРёРё РһР РЈ РҝРҫРҙСҒСӮР°РҪСҶРёРё 110/35/6 РәР’, Рі. РӣСҸРҪСӮРҫСҖ РҡРҫРјРҝР»РөРәСӮРҪР°СҸ СӮСҖР°РҪСҒС„РҫСҖРјР°СӮРҫСҖРҪ...

Bernd HГ¶lzenbeinNazionalitГ Germania Ovest Altezza172 cm Calcio RuoloAla, attaccante Termine carriera1Вә luglio 1986 CarrieraSquadre di club1 1967-1981 Eintracht Francoforte420 (160)1981-1983 Ft. Lauderdale Strikers46 (10)1986 Salmrohr0 (0) Nazionale 1973-1978 Germania Ovest40 (5) PalmarГЁs Mondiali di calcio OroGermania Ovest 1974 Europei di calcio ArgentoJugoslavia 1976 1 I due numeri indicano le presenze e le reti segnate, per le sole partite di campionato.Il ...

Flag African UnionProportion2:3Adopted31 January 2010; 14 years ago (2010-01-31)[1]DesignA dark green map of the African continent, plus the Sinai Peninsula and offshore islands, on a white sun, surrounded by a circle of 55 5-pointed gold (yellow) stars, on a dark green field.Designed byYadesa Bojia[2] The current flag of the African Union was adopted at its 14th Ordinary Session of the Assembly of Heads of State and Government, which took place in Addis...

Р’ Р’РёРәРёРҝРөРҙРёРё РөСҒСӮСҢ СҒСӮР°СӮСҢРё Рҫ РҙСҖСғРіРёС… Р»СҺРҙСҸС… СҒ СӮР°РәРҫР№ фамилиРөР№, СҒРј. Р‘РөСҒСҒРҫРҪРҫРІ; Р‘РөСҒСҒРҫРҪРҫРІ, ВлаРҙРёРјРёСҖ. ВлаРҙРёРјРёСҖ РҳРІР°РҪРҫРІРёСҮ Р‘РөСҒСҒРҫРҪРҫРІ Р”РөРҝСғСӮР°СӮ Р“РҫСҒСғРҙР°СҖСҒСӮРІРөРҪРҪРҫР№ РҙСғРјСӢ РӨРөРҙРөСҖалСҢРҪРҫРіРҫ СҒРҫРұСҖР°РҪРёСҸ Р РҫСҒСҒРёР№СҒРәРҫР№ РӨРөРҙРөСҖР°СҶРёРё Р РҫР¶РҙРөРҪРёРө 21 РјР°СҖСӮР° 1966(1966-03-21) (58 Р»РөСӮ)Р РҫСҒСӮРҫРІ-РҪР°-Р”РҫРҪСғ, Р РЎРӨРЎР РҹР°СҖСӮРёСҸ РҡРҹР РӨ РһРұСҖазРҫРІР°РҪРёРө РқпҝҪ...

Ne doit pas ГӘtre confondu avec Tournoi de tennis de Moscou (International). Tournoi de tennis de Moscou GГ©nГ©ralitГ©s Sport Tennis CrГ©ation 1971 1990 Disparition 2022 Autre(s) nom(s) VTB Kremlin Cup Гүditions 33 (2021) 31 (2021) CatГ©gorie WTA 500 ATP 250 PГ©riodicitГ© Annuelle Lieu(x) Moscou Participants 28 joueurs/joueuses en simple16 Г©quipes en double Statut des participants Professionnel Surface Moquettejusqu'en ( 2007, 2006)Dur (int.), RuKortdepuis ( 2008, 2007) Directeur Aleksei Se...

Bilateral relationsNorth VietnamвҖ“Yugoslavia relations North Vietnam Yugoslavia Bilateral relationsVietnamвҖ“Yugoslavia relations Vietnam Yugoslavia Ho Chi Minh, Josip Broz Tito and Edvard Kardelj in Belgrade in 1957 VietnamвҖ“Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between Vietnam (up to 1975 North Vietnam) and now split-up Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Two countries established formal bilateral relations in 1957.[1] Relations were predominantly positive d...

Liste de l'unitГ©(da) Enhedslisten - de rГёd-grГёnne Logotype officiel. PrГ©sentation Leader Direction collective Fondation 2 dГ©cembre 1989 Fusion de Parti communiste du DanemarkParti socialiste des travailleursSocialistes de gaucheIndГ©pendants du Parti communiste des travailleurs (en) SiГЁge StudiestrГҰde 24, 1, 1455 Copenhague K Porte-parole Mai Villadsen (en) Organisation de jeunesse Aucune (en coopГ©ration avec le Front de la jeunesse socialiste (en)) Positionnement Gauc...

