GOES-16
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Seorang penambang batu bara menyelesaikan tinjauan penyaringan untuk paru-paru hitam. Dalam kedokteran, penapisan atau penyaringan (Inggris: screeningcode: en is deprecated ) adalah cara yang digunakan untuk mencari keadaan atau penanda risiko yang belum diketahui.[1][2][3] Pengujian ini dapat diterapkan kepada individu atau seluruh populasi. Orang yang diuji mungkin tidak menunjukkan tanda atau gejala penyakit apa pun atau menunjukkan satu atau dua gejala yang dengan ...

1998 American strikes in Afghanistan and Sudan Operation Infinite ReachPart of the Afghan conflictMap showing the two sites of attacksLocationsKhartoum, Sudan15°38′45″N 32°33′42″E / 15.64583°N 32.56167°E / 15.64583; 32.56167Khost Province, AfghanistanPlanned7–20 August 1998TargetAl-Shifa pharmaceutical factory and Afghan training campDate20 August 1998; 25 years ago (1998-08-20)Executed by United States NavyOutcomeUnited States...

Cet article concerne le quotidien Le Vélo. Pour le service de vélo en libre service marseillais, voir Le vélo (vélopartage). Le Vélo Pays France Langue Français Fondateur Pierre Giffard Date de fondation 1er décembre 1892 Date du dernier numéro 20 novembre 1904 Rédacteur en chef Paul RousseauGaston de Pawlowski modifier Le Vélo est un quotidien français spécialisé dans le sport, qui parut en France à la fin du XIXe siècle et au début du XXe siècle. C...
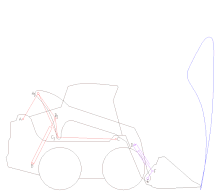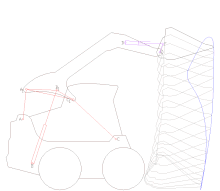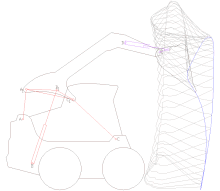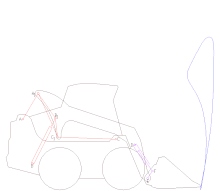
Artikel ini tidak memiliki referensi atau sumber tepercaya sehingga isinya tidak bisa dipastikan. Tolong bantu perbaiki artikel ini dengan menambahkan referensi yang layak. Tulisan tanpa sumber dapat dipertanyakan dan dihapus sewaktu-waktu.Cari sumber: Mesin angkut – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Pelacakan model CAD dari mekanisme mesin angkut skid Mesin angkut adalah mesin alat berat yang digunakan dalam konstruksi untuk memindahka...

Motorcycle speedway venue in Holsted, Denmark Holsted Speedway CenterLocationHedevejen 1, 6670 Holsted, DenmarkCoordinates55°27′54″N 8°54′47″E / 55.46500°N 8.91306°E / 55.46500; 8.91306Opened4 June 1989Major eventsmotorcycle speedwayOvalLength(300 metres) 0.300 km Holsted Speedway Center or Moldow Speedway Arena is a motorcycle speedway facility located about 6 kilometres south of Holsted, Denmark. The track is off the Ribevej road that runs south from rail...

Airline alliance Vanilla AllianceLaunch date21 September 2015; 8 years ago (2015-09-21)Full members5Destination airports89Destination countries26Annual passengers (M)2.3[1]Fleet size46ManagementMarie-Joseph Malé, president[2] The Vanilla Alliance (French: Alliance Vanille) is an airline alliance formed in September 2015. The alliance is the fourth largest in the world as of 2018, trailing Oneworld, Star Alliance, and SkyTeam.[3] All of the airlines w...

Noah HawleyLahir1967 (umur 56–57)New York City, New York, Amerika Serikat[1]PekerjaanPenulis televisi, produser televisi, penulis naskah, pengarangKebangsaanAmerika SerikatAlmamaterSarah Lawrence CollegeKarya terkenal Fargo Legion PasanganKyle HawleyAnak2Kerabat Tom Hawley (ayah) Louise Armstrong (ibu) Websitenoahhawley.com Noah Hawley (kelahiran c. 1967) adalah seorang penulis, produser, penulis naskah dan pengarang asal Amerika Serikat. Ia dikenal karena membua...

DctP component of Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporterIdentifiersSymbolDctPPfamPF03480Pfam clanCL0177InterProIPR018389TCDB2.A.56Available protein structures:Pfam structures / ECOD PDBRCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBjPDBsumstructure summary DctQ component of Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporterIdentifiersSymbolDctQPfamPF04290InterProIPR007387TCDB2.A.56Available protein structures:Pfam structures / ECOD PDBRCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBjPDBsumstructure summaryDctM-li...

SMK Negeri 10 PadangInformasiDidirikan2007JenisNegeriAkreditasiBNomor Statistik Sekolah401086111010Nomor Pokok Sekolah Nasional10307617Kepala SekolahMahyunis, S.Pd.Rentang kelasX, XI, XIIKurikulumKurikulum 2013AlamatLokasiJalan Flamboyan Simpang Kantor Camat Koto Tangah, Lubuk Buaya, Koto Tangah, Padang, Sumatera Barat, IndonesiaTel./Faks.(0751) 484305Situs webhttps://smkn10-padang.sch.id/[email protected] SMK Negeri 10 Padang adalah sekolah menengah kejuruan negeri ya...

Events at the1993 World ChampionshipsTrack events100 mmenwomen200 mmenwomen400 mmenwomen800 mmenwomen1500 mmenwomen3000 mwomen5000 mmen10,000 mmenwomen100 m hurdleswomen110 m hurdlesmen400 m hurdlesmenwomen3000 msteeplechasemen4 × 100 m relaymenwomen4 × 400 m relaymenwomenRoad eventsMarathonmenwomen10 km walkwomen20 km walkmen50 km walkmenField eventsHigh jumpmenwomenPole vaultmenLong jumpmenwomenTriple jumpmenwomenShot putmenwomenDiscus throwmenwomenHammer throwmenJavelin throwmenwomenCom...

Menteri Besar Pahangمنتري بسار ڤهڠPetahanaWan Rosdy Wan Ismailsejak 15 Mei 2018GelarYang Amat Berhormat(resmi)StatusKepala pemerintahanAnggotaDewan Eksekutif Negara Bagian PahangAtasanDewan Undangan Negeri PahangKediamanJalan Telok Sisek, 25000 Kuantan, PahangKantorWisma Sri Pahang, 25502 Kuantan, PahangDitunjuk olehAl-Sultan Abdullahsebagai Sultan PahangMasa jabatan5 tahunPejabat perdanaMahmud MatDibentuk1 Februari 1948; 76 tahun lalu (1948-02-01)Situs webwww.pahang.gov...

This article forms part of the seriesEastern Orthodox Christianityin North America History History of Eastern Orthodoxy in North America Eastern Orthodoxy in North America timeline Eastern Orthodoxy in the United States bibliography Ligonier Meeting People Saints Bishops Writers Jurisdictions (list) Assembly of Bishops Ecumenical Patriarchate Greek Albanian ACROD Ukrainian Palestinian/Jordanian GOAC UOCC GOMM Antiochian AOAM Russian ROCOR Serbian Romanian Bulgarian Georgian OCA Other AOCC Mac...

هذه المقالة عن الظاهر لإعزاز دين الله الفاطمي. لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع فاطمي (توضيح). خليفة فاطمي الظاهر لإعزاز دين الله دينار يعود إلى عهد الخليفة الظاهر لإعزاز دين الله معلومات شخصية الميلاد 20 يونيو 1005 [1] القاهرة تاريخ الوفاة 13 يونيو 1036 (30 سنة) [1] سبب الوف...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يوليو 2019) خواكين إيبارا معلومات شخصية الميلاد 20 يوليو 1726 سرقسطة الوفاة 13 سبتمبر 1785 (59 سنة) مدريد مواطنة إسبانيا الحياة العملية المهنة طابع حروف ...

National governing body South African Bridge FederationSportBridgeAbbreviationSABFFounded1954AffiliationWorld Bridge FederationAffiliation date1960Regional affiliationAfrican Bridge FederationPresidentJames Grant[1]SecretaryKit GilmourOfficial websitewww.sabf.co.za The South African Bridge Federation (SABF) is the national governing body, custodian and regulator for the card game of bridge in South Africa. SABF is affiliated to the world governing body World Bridge Federation (WBF),&#...
شين وارن (بالإنجليزية: Shane Warne) معلومات شخصية الميلاد 13 سبتمبر 1969 [1][2] أبر فيرنتري جولي، فيكتوريا [لغات أخرى] الوفاة 4 مارس 2022 (52 سنة) [3] جزيرة ساموي[3] سبب الوفاة نوبة قلبية[4] الطول 183 سنتيمتر مركز اللعب رامي [لغات أخر�...

Cover of the first North American DVD box set by Viz Ranma ½ (らんま½) is a Japanese anime series adapted from the manga of the same name by Rumiko Takahashi. It was created by Studio Deen and aired weekly between April 15, 1989 and September 16, 1989 on Fuji TV before being canceled after 18 episodes due to low ratings. Shortly after, the series was reworked by most of the same staff, retitled Ranma ½ Nettōhen (らんま½ 熱闘編) and launched in a different time slot, running bet...

Church building other than the parish church For the fantasy novel by Alex Bledsoe, see Chapel of Ease (novel). St Nicholas' Chapel in King's Lynn, England's largest chapel of ease All Saints' Church at Buncton in West Sussex dates from the 11th or 12th century. Trinity Church in 1879, the chapel-of-ease in the City of Hamilton, Bermuda, for the then-Bishop of Newfoundland and Bermuda (the Cathedral of St. John the Baptist was at St. John's, Newfoundland). A chapel of ease (or chapel-of-ease)...

1945 novembre 1946 Élection législative de juin 1946 dans l'Aisne 6 sièges de députés à l'Assemblée constituante 2 juin 1946 Type d’élection Élections législatives Corps électoral et résultats Population 453 411 Votants 225 738 83,97 % 2 Parti communiste français – Adrien Renard Voix 79 668 35,82 % 0,5 Députés élus 3 1 Section française de l'Internationale ouvrière – Marcel Levindrey Voix ...

「斎藤安雄」とは別人です。 ウラジミール・プーチンとの信任状奉呈式に臨む齋藤泰雄(右)(2006年7月) 齋藤 泰雄(さいとう やすお、1948年(昭和23年)1月5日 - )は、日本の外交官。元・フランス国駐箚特命全権大使。日本オリンピック委員会副会長。 経歴 岡山県出身。金光学園中学校・高等学校から東京大学法学部へ進学[1]。東京大学在学中の1970年(昭和...

