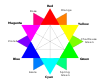
Unique hues
|
Read other articles:

Dinding beton pracetak di sebuah rumah yang sedang dibangun Beton pracetak adalah produk konstruksi yang dibuat dengan cara mencetak beton dalam sebuah cetakan yang dapat digunakan kembali. Beton tersebut kemudian menjalani perawatan (curing) di lingkungan terkontrol dan dikirimkan menuju lokasi konstruksi. Dengan kata lain, beton dicetak di lokasi yang berbeda dengan lokasi konstruksi, seperti metode cast-in-situ. Beton pracetak digunakan di dinding eksterior dan interior. Produksi beton pra...

Ketua Umum Partai Persatuan PembangunanPetahanaMuhamad Mardiono(pelaksana tugas)sejak 5 September 2022KediamanKantor Dewan Pimpinan Pusat Partai Persatuan PembangunanMasa jabatan5/4 Tahun, dipilih Melalui MuktamarPejabat pertamaMohammad Syafa'at Mintaredja Partai Persatuan Pembangunan adalah partai politik di Indonesia yang dipimpin oleh Ketua Umum dan dipilih melalui muktamar. Pada Mukernas September 2022, Muhamad Mardiono terpilih sebagai Plt Ketua Umum PPP. Berikut adalah daftar Ketua...

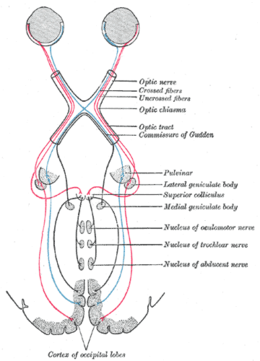
Provision to cells and organisms to support life For other uses, see Nutrition (disambiguation). An Amblypodia anita (purple leaf blue butterfly) gathering nutrients from guano Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficient nutrients causes malnutrition. Nutritional science is the study of nutrition, t...

Belarusian politician Sergei GaidukevichСяргей ГайдукевічChairman of the Liberal Democratic Party of BelarusIn office1995 – 21 September 2019Preceded byPosition establishedSucceeded byOleg Gaidukevich Personal detailsBorn (1954-09-08) September 8, 1954 (age 69)Minsk, Belarusian SSR, Soviet Union (now Belarus)Political partyLiberal Democratic Party Sergei Gaidukevich (Belarusian: Сяргей Гайдукевіч, Russian: Сергей Гайдукевич; born...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento politici italiani non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Commento: Fonti insufficienti Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Sergio Flamigni Deputato della Repubblica ItalianaLegislaturaV, VI, VII GruppoparlamentarePCI CircoscrizioneBologna Incarichi parlamentari Membro della Commissione Pres...

Informal public venue for pianist For other uses, see Piano bar (disambiguation). A piano bar (also known as a piano lounge) consists of a piano or electronic keyboard played by a professional musician. Piano bars can be located in a cocktail lounge, bar, hotel lobby, office building lobby, restaurant, or on a cruise ship. Usually the pianist receives a small salary plus tips in a jar or basket on or near the piano, especially from patrons requesting a song traditionally written on a beverage...

Ато Эссандоангл. Ato Essandoh Имя при рождении англ. Ato Essilfi Bracato Essandoh Дата рождения 29 июля 1972(1972-07-29) (51 год) Место рождения Скенектади, Нью-Йорк, США Гражданство США Профессия актёр Карьера 2001 — н. в. IMDb ID 1017951 atoessandoh.com Медиафайлы на Викискладе А́то Эссандо (а�...

Protected lakes in Kazakhstan Lakes of the lower Turgay and IrgizОзёра в низовьях рек Иргиз и ТургайLakes of the lower Turgay and Irgiz Sentinel-2 satellite pictureLocation in KazakhstanTypeInland wetlandsLocationAktobe Region, KazakhstanNearest cityNuraCoordinates48°42′N 62°11′E / 48.700°N 62.183°E / 48.700; 62.183Area348,000 ha (3,480 km2)Created1976Operated byMain Department of Zapovedniks and Game Management ...

Governor of Tasmania For the character in the TV series 24, see Kate Warner (24 character). Professor the HonourableKate WarnerAC FAALWarner in 201628th Governor of TasmaniaIn office10 December 2014 – 16 June 2021MonarchElizabeth IIPremierWill Hodgman Peter GutweinLieutenantAlan BlowPreceded byPeter UnderwoodSucceeded byBarbara Baker Personal detailsBornCatherine Ann Friend (1948-07-14) 14 July 1948 (age 75)Hobart, TasmaniaNationalityAustralianSpouse Richard Warner ...
2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会波兰代表團波兰国旗IOC編碼POLNOC波蘭奧林匹克委員會網站olimpijski.pl(英文)(波兰文)2020年夏季奥林匹克运动会(東京)2021年7月23日至8月8日(受2019冠状病毒病疫情影响推迟,但仍保留原定名称)運動員206參賽項目24个大项旗手开幕式:帕维尔·科热尼奥夫斯基(游泳)和马娅·沃什乔夫斯卡(自行车)[1]闭幕式:卡罗利娜·纳亚(皮划艇)&#...

Regno di ArmeniaDati amministrativiNome ufficialeΒασίλειον τῆς Kομμαγηνής Lingue ufficialiarmenogrecosiriaco Lingue parlateKoinè CapitaleSamosata PoliticaForma di StatoMonarchia assoluta Nascita163 a.C. con Tolomeo di Commagene Causaseparazione della Commagene dal Regno di Sofene Fine72 con Antioco IV Epifane Causaannessione romana per volere di Vespasiano Territorio e popolazioneBacino geograficoRegno di Armenia Religione e societàReligione di StatoPoliteismo, Zoroast...

Summary of algorithms for nonlinear dimensionality reduction Top-left: a 3D dataset of 1000 points in a spiraling band (a.k.a. the Swiss roll) with a rectangular hole in the middle. Top-right: the original 2D manifold used to generate the 3D dataset. Bottom left and right: 2D recoveries of the manifold respectively using the LLE and Hessian LLE algorithms as implemented by the Modular Data Processing toolkit. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction, also known as manifold learning, is any of vario...

Fried plantain chip dish Preparation of chifles in Ecuador Chifles in Thailand are known as ‘banana chips‘. Chifles in the 2017 Encebollado World Cup (Esmeraldas, Ecuador) Gastronomy of Ecuador Chifles in the 2015 Encebollado World Cup (Esmeraldas, Ecuador) Round homemade chifles in Guayaquil, Ecuador Detailed close-up of chifles Ecuatorial plantain Chifles, fried plantain chips, are a side dish, snack food, or finger food of Ecuador, Thailand and Peru. In Ecuador The cuisine of Ecuador i...

Monti PeloritaniI monti Peloritani visti da TorregrottaContinenteEuropa Stati Italia Catena principaleAppennino siculo Cima più elevataMontagna Grande (1 374 m s.l.m.) Tipi di roccegneiss, fillade Posizione dei Monti Peloritani in Sicilia Profilo di Pizzo di Vernà da Fondachelli-Fantina Il monte Scuderi La Rocca di Novara vista da Fondachelli Fantina i Ritagli di Lecca situati in prossimità della Rocca di Novara, visti dal lato del torrente Patrì I monti Peloritani (i ...

Puyi Puyi i officiell kejsarskrud. Kejsare av Qingdynastin Regeringstid 2 december 1908–12 februari 1912 Företrädare Guangxu Efterträdare Ämbetet upplöst Kejsare av Manchukuo Regeringstid 1934–1945 Gemål Wanrong, Wenxiu, Tan Yuling och Li Yuqin. Ätt Aisin Gioro Föräldrar Zaifeng och Youlan Född 7 februari 1906Peking Död 17 oktober 1967 (61 år)Peking Aisin Gioro Puyi eller Pu Yi (kinesiska: 溥儀, Pǔyí), född 7 februari 1906 i Peking, död 17 oktober 1967 i Peking, va...

« Ministère des Affaires étrangères et européennes » redirige ici. Pour l'équivalent luxembourgeois, voir Ministère des Affaires étrangères et européennes (Luxembourg). Pour les articles homonymes, voir Ministère des Affaires étrangères et Quai d'Orsay (homonymie). Ministère de l'Europe et des Affaires étrangèresHistoireFondation 1547 : secrétaire d'État aux Affaires étrangères 1789 : ministère des Affaires étrangères ou des Relations extérieuresC...
薩哈林鐵路 Сахалинская железная дорога哈巴羅夫斯克-南薩哈林斯克列車區域 俄羅斯薩哈林州營運日期1992–2010前身遠東鐵路局(1945-1992)繼承遠東鐵路局(2010-)軌距1,520毫米(4英尺11 27⁄32英寸)總部南薩哈林斯克 俄羅斯鐵路遠東鐵路局薩哈林地域部 圖例 653.7 諾格利基(俄语:Ноглики (станция)) 610.0 尼什(俄语:Ныш (станция)) 592....

Water-gel explosive This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Tovex – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Tovex Firebreak II used on Upper Bear Creek Trail in the Angeles National Forest Tovex (also known as Trenchrite, Seismogel, and Seis...

كامينغز (بالإنجليزية: Jason Cummings) معلومات شخصية الاسم الكامل جايسون كامينغز الميلاد 1 أغسطس 1995 (العمر 29 سنة)ادنبره ، اسكتلندا الطول 1.78 م (5 قدم 10 بوصة) مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية إسكتلندا معلومات النادي النادي الحالي سنترال كوست مارينرز الرقم 9 مسيرة الشباب سنوات ...

Presidente della Commissione europea Ursula von der Leyen, presidente della Commissione europea Organizzazione Unione europea TipoCapo dell'esecutivo In caricaUrsula von der Leyen (PPE) da1º dicembre 2019 Istituito1957 daTrattati di Roma PredecessoreJean-Claude Juncker Riforme2009 Nominato daParlamento europeo SedeBruxelles Sito webec.europa.eu Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale Il presidente della Commissione europea è la persona che presiede e guida l'organo esecutivo europeo,...