Sikasso
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Food LionLogo Food Lion sejak 2014Sebuah toko di Tega Cay di Carolina Selatan, 2012SebelumnyaFood Town (1957–1983)JenisToko kelontongIndustriEceranDidirikan12 Desember 1957; 66 tahun lalu (1957-12-12)PendiriBrown KetnerRalph KetnerWilson SmithKantorpusatSalisbury, Carolina Utara, ASCabang1,103Wilayah operasiAtlantik Tengah (Amerika Serikat)Negara bagian Atlantik SelatanTokohkunciMeg Ham, PresidenGreg Finchum, Wakil Presiden Senior Karen Fernald, Wakil Presiden Senior,ProdukBahan ...

KepuharjoDesaKantor Desa KepuharjoNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TimurKabupatenMalangKecamatanKarangplosoKode pos65152Kode Kemendagri35.07.23.2002 Luas... km²Jumlah penduduk... jiwaKepadatan... jiwa/km² Kepuharjo adalah sebuah desa di wilayah Kecamatan Karangploso, Kabupaten Malang, Provinsi Jawa Timur. Kepuharjo merupakan wilayah di Kecamatan Karangploso, Kabupaten Malang. Asal mula kata kepuharjo diambil dari nama sebuah pohon yang banyak dijumpai di desa tersebut yaitu pohon Kepuh, da...

1979 Indian filmTayaramma BangarayyaPoster of Tayaramma BangarayyaDirected byKommineni Seshagiri RaoWritten byKommineni Seshagiri Rao(story / screenplay) Dialogue byJandhyala Produced byEdida Nageswara RaoAakasam SriramuluStarringKaikala SatyanarayanaSowcar JanakiCinematographyP. Bhaskar RaoMusic byChakravarthyRelease date12 January 1979CountryIndiaLanguageTelugu Tayaramma Bangarayya is a 1979 Indian Telugu-language film starring Sowcar Janaki as Tayaramma and Kaikala Satyanarayana as Bangar...

Anti-democratic, reactionary philosophy founded by Curtis Yarvin in 2007 Not to be confused with Counter-Enlightenment or Intellectual dark web. This article is part of a series onConservatismin the United States Schools Compassionate Fiscal Fusion Libertarian Moderate Movement Neo Paleo Progressive Social Traditionalist Principles American exceptionalism Anti-communism Christian nationalism Classical liberalism Constitutionalism Familialism Family values Federalism States' rights Judeo-Chris...

Jeanna FineFine, 2000Lahir29 September 1964 (umur 59)[1]New York, New York, AS[1]Nama lainJeana Fine, Gina Fine, Virginia Paymore, Angel Rush, Devon Delight, Geanna Fine, Jenna Fine, Angelique Gauthier, Vanna Paymore, Angel Payson,[1] Vanna BlackTinggi5 ft 7 in (1,70 m)[1] Jeanna Fine (lahir 29 September 1964) adalah mantan aktris porno dan penari erotis asal Amerika.[1] Aktris film dewasa Barbara Dare berkomentar betapa baik J...

Tram system in Barcelona TrambaixA tram leaving Cornellà Centre station towards Francesc MaciàOverviewNative nameTrambaixLocaleBarcelonaTransit typeTramNumber of lines3Number of stations64Annual ridershipApprox. 15 million (2014)Websitewww.tram.catOperationBegan operation2004Operator(s) Tramvia Metropolità S.A.CharacterAt-gradeRolling stockAlstom Citadis 302TechnicalSystem length32.089 km (19.939 mi)Track gauge1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gaugeElect...

Term for a visionless project Design by committee is a pejorative term for a project that has many designers involved but no unifying plan or vision. Usage of the term Remote controls with as many as 78 buttons have been cited as an example of a product designed by committee. The term is used to refer to suboptimal traits that such a process may produce as a result of having to compromise between the requirements and viewpoints of the participants, particularly in the presence of poor leaders...

EDTLogo Stato Italia Fondazioneottobre 1976 a Torino Sede principaleTorino SettoreEditoria Prodottimusicologia, viaggi, infanzia, gastronomia Sito webwww.edt.it Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manuale EDT (Edizioni Di Torino) è una casa editrice italiana fondata a Torino nel 1976 da Enzo Peruccio. Attiva in origine nel campo musicale, ha ampliato nel corso degli anni il proprio catalogo includendo saggistica, narrativa, libri per ragazzi, gastronomia e turistica, con le guide Lone...
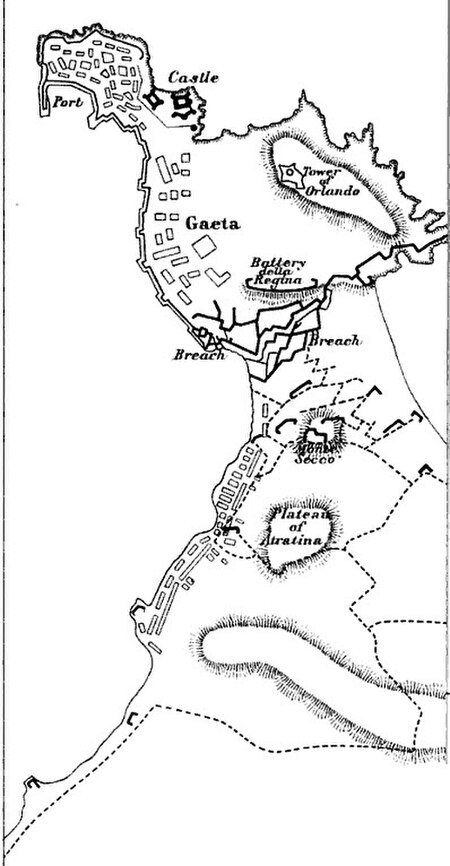
1815 siege during the Neapolitan War Siege of GaetaPart of the Neapolitan WarMap of the 1806 Siege of Gaeta showing the terrainDate28 May – 8 August 1815LocationGaeta, present-day Italy41°13′00″N 13°34′00″E / 41.2167°N 13.5667°E / 41.2167; 13.5667Result Coalition victory[1]Belligerents Austrian Empire United Kingdom Kingdom of Sicily Kingdom of NaplesCommanders and leaders Joseph Freiherr von Lauer Maresciallo di Campo Aless...

Hollywood Music in Media AwardsDeskripsiMedia Musik VisualNegaraAmerika SerikatSitus webhttp://www.hmmawards.com/ Hollywood Music in Media Awards (HMMA) adalah sebuah penghargaan musik dalam film, televisi, permainan video, iklan, dan trailer. Nominasi ditentukan oleh badan penasehat dan komite seleksi yang terdiri dari para jurnalis, eksekutif musik, penulis lagu, dan komponis. Pranala luar Situs web resmi

American political journalist, author, professor, and advocate Norman CousinsBornJune 24, 1915West Hoboken, New Jersey, U.S.DiedNovember 30, 1990 (aged 75)Los Angeles, California, U.S.Alma materTeachers College, Columbia University (B.A.)Signature Norman Cousins[1] (June 24, 1915 – November 30, 1990) was an American political journalist, author, professor, and world peace advocate. Early life Cousins was born to Jewish immigrant parents Samuel Cousins and Sarah Babushkin Cousin...

Governing body of association football in Switzerland Swiss Football AssociationUEFAFounded7 April 1895; 129 years ago (7 April 1895)FIFA affiliation1904UEFA affiliation1954PresidentDominique BlancWebsitehttp://www.football.ch The Swiss Football Association (German: Schweizerischer Fussballverband, French: Association Suisse de Football, Italian: Associazione Svizzera di Football/Calcio, Romansh: Associaziun Svizra da Ballape) is the governing body of football in Switzerland. It ...

关于江苏省的2019冠状病毒病疫情情况,请见「2019冠狀病毒病江蘇省疫情」。 维基百科中的醫學内容仅供参考,並不能視作專業意見。如需獲取醫療幫助或意見,请咨询专业人士。詳見醫學聲明。 在這條目內未有標明年份的日期都代表是2021年。 若非特別註明,本條目所有時間皆為東八區標準時間(UTC+8)。 南京禄口国际机场2019冠状病毒病聚集性疫情南京禄口...

Accident ferroviaire de Villecomtal Caractéristiques de l'accident Date1er août 1922 TypeCollision SiteLaguian-Mazous Caractéristiques de l'appareil Morts33 Blessés32 modifier L'accident ferroviaire de Villecomtal a eu lieu en France le 1er août 1922, dans le département du Gers, entre les gares de Miélan et de Villecomtal-sur-Arros, à proximité du village de Laguian-Mazous. La majorité des gros titres de la presse de l'époque le localisent à Villecomtal[1], mais d'autres l...
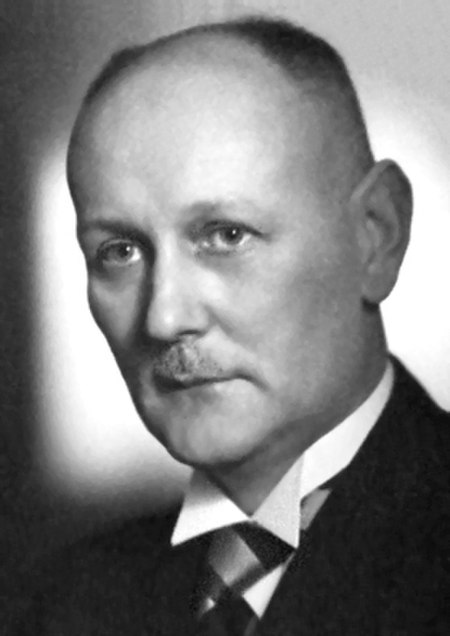

Gerhard Domagk Gerhard Johannes Paul Domagk (30 Oktober 1895 - 24 April 1964) adalah seorang dokter Jerman, yang pada 1932 menciptakan preparat sulfonamida yang pertama, yang efektif untuk melawan infeksi bakteri seperti Pneumococcus, yang menyebabkan pneumonia. Domagk dianugerahi Penghargaan Nobel dalam Fisiologi atau Kedokteran pada 1939, tetapi Adolf Hitler melarangnya menerima penghargaan itu, sehingga ia baru bisa menerimanya pada 1947. lbsPenerima Penghargaan Nobel Fisiologi atau Kedokt...

Alley view of Clarion Alley (2017) Clarion Alley is a small street between Mission and Valencia Streets and 17th and 18th Streets in the Mission District in San Francisco, California. It is notable for the murals painted by the Clarion Alley Mural Project.[1] Map History Originally called Cedar Lane, the alley's name was changed around the turn of the twentieth century to Clarion Alley.[2] The street is notable for community and arts activity, including the Clarion Alley Mural...

Croatian journalist, writer and columnist Boris DežulovićBorn (1964-11-20) 20 November 1964 (age 59)Split, SR Croatia, YugoslaviaOccupationJournalist and novelistNationalityCroatianPeriod1984–presentPartnerRose FistanićChildrenDora Dežulović Boris Dežulović (born 20 November 1964)[1] is a Croatian journalist, writer and columnist, best known as one of the founders of the now defunct satirical magazine Feral Tribune. Biography Dežulović studied art history at the Un...

Sudan padaOlimpiadeKode IOCSUDKONKomite Olimpiade SudanMedali 0 1 0 Total 1 Penampilan Musim Panas19601964196819721976–19801984198819921996200020042008201220162020 Sudan mula-mula berpartisipasi dalam Permainan Olimpiade pada 1960, dan telah mengirim para atlet untuk berkompetisi dalam sebagian besar Olimpiade Musim Panas sejak itu. Negara tersebut tak menghadiri Permainan 1964, memboikot Olimpiade Musim Panas 1976 bersama dengan sebagian besar negara Afrika, dan ikut serta dalam pemboikota...

Russian statesman (1786–1855) CountSergey UvarovСергей УваровUvarov's portrait by Orest Kiprensky, 1815.Born(1786-08-25)August 25, 1786Moscow, Russian EmpireDiedOctober 4, 1855(1855-10-04) (aged 69)Moscow, Russian EmpireSignature This article is part of a series onConservatism in Russia Ideologies Eurasianism Duginism Monarchism Tsarism National conservatism Populism Putinism Russian nationalism All-Russian Christian Ultra Slavophilia Pochvennichestvo Social conservatism Tr...
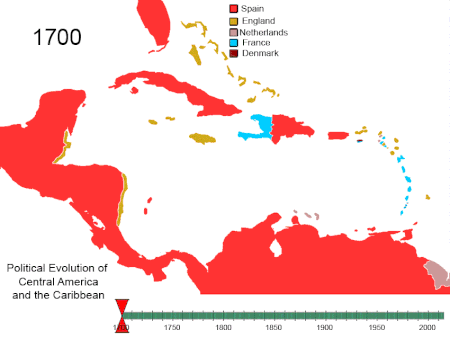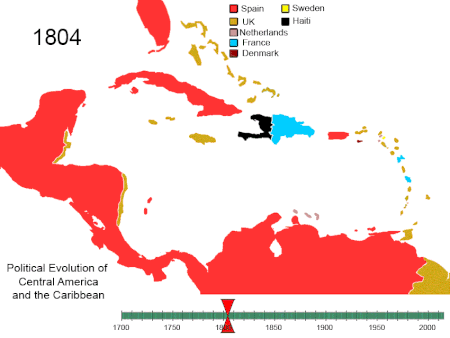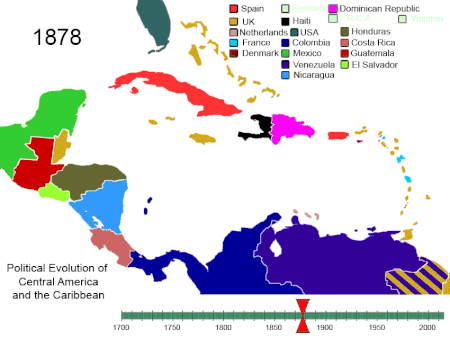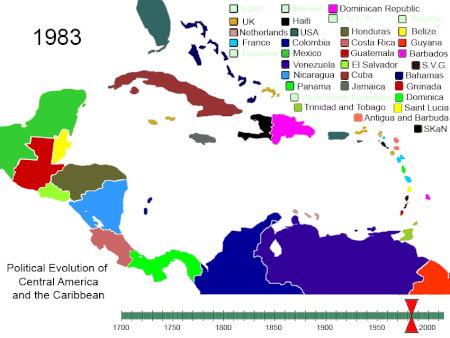
Artikel ini bukan mengenai Sejarah Amerika Serikat. Amerika Utara 1750-2008. Amerika Tengah dan Karibia 1700-sekarang Amerika Selatan 1700-sekarang Sejarah Amerika adalah sejarah kolektif Amerika Utara, Amerika Tengah, Karibia dan Amerika Selatan. Sejarah Amerika dimulai dengan migrasi penduduk dari Asia selama Zaman Es. Kelompok tersebut terisolasi dari Dunia Lama hingga datangnya bangsa Eropa pada abad ke-10 dan ke-15. Nenek moyang penduduk asli Amerika pemburu dan pengumpul makanan yang be...




