On Gaia: A Critical Investigation of the Relationship between Life and Earth
| |||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
Nina Wang Nina Wang (terlahir Kung Yu Sum (bahasa Tionghoa: 龔如心, pinyin: Gŏng Rúxīn) (29 September 1937[1] – 3 April 2007) adalah perempuan Asia terkaya, dengan harta kekayaan bersih diperkirakan berjumlah AS$4,2 miliar pada saat kematiannya.[2] Wang adalah janda seorang jutawan kimia Hong Kong Teddy Wang (Wang Teh Huei, 王德輝), yang hilang pada 1990 setelah diculik. Awal kehidupan Kung Yu Sum dilahirkan di Shanghai. Di sana ia menjadi teman bermain masa kecil ...

« Sarkozy » redirige ici. Pour les autres significations, voir Sarkozy (homonymie), Nagy et Bocșa. Nicolas Sarkozy Nicolas Sarkozy en 2010. Fonctions Membre de droit du Conseil constitutionnel En fonction depuis le 15 mai 2012[b](11 ans, 11 mois et 15 jours) Président Jean-Louis DebréLaurent Fabius Président des Républicains 30 mai 2015 – 23 août 2016(1 an, 2 mois et 24 jours) Vice-président Nathalie Kosciusko-MorizetLaurent WauquiezIsabelle...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Edward Said Edward Said en 2002.Información personalNombre de nacimiento Edward Wadie SaïdNombre en inglés Edward Wadie Said Nacimiento 1 de noviembre de 1935 Jerusalén, Mandato británico de PalestinaFallecimiento 25 de septiembre de 2003 Nueva York, Nueva York, Estados UnidosCausa de muerte Leucemia Nacionalidad EstadounidensePalestinoFamiliaCónyuge Mariam C. SaidMaire Jaanus (1962-1970) EducaciónEducado en Universidad de HarvardUniversidad de PrincetonEscuela Northfield Monte He...

Semi-autonomous European city-state (1920-1939) For the Napoleonic client-state, see Free City of Danzig (Napoleonic). Free City of DanzigFreie Stadt Danzig (German)Wolne Miasto Gdańsk (Polish)1920–1939 Flag Coat of arms Motto: Nec Temere, Nec TimideNeither rashly nor timidlyAnthem: Für Danzig Location of the Free City of Danzig in Europe (1930)Danzig (purple) with parts of Germany (pink) and Poland (green)StatusFree City under League of Nations protectionCapitalDanzig...

Beau Bassin-Rose HillKotaMotto: Tenax et fidelusBeau-Bassin Rose-HillLokasi Dewan KotaKoordinat: 20°14′23.3″S 57°28′18.1″E / 20.239806°S 57.471694°E / -20.239806; 57.471694Koordinat: 20°14′23.3″S 57°28′18.1″E / 20.239806°S 57.471694°E / -20.239806; 57.471694Negara MauritiusDistrikPlaines WilhemsDihuni1722Dibentuk1868Pemerintahan[1] • JenisKotamadya • WalikotaFong Suk Koon Ken Fat ...

Voce principale: Juventus Football Club. Juventus FCStagione 1952-1953 Sport calcio Squadra Juventus Allenatore György Sárosi Presidente Gianni Agnelli Serie A2º Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Mari, Præst (30)Totale: Mari, Præst (30) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: J. Hansen (22)Totale: J. Hansen (22) StadioComunale 1951-1952 1953-1954 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti la Juventus Football Club nelle competizioni ufficiali della sta...

Запрос «Борки (станция)» перенаправляется сюда. На эту тему нужно создать отдельную статью. Крушение императорского поезда Последствия крушения поезда Подробные сведения Дата 17 (29) октября 1888 Время 09:10 MSK (06:10 UTC) Место Борчанская волость, Змиевской уезд, Харьковск�...

Voce principale: Kasseler Sport-Verein Hessen Kassel. Kasseler Sport-Verein Hessen KasselStagione 1994-1995Sport calcio Squadra Hessen Kassel Allenatore Franz Brungs Regionalliga sud13° posto 1993-1994 1995-1996 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa voce raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti il Kasseler Sport-Verein Hessen Kassel nelle competizioni ufficiali della stagione 1994-1995. Indice 1 Stagione 2 Rosa 3 Organigramma societario 4 Calciomercato 4.1 Sessione estiva 5 Risult...

Desktop application BumpTopOriginal author(s)Anand AgarawalaDeveloper(s)GoogleInitial releaseApril 8, 2009 (2009-04-08)Final release2.5 / March 31, 2010; 14 years ago (2010-03-31) Repositorygithub.com/BumpTop/BumpTop Operating systemWindows XP and later, Mac OS X Snow Leopard and laterSize17–21 MBTypeDesktop environmentLicenseApache license 2.0Websitebumptop.github.io BumpTop was a 3D desktop environment that simulates the normal behavior and physical proper...
الفَتْحُ الإسْلَامِيُّ لِلغَالِ جزء من الفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّةُ خريطة تُظهرُ زَحف المُسلمين نحو الغال آتين من الأندلُس خِلال العهد الأُموي معلومات عامة التاريخ 100هـ \ 719م - 141هـ \ 759م الموقع الغال وإفرنجية (جنوب فرنسا وسويسرا وإيطاليا المُعاصرة) النتيجة نصرٌ إسلاميٌ أ�...

General election in the UK 1931 United Kingdom general election ← 1929 27 October 1931 1935 → ← outgoing memberselected members →All 615 seats in the House of Commons308 seats needed for a majorityTurnout76.4%, 0.1% First party Second party Third party Leader Stanley Baldwin Arthur Henderson John Simon Party Conservative Labour National Liberal Alliance National National Leader since 23 May 1923 1 September 1931 5 October 1931 Lea...
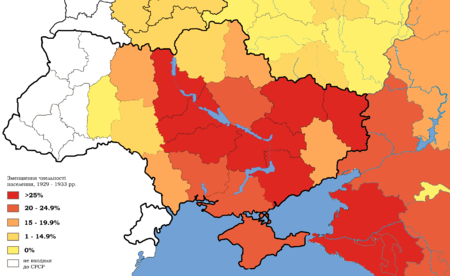
Untuk bencana kelaparan yang sama terutama di Ukraina dan Kazakhstan, lihat Holodomor dan Bencana kelaparan Kazakhstan 1932–33. Bencana kelaparan di USSR, 1933. Wilayah paling terkena bencana kelaparan ditandai dengan warna hitam. Depopulasi Ukraina dan selatan Rusia, 1929–33 Bencana kelaparan Soviet 1932–33 adalah sebuah bencana kelaparan besar yang menewaskan jutaan orang di wilayah penghasil bahan pokok utama di Uni Soviet, termasuk Ukraina, Kaukasus Utara, Wilayah Volga dan Kazakhst...

عنتبطولات دوري كرة القدم في العراقكأس كاجولز 1923–1936 1923–24 1924–25 1926–27 1927–28 1928–29 1929–30 1930–31 1931–32 1932–33 1933–34 1934–35 1935–36 كأس الملك غازي 1931–1935 1931–32 1932–33 1933–34 1934–35 دوري المؤسسات - بغداد 1948–1973عنتمواسم دوري المؤسسات (بغداد) 1948–49 1949–50 1950–51 1951–52 1952–53 1953–54 1954–55 1955–56 1956–57 1957–...

This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (March 2024) Houthi executive body Supreme Political Councilالمجلس السياسي الأعلىCentral governmentOverviewEstablished28 July 2016 (2016-07-28)StateYemenLeaderChairman (Mahdi al-Mashat)HeadquartersSanaaWebsiteyemen.gov.ye (dead)(27 April 2021 archive) The Supreme Political Council (SPC; Arabic: المجلس السياسي الأعلى al-...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Ventimiglia (disambigua). Ventimigliacomune Ventimiglia – VedutaLa città vecchia di Ventimiglia LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Liguria Provincia Imperia AmministrazioneSindacoFlavio Di Muro (Lega) dal 29-5-2023 TerritorioCoordinate43°47′25″N 7°36′30″E43°47′25″N, 7°36′30″E (Ventimiglia) Altitudine9 m s.l.m. Superficie53,73 km² Abitanti22 922[1] (28-2-2024...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (نوفمبر 2019) كأس كرواتيا 1998–99 تفاصيل الموسم كأس كرواتيا النسخة 8 البلد كرواتيا التاريخ بداية:19 أغسطس 1998 �...

Transfer of genes from unrelated organisms HGT redirects here. For other uses, see HGT (disambiguation). This article is about the natural process. For artificial gene transfer, see Gene delivery. Tree of life showing vertical and horizontal gene transfers Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT)[1][2][3] is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the (vertical) transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction).&#...

Ukrainian general and politician Stepan PoltorakСтепан Полторак14th Minister of Defence of UkraineIn office14 October 2014 – 29 August 2019PresidentPetro PoroshenkoVolodymyr ZelenskyPreceded byValeriy HeleteySucceeded byAndriy Zahorodniuk Personal detailsBornStepan Tymofiyovych Poltorak (1965-02-11) 11 February 1965 (age 59)Vesela Dolyna, Odesa Oblast, Ukrainian SSR, Soviet UnionMilitary serviceAllegiance Soviet Union (1983–1991) Ukraine (1992–2018)Branch...

30th season of Europe's secondary club football tournament organised by UEFA 2000–01 UEFA CupWestfalenstadion, in Dortmund, hosted the final.Dates8 August 2000 – 16 May 2001Final positionsChampions Liverpool (3rd title)Runners-up AlavésTournament statisticsMatches played205Goals scored566 (2.76 per match)Top scorer(s)Goran Drulić (Red Star Belgrade)Javi Moreno (Alavés)Marcin Kuźba (Lausanne)Demis Nikolaidis (AEK Athens)6 goals each← 1999–2000 2001–02 → Intern...
