LWD Junak
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Bendera negara-negara yang menggunakan warna-warna Pan-Afrika. Pan-Afrikanisme adalah suatu gerakan yang bertujuan menyatukan Afrika.[1] Selain merupakan suatu gerakan, Pan Afrikanisme juga merupakan suatu pandangan sosiopolitik dunia dan filosofi moral yang bertujuan untuk penduduk Afrika asli dan yang berasal dari diaspora Afrika untuk menjadi bagian dalam Komunitas Afrika Global.[2] Pada awalnya, Kongres Pan-Afrikanisme pertama yang diadakan di London pada tahun 1900 mengha...

Head of the Catholic Church from 974 to 983 PopeBenedict VIIBishop of RomeChurchCatholic ChurchPapacy beganOctober 974Papacy ended10 July 983[1]PredecessorBenedict VISuccessorJohn XIVPersonal detailsBornRome, Papal StatesDied(983-07-10)10 July 983Rome, Papal StatesPrevious post(s)Cardinal-Priest of San Teodoro (972–974)Other popes named Benedict Benedict VII was buried at Santa Croce in Gerusalemme (16th/17th century illustration) Pope Benedict VII (Latin: Benedictus VII; ...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

2018 Indian filmUtharavu MaharajaDirected byAsif KuraishiWritten byAsif KuraishiProduced byUdhayaStarringUdhaya Priyanka Thimmesh PrabhuCinematographyBalajee RanghaEdited byR. SathyanarayananMusic byNaren BalakumarProductioncompanyJaeshan StudiosRelease date 16 November 2018 (2018-11-16) CountryIndiaLanguageTamil Utharavu Maharaja is a 2018 Tamil language film directed by Asif Kuraishi. The film stars Udhaya, who also produced the film, Priyanka Thimmesh, and Prabhu in the lea...

Former administrative unit in Bangladesh Ancient ruins of Bikrampur Bikrampur (City of Courage) was a pargana situated 19 kilometres (12 mi) south of Dhaka, the modern capital city of Bangladesh. In the present day, it is known as the Munshiganj District of Bangladesh. It is a historic region in Bengal and was a part of the Bhawal Estate.[citation needed] History Part of a series on the History of Bangladesh Etymology Timeline Traditional Urheimat Ancient Neolithic, c. 7600 – c...

American journalist Serge SchmemannBorn (1945-04-12) April 12, 1945 (age 79)FranceNationalityAmericanOccupation(s)Writer and editorial page editorParentAlexander Schmemann Serge Schmemann (born April 12, 1945) is a French-born American writer and member of the editorial board of The New York Times who specializes in international affairs.[1] He was editorial page editor of the Paris-based International Herald Tribune, the erstwhile global edition of The New York Times, from 2003 ...

Voce principale: Milano. La Cattedrale di Santa Maria Nascente, più nota come Duomo di Milano, uno dei simboli della città Per chiese di Milano si intendono gli edifici di culto cristiani della città di Milano. Indice 1 Generalità 2 Elenco chiese 2.1 IV secolo 2.2 V secolo 2.3 VII secolo 2.4 IX secolo 2.5 X secolo 2.6 XI secolo 2.7 XII secolo 2.8 XIII secolo 2.9 XIV secolo 2.10 XV secolo 2.11 XVI secolo 2.12 XVII secolo 2.13 XVIII secolo 2.14 XIX secolo 2.15 XX secolo 3 Chiese scomparse ...

English footballer and manager For the Leicester City and Brentford player, see Dean Smith (footballer, born 1958). Dean Smith Smith in 2011Personal informationFull name Dean Smith[1]Date of birth (1971-03-19) 19 March 1971 (age 53)Place of birth West Bromwich, EnglandHeight 6 ft 0 in (1.83 m)[2]Position(s) Centre-backTeam informationCurrent team Charlotte FC (head coach)Youth career1986–1989 Newcastle UnitedSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)1989–1994 ...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) الجزر العذراء البريطانية في الألعاب الأولمبية تقوم اللجنة الأولمبية للجزر العذراء البريطانية بالإشراف ...

Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України Тип військове формуванняЗасновано 1992Країна Україна Емблема управління Військово-музичне управління Збройних сил України — структурний підрозділ Генерального штабу Збройних сил України призначений для планува...

Частина серії проФілософіяLeft to right: Plato, Kant, Nietzsche, Buddha, Confucius, AverroesПлатонКантНіцшеБуддаКонфуційАверроес Філософи Епістемологи Естетики Етики Логіки Метафізики Соціально-політичні філософи Традиції Аналітична Арістотелівська Африканська Близькосхідна іранська Буддій�...

Village in Al Wakrah Municipality, QatarAl Kharrara الخرارةVillageLimestone escarpments near Al KharraraAl KharraraCoordinates: 24°54′2″N 51°10′17″E / 24.90056°N 51.17139°E / 24.90056; 51.17139Country QatarMunicipalityAl Wakrah MunicipalityZoneZone 95District no.683Area[1] • Total12.4 km2 (4.8 sq mi)Elevation[2]45 m (148 ft) Al Kharrara (Arabic: الخرارة, romanized: Al-Kharārah; also sp...

Taiwanese computer and electronics company Not to be confused with APUS Group, ASOS (retailer), Asos, or Esus. ASUSTeK Computer Inc.Headquarters in TaipeiNative name華碩電腦股份有限公司Romanized nameHuáshuò Diànnǎo Gǔfèn Yǒuxiàn GōngsīCompany typePublicTraded asTWSE: 2357IndustryComputer hardwareElectronicsNetworking hardwareFoundedApril 2, 1989; 35 years ago (1989-04-02)FoundersTed HsuM. T. LiaoWayne TsiahT. H. TungLuca D. M.HeadquartersBeitou District, ...

Дніпровський ботанічний сад Вхід до Дніпровського ботанічного саду.Вхід до Дніпровського ботанічного саду. 48°26′09″ пн. ш. 35°02′31″ сх. д. / 48.436000000027775059° пн. ш. 35.04200000002777671° сх. д. / 48.436000000027775059; 35.04200000002777671Координати: 48°26′09″ пн. ш. 35°02′31�...
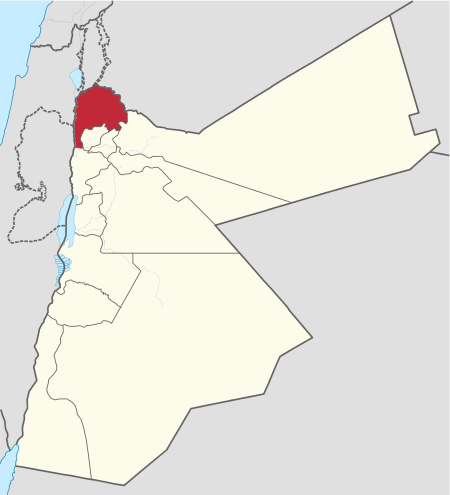
يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) محافظة إربد. تتناول هذه القائمة المواقع الأثرية المسجَّلة رسمياً لدى دائرة الآثار العامة التابعة لوزارة...

此條目可能包含原创研究。请协助補充参考资料、添加相关内联标签和删除原创研究内容以改善这篇条目。详细情况请参见讨论页。 提示:此条目页的主题不是麻雀行动。 黃雀行動六四事件、香港主權移交的一部分日期1989年6月4日-1997年6月30日地点香港结果 行動成功,獲救的民運人士經香港送往西方國家参战方 英国 秘密情報局 英屬香港 支聯會 三合會 �...

For the former MSNBC series that originally aired under this title, see 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue (TV series). American TV series or program Race for the White HouseGenreDocumentaryCountry of originUnited StatesNo. of seasons2No. of episodes12ProductionExecutive producersKevin SpaceyDana BrunettiRunning time60 minutesOriginal releaseNetworkCNNReleaseMarch 6, 2016 (2016-03-06) –present Race for the White House is an American political television show that discusses various US presid...

Part of a series onTropical cyclones Structure Central dense overcast Development Eye Effects By Region Warnings and watches Storm surge Preparedness Response Climatology and tracking Basins Climate change effects RSMCs Scales Observation Forecasting Rainfall forecasting Rainfall climatology Tropical cyclone naming History List of historical names Lists of retired names: Atlantic, Pacific hurricane, Pacific typhoon, Philippine, Australian, South Pacific OutlineMedia coverage Tropical cyclone...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Eurimages – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Logo Eurimages is a cultural support fund of the Council of Europe, established in 1989 (35 years ago) (1989). Eurimages promotes indepe...


