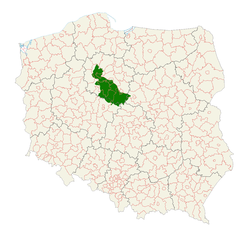
Kuyavia
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Mateusz BiskupInformasi pribadiLahir8 Februari 1994 (umur 30) OlahragaNegara PolandiaOlahragaDayung Mateusz Biskup (lahir 8 Februari 1994) adalah seorang atlet dayung Polandia. Dia berkompetisi di cabang men's quadruple sculls pada Olimpiade Musim...

Church in Northamptonshire, EnglandHoly Cross ChurchHoly Cross Church, Daventry52°15′30″N 1°09′33″W / 52.258264°N 1.159160°W / 52.258264; -1.159160LocationChurch Walk, Daventry, Northamptonshire, NN11 4BLCountryEnglandDenominationChurch of EnglandWebsitewww.holycrosschurchdaventry.org.uk/welcome.htmHistoryStatusActiveArchitectureFunctional statusParish churchHeritage designationGrade I listedYears built1752-1758AdministrationProvinceCanterburyDiocesePeterb...
Frankrike i olympiska spelen IOK-landskodFRA KommittéComité National Olympique et Sportif FrançaisOlympiska sommarspelen 2004 i AtenDeltagare308 deltagare i 27 grenar • Damer113 • Herrar195FanbärareJackson Richardson Medaljsummering Guld11 Silver9 Brons13 Totalt33 Placering7:e Frankrike i olympiska sommarspelen1896 • 1900 • 1904 • 1908 • 1912 • 1920 • 1924 • 1928 • 1932 • 193...

Adegan alegori dari Augustan Ara Pacis, 13 SM, sebuah titik tinggi dari gaya Yunani-Romawi. Kajian seni pahat Romawi ditimbulkan oleh hubungannya dengan seni pahat Yunani. Beberapa contoh dari seni pahat Yunani terkenal, seperti Apollo Belvedere dan Barberini Faun, hanya dikenal dari salinan-salinan Kekaisaran Romawi atau Helenistik. Referensi Elsner, Jas, Style in Critical Terms for Art History, Nelson, Robert S. and Shiff, Richard, 2nd Edn. 2010, University of Chicago Press, ISBN 0226571696...

The LambSeena Owen dan Douglas Fairbanks dalam The LambSutradaraW. Christy CabanneSkenarioChristy CabanneCeritaGranville WarwickBerdasarkanThe New Henriettaoleh Bronson Howard, Victor Mapes dan Winchell SmithPemeranDouglas FairbanksSeena OwenSinematograferWilliam E. FildewDistributorTriangle DistributingTanggal rilis 23 September 1915 (1915-09-23) (New York City) 07 November 1915 (1915-11-07) (Seluruh negeri) Durasi56 menitNegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaBisuIntertitel Inggris Th...

Спорадическая группа — одна из 26 исключительных групп в теореме о классификации простых конечных групп. Простая группа — это группа G, не содержащая каких-либо нормальных подгрупп, отличных от самой группы G и тривиальной (единичной) подгруппы. Теорема классификаци...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...

Lembaga Pendidikan Perkebunan (LPP) yang merupakan asosiasi milik BUMN Perkebunan, merupakan sebuah lembaga pendidikan yang diperuntukkan bagi karyawan industri perkebunan. Lembaga ini telah beridiri sejak tahun 1950. Sebelumnya, nama lembaga ini adalah College Gula Negara (CGN). Sejarah Sejarah LPP diawali oleh berdirinya College Gula Negara (CGN) pada tahun 1950, untuk memenuhi kebutuhan tenaga ahli bidang industri gula pasca rasionalisasi perusahan-perusahaan eks Belanda yang kemudian diub...

Vincent Auriol Presiden Republik Prancis ke-16Ko-Pangeran AndorraMasa jabatan16 Januari 1947 – 16 Januari 1954PendahuluAlbert Lebrun(bukan presiden pada 1940-1947; Lebrun adalah Presiden terakhir setelah)Léon Blum(Presiden Pemerintahan Sementara)PenggantiRene Coty Informasi pribadiLahir27 Agustus 1884Revel, PrancisMeninggal1 Januari 1966(1966-01-01) (umur 81)Muret, PrancisPartai politikSosialis (SFIO)Suami/istriMichelle AucouturierSunting kotak info • L • B Jule...

1993 Lithuanian presidential election 14 February 1993 1997–98 → Nominee Algirdas Brazauskas Stasys Lozoraitis Jr. Party LDDP Independent Popular vote 1,212,075 772,922 Percentage 61.06% 38.94% President before election Algirdas Brazauskas (acting) LDDP Elected President Algirdas Brazauskas LDDP Presidential elections were held in Lithuania on 14 February 1993.[1] They were the first presidential elections under the new October 1992 constitution and the first...

Questa voce sull'argomento stagioni delle società calcistiche italiane è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Voce principale: San Felice Aversa Normanna. San Felice Aversa NormannaStagione 2013-2014Sport calcio Squadra Aversa Normanna Allenatore Franco Fabiano poi Nello Di Costanzo poi Nicola Provenza Presidente Giovanni Spezzaferri Lega Pro Seconda Divisione11º posto nel girone B. Mag...

Bendera Kostanay Kostanay merupakan sebuah kota di Kazakhstan. Kota ini letaknya di bagian utara. Tepatnya di Provinsi Kostanay. Pada tahun 2010, kota ini memiliki jumlah penduduk sebesar 301.317 jiwa dan memiliki luas wilayah 240 km². Kota ini memiliki angka kepadatan penduduk 1.255 jiwa/km². Pranala luar http://www.kostanay.kz Diarsipkan 2008-11-03 di Wayback Machine. Photos Kostanay Artikel bertopik geografi atau tempat Kazakhstan ini adalah sebuah rintisan. Anda dapat membantu Wiki...

1907 armed uprising against Japanese rule of Taiwan Beipu UprisingDateNovember 1907LocationHoppo, Shinchiku Chō, TaiwanResult Japanese victoryBelligerents HakkaSaisiyat JapanCommanders and leaders Tsai Ching-lin Sakuma SamataCasualties and losses ~100 killed 57 killedvteTaiwanese rebellions against Japanese rule Xincheng Incident 1896 Hitome-no-seki Incident (人止關事件) 1902 Shimaigahara Incident (姊妹原事件) 1903 Wili Incident (威里事件) 1906 Beipu Uprising 1907 Truku W...

Species of flowering plant in the rose family Rosaceae Cloudberry redirects here. For the computer storage solution company, see CloudBerry Lab. Rubus chamaemorus Ripe cloudberry Conservation status Least Concern (IUCN 3.1)[1] Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae Clade: Tracheophytes Clade: Angiosperms Clade: Eudicots Clade: Rosids Order: Rosales Family: Rosaceae Genus: Rubus Subgenus: Rubus subg. Chamaemorus Species: R. chamaemorus Binomial name Rubus chamaemorusL. 1...

Craftsperson who makes objects from silver or gold This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Silversmith – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Embossed silver sarcophagus of Saint Stanislaus in the Wawel Cathedral, created in the main cen...

1990 US law protecting Native American remains and artifacts Native American Grave Protection and Repatriation ActLong titleAn Act to provide for the protection of Native American graves, and for other purposes.Acronyms (colloquial)NAGPRAEnacted bythe 101st United States CongressEffectiveNovember 16, 1990CitationsPublic law101-601Statutes at Large104 Stat. 3048CodificationTitles amended25 U.S.C.: IndiansU.S.C. sections created25 U.S.C. ch. 32 § 3001 et seq.Legislative hist...

Permutasi Kubus Rubik memiliki sebuah struktor terkelmpok; kelompok tersebut adalah sebuah konsep fundamental yang berhubungan dengan aljabar abstrak. Aljabar abstrak adalah bidang subjek matematika yang mempelajari struktur aljabar, seperti grup, gelanggang, medan, modul, ruang vektor, dan aljabar medan. Frasa aljabar abstrak diciptakan pada awal abad ke-20 untuk membedakannya dengan bidang yang biasa disebut sebagai aljabar, yaitu studi aturan manipulasi rumus dan ekspresi aljabar yang meli...

United States historic placeDurham Mill and FurnaceU.S. National Register of Historic Places Durham Mill (Durham Post Office). November 2012.Show map of PennsylvaniaShow map of the United StatesLocationDurham Rd., Durham Township, Pennsylvania.Coordinates40°34′34.9″N 75°13′25.6″W / 40.576361°N 75.223778°W / 40.576361; -75.223778Area3.5 acres (1.4 ha)Built1727, 1820NRHP reference No.76001608[1]Added to NRHPNovember 21, 1976 Durham Mill...

American photographer and musician (1941–1998) For the food brand founded by McCartney, see Linda McCartney Foods. Linda McCartneyMcCartney in 1976BornLinda Louise Eastman(1941-09-24)September 24, 1941Manhattan, New York, U.S.DiedApril 17, 1998(1998-04-17) (aged 56)Tucson, Arizona, U.S.Occupations Photographer musician vegetarian cook book author activist Years active1965–1998Spouses Melville See Jr. (m. 1962; div. 1965) Paul M...

1939 film Robert and BertramDirected byHans H. ZerlettWritten byGustav Raeder (play)Hans H. ZerlettProduced byHelmut SchreiberStarringRudi GoddenKurt SeifertCarla RustFritz KampersCinematographyFriedl Behn-GrundEdited byElla EnsinkMusic byLeo LeuxProductioncompanyTobis FilmDistributed byTobis FilmRelease date 7 July 1939 (1939-07-07) CountryGermanyLanguageGerman Robert and Bertram (German: Robert und Bertram) is a 1939 German musical comedy film directed by Hans H. Zerlett and ...