Isenburg-Limburg
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Questa voce sugli argomenti scienziati statunitensi e medici statunitensi è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. John Franklin Enders Premio Nobel per la medicina 1954 John Franklin Enders (West Hartford, 10 febbraio 1897 – Waterford, 8 settembre 1985) è stato un biologo, batteriologo, virologo e immunologo statunitense, vincitore di premio Nobel per la medicina. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Onorificenze 3 Note 4 Altri progetti 5 Collegamenti ...

Seorang farmakoterapis di dalam laboratorium Universitas Semmelweis Farmakoterapi adalah sub ilmu dari farmakologi yang mempelajari tentang penanganan penyakit melalui penggunaan obat.[1] Dalam ilmu ini obat-obatan digunakan untuk membuat diagnosis, mencegah timbulnya, dan cara menyembuhkan suatu penyakit.[1] Selain itu, farmakoterapi juga mempelajari khasiat obat pada berbagai penyakit, bahaya yang dikandungnya, kontraindikasi obat, pemberian obat yang tepat.[1] Bagia...
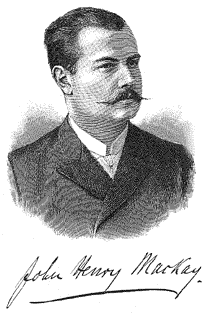
John Henry MackayLahir(1864-02-06)6 Februari 1864Greenock, SkotlandiaMeninggal16 Mei 1933(1933-05-16) (umur 69)Stahnsdorf, JermanNama penaSagittaPekerjaanPenulis, filsufKebangsaanganda Inggris/JermanGenrenon-fiksiTemaFilsafat politikAliran sastraNaturalismeKarya terkenalDie Anarchisten (anarkis) Der Freiheitsucher (Pencari Kebebasan) John Henry Mackay (6 Februari 1864 – 16 Mei 1933) adalah seorang anarkis egois, pemikir dan penulis. Lahir di Skotlandia dan ...

Topik artikel ini mungkin tidak memenuhi kriteria kelayakan umum. Harap penuhi kelayakan artikel dengan: menyertakan sumber-sumber tepercaya yang independen terhadap subjek dan sebaiknya hindari sumber-sumber trivial. Jika tidak dipenuhi, artikel ini harus digabungkan, dialihkan ke cakupan yang lebih luas, atau dihapus oleh Pengurus.Cari sumber: Universitas Buddhi Dharma – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatn...

For related races, see 2022 United States House of Representatives elections. 2022 United States House of Representatives elections in Pennsylvania ← 2020 November 8, 2022 2024 → All 17 Pennsylvania seats to the United States House of Representatives Majority party Minority party Party Democratic Republican Last election 9 9 Seats won 9 8 Seat change 1 Popular vote 2,436,919 2,702,262 Percentage 47.30% 52.45% Swing 2.07% 1.82% Election ...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

ESA human spaceflight programme from 2001 For the rumored American spy plane, see Aurora (aircraft). For other uses, see Aurora (disambiguation). This space art, titled The Next Stop, was selected by the ESA when discussing its Aurora program.[1] The Aurora programme (sometimes called Aurora Exploration Programme, or simply Exploration Programme) was a human spaceflight programme of the European Space Agency (ESA) established in 2001. The objective was to formulate and then to impleme...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Café. Waiting. LoveSutradaraChiang Chin-linProduserAngie Chai Giddens KoSkenarioGiddens KoBerdasarkanCafé. Waiting. Loveoleh Giddens KoPemeranVivian Sung Bruce HungMegan Lai Marcus Chang Pauline Lan Lee Luo Vivian ChowPenata musikChris HouSinematograferYang Fong-mingPenyuntingIan LinPerusahaanproduksiK4s Motion StudioVieVision PicturesAmazing Film StudioStar Ritz ProductionsTanggal rilis 15 Agustus 2014 (2014-08-15) Durasi120 menitNegaraTaiwanBahasaMandarinPendapatankotorNT$37.1 ...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Swiss Alliance of Consumer Organisations – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Swiss Alliance of Consumer Organisations(in German) Allianz der Konsumentenschutz-Organisationen(in French) Allian...

روت أديلي دي فيتري 2022 تفاصيل السباقسلسلة26. روت أديليمسابقاتطواف أوروبا للدراجات 2022 1.1كأس فرنسا لركوب الدراجات على الطريقالتاريخ1 أبريل 2022المسافات176٫7 كمالبلد فرنسانقطة البدايةفيترينقطة النهايةفيتريالفرق19عدد المتسابقين في البداية118عدد المتسابقين في النهاية98متوسط ا...

Retired British ocean liner For other ships with the same name, see Queen Mary (ship). RMS Queen Mary Queen Mary at Long Beach, California, in 2010 History NameQueen Mary NamesakeMary, Queen of the United Kingdom Owner 1936–49: Cunard-White Star Line 1949–67: Cunard Line 1967–present: City of Long Beach Port of registryLiverpool RouteSouthampton, New York, via Cherbourg (normal transatlantic voyage East and West bound) Ordered3 April 1929 Builder John Brown & Company Clydebank, Scot...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) دوري الدرجة الأولى الكويتي الجهة المنظمة الاتحاد الكويتي لكرة القدم تاريخ الإنشاء 1965؛ منذ 59 سنو�...

اتفاقية الأمم المتحدة لمكافحة الفسادمعلومات عامةالنوع معاهدة — وثيقة من الأمم المتحدة[1] الموضوع فساد الإيداع أمين عام الأمم المتحدة موقع الويب unodc.org… (الإنجليزية) تعديل - تعديل مصدري - تعديل ويكي بيانات اتفاقية الأمم المتحدة لمكافحة الفساد هي اتفاقية متعددة الأطراف �...

Rugby in Singapore This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Rugby union in SingaporeNational Stadium, Singapore (capacity 55,000)CountrySingaporeGoverning bodySingapore Rugby UnionNational team(s)SingaporeFirst playedLate 19th centuryRegistered players9,400[1]Clubs13International compe...

Fictional family This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (June 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message)This article is written like a personal reflection, personal essay, or argumen...

Shinto shrine in Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan Itsukushima Shinto ShrineUNESCO World Heritage SiteThe torii of Itsukushima Shrine, the site's most recognizable landmark, appears to float in the water.LocationItsukushima, JapanCriteriaCultural: i, ii, iv, viReference776Inscription1996 (20th Session)Area431.2 haBuffer zone2,634.3 haWebsitewww.en.itsukushimajinja.jpCoordinates34°17′45″N 132°19′11″E / 34.29583°N 132.31972°E / 34.29583; 132.31972Japanese name...

Erik Hamrén Tanggal lahir 27 Juni 1957 (umur 67)Tempat lahir Ljusdal, SwediaKepelatihanTahun Tim 1987–1988 Enköpings SK1989 Väsby IK1990–1991 IF Brommapojkarna1992–1993 Vasalunds IF1994 Degerfors IF1995–1997 AIK1998–2003 Örgryte IS2003–2008 Aalborg BK2008–2010 Rosenborg2009– Swedia Erik Hamrén (lahir 27 Juni 1957) adalah seorang mantan pemain sepak bola berkewarganegaraan Swedia yang saat ini menjadi manajer tim nasional sepak bola Swedia.[1][2] Refe...

Japanese central coordination law enforcement agency Law enforcement agency National Police Agency警察庁Keisatsu-chōThe KyokujitsushouAbbreviationNPAAgency overviewFormedJuly 1, 1954 (1954-07-01)Preceding agencyNational Rural Police Headquarters [ja] (国家地方警察本部, Kokka Chihō Keisatsu Honbu)Employees7,995 (2020)[1]Annual budget¥360.348 billion (2020)[2]Legal personalityLaw enforcement agencyJurisdictional structureNational agencyJ...

Period during the High Middle Ages in Georgia Part of a series on theHistory of Georgia Prehistoric Georgia Shulaveri–Shomu cultureKura–Araxes cultureLegend of KartlosTrialeti cultureColchian cultureDiauehiMushki Ancient history ColchisAryan KartliKingdom of IberiaPharnavazid dynastyGeorgia in the Roman eraArtaxiad dynasty of IberiaCampaign of PompeyIberian–Armenian WarLazicaArsacid dynasty of IberiaSasanian IberiaChosroid dynastyChristianization of Iberia Middle Ages Iberian WarLazic W...
