International economic cooperation policy of Japan
|
Read other articles:

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang munisipalitas di Swiss. Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Castañeda. Castaneda Lambang kebesaranNegaraSwissKantonGraubündenDistrikMoesaLuas[1] • Total3,96 km2 (1,53 sq mi)Ketinggian750 m (2,460 ft)Populasi (Kesalahan: waktu tidak sah.[2]) • Total233 • Kepadatan59/km2 (150/sq mi)Kode pos6540Kode area telepon3805Dikelilingi olehBuseno, Grono, Roveredo, Santa Maria in Calanca, San...

Gastropub in Bray, Berkshire, England The Hind's HeadThe Hind's Head in 2009Location of the Hind's Head, in Bray, BerkshireRestaurant informationOwner(s)Heston BlumenthalHead chefPete GrayFood typeBritishDress codeNoneRating (Michelin Guide) AA RosettesStreet addressHigh StreetCityBrayCountyBerkshirePostal/ZIP CodeSL6 2ABCountryEnglandCoordinates51°30′30″N 0°42′07″W / 51.508225°N 0.702066°W / 51.508225; -0.702066ReservationsYesWebsitewww.hindsheadbray.comTh...

In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Alessio and the second or maternal family name is Robles. Vito Alessio RoblesJosé Vito Alessio RoblesRobles c. 1917Deputy of the Congress of the Union for the 4th district of the Federal DistrictIn office1 September 1920 – 31 August 1922Preceded byPaulino FontesSucceeded byRafael Pérez Taylor Personal detailsBornVito Alessio Robles(1879-08-14)August 14, 1879Saltillo, CoahuilaDiedJune 11, 1957(1957-06-11) (aged 77...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

2003 single by HIMThe SacramentSingle by HIMfrom the album Love Metal Released27 June 2003Recorded2003Length4:32LabelBMGSongwriter(s)Ville ValoProducer(s)HIMHIM singles chronology Buried Alive by Love (2003) The Sacrament (2003) Solitary Man (2004) The Sacrament is a song by the Finnish band HIM, released in 2003. It is the sixth track and third single from the album Love Metal. The music video was directed by Bam Margera. The song was used over the end credits of the 2007 Japanese anime, Hig...

Artikel ini memiliki beberapa masalah. Tolong bantu memperbaikinya atau diskusikan masalah-masalah ini di halaman pembicaraannya. (Pelajari bagaimana dan kapan saat yang tepat untuk menghapus templat pesan ini) Topik artikel ini mungkin tidak memenuhi kriteria kelayakan biografi tokoh. Harap penuhi kelayakan artikel dengan: menyertakan sumber-sumber tepercaya yang independen terhadap subjek dan sebaiknya hindari sumber-sumber trivial. Jika tidak dipenuhi, artikel ini harus digabungkan, diali...

Ця стаття потребує додаткових посилань на джерела для поліпшення її перевірності. Будь ласка, допоможіть удосконалити цю статтю, додавши посилання на надійні (авторитетні) джерела. Зверніться на сторінку обговорення за поясненнями та допоможіть виправити недоліки. Мат...

2016年美國總統選舉 ← 2012 2016年11月8日 2020 → 538個選舉人團席位獲勝需270票民意調查投票率55.7%[1][2] ▲ 0.8 % 获提名人 唐納·川普 希拉莉·克林頓 政党 共和黨 民主党 家鄉州 紐約州 紐約州 竞选搭档 迈克·彭斯 蒂姆·凱恩 选举人票 304[3][4][註 1] 227[5] 胜出州/省 30 + 緬-2 20 + DC 民選得票 62,984,828[6] 65,853,514[6]...

Mandarin popular music MandopopStylistic originsChinese musicTaiwanese Musichip hopR&BpoprockjazzfolkCultural origins1920s–1940s, Shanghai, Republic of ChinaOther topicsCantopopTaiwanese popJ-popK-popV-popChinese rock MandopopTraditional Chinese華語流行音樂Simplified Chinese华语流行音乐TranscriptionsStandard MandarinHanyu PinyinHuáyǔ liúxíng yīnyuèYue: CantoneseJyutpingWaa4jyu5 lau4hang4 jam1ngok6 Mandopop or Mandapop refers to Mandarin popular music. The genre ha...

Robur-le-Conquérant Frontispice du roman. Auteur Jules Verne Pays France Genre Roman d'anticipation Éditeur Pierre-Jules Hetzel Date de parution 1886 Illustrateur Léon Benett Nombre de pages 318 Chronologie Série Voyages extraordinaires Frritt-Flacc Nord contre Sud modifier Robur-le-Conquérant est un roman d'anticipation de Jules Verne, paru en 1886. Historique Le roman paraît d'abord en feuilleton dans le Journal des débats politiques et littéraires, du 29 juin au 18 août 188...
Marklkofen. Marklkofen adalah kota yang terletak di distrik Dingolfing di Bayern, Jerman. Kota Marklkofen memiliki luas sebesar 40.72 km² . Marklkofen pada tahun 2006, memiliki penduduk sebanyak 3.674 jiwa. lbsKota dan kotamadya di Dingolfing-LandauDingolfing | Eichendorf | Frontenhausen | Gottfrieding | Landau an der Isar | Loiching | Mamming | Marklkofen | Mengkofen | Moosthenning | Niederviehbach | Pilsting | Reisbach |...
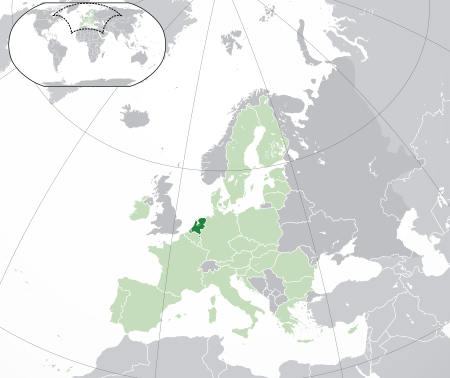
Country in northwestern Europe For other uses, see Netherlands (disambiguation). Constituent country in Kingdom of the NetherlandsNetherlandsNederland (Dutch)Constituent country FlagCoat of armsMotto: Je maintiendrai (French)(I will maintain)Anthem: Wilhelmus (Dutch)(William of Nassau)Netherlands on the globeMetropolitan Netherlands in EuropeMunicipalities in the CaribbeanLocation of Netherlands (dark green)– in Europe (light green & dark gre...

提示:此条目页的主题不是萧。 簫琴簫與洞簫木管樂器樂器別名豎吹、豎篴、通洞分類管樂器相關樂器 尺八 东汉时期的陶制箫奏者人像,出土於彭山江口汉崖墓,藏於南京博物院 箫又稱洞簫、簫管,是中國古老的吹管樂器,特徵為單管、豎吹、開管、邊稜音發聲[1]。「簫」字在唐代以前本指排簫,唐宋以來,由於單管豎吹的簫日漸流行,便稱編管簫爲排簫�...

SchoolTaranaki Diocesan School for Girlsold seal for St Mary's Diocesan SchoolAddressBroadway Stratford 4332 New ZealandCoordinates39°19′56″S 174°16′47″E / 39.3322°S 174.2798°E / -39.3322; 174.2798InformationTypeIntegrated single sex secondary (Year 9-13)MottoFiat Voluntas Tua - Thy Will Be DoneEstablished1914Ministry of Education Institution no.180PrincipalMatt ColemanSchool roll137 (February 2024)[1]Websitewww.taranakidio.school.nz Taran...

1935 film Million Dollar HaulDirected byAlbert HermanWritten byRobert WalkerVictor PotelProduced byBert SternbachLouis WeissStarringReed HowesJanet ChandlerWilliam FarnumCinematographyHarry ForbesEdited byRalph HoltProductioncompanyWeiss ProductionsDistributed byStage & Screen ProductionsRelease date April 3, 1935 (1935-04-03) Running time63 minutesCountryUnited StatesLanguageEnglish Million Dollar Haul is a 1935 American mystery film directed by Albert Herman and starring ...

Álvaro Colom Presiden GuatemalaMasa jabatan14 Januari 2008 – 14 Januari 2012Wakil PresidenRafael EspadaPendahuluÓscar BergerPenggantiOtto Pérez Molina Informasi pribadiLahir(1951-06-15)15 Juni 1951Kota Guatemala, GuatemalaMeninggal23 Januari 2023(2023-01-23) (umur 71)Kota Guatemala, GuatemalaPartai politikPersatuan Nasional untuk PengharapanSuami/istriSandra Torres (2003–2011)Alma materUniversitas San Carlos GuatemalaSunting kotak info • L • B Álvaro Colom ...

Si ce bandeau n'est plus pertinent, retirez-le. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus. Cet article ne cite pas suffisamment ses sources (avril 2013). Si vous disposez d'ouvrages ou d'articles de référence ou si vous connaissez des sites web de qualité traitant du thème abordé ici, merci de compléter l'article en donnant les références utiles à sa vérifiabilité et en les liant à la section « Notes et références ». En pratique : Quelles sources sont attendues ? Com...

Federal electoral district in British Columbia, Canada Saanich—Gulf Islands British Columbia electoral districtSaanich—Gulf Islands in relation to other electoral districts in the Vancouver Island areaFederal electoral districtLegislatureHouse of CommonsMP Elizabeth MayGreenDistrict created1987First contested1988Last contested2021District webpageprofile, mapDemographicsPopulation (2011)[1]104,285Electors (2021)93,538Area (km²)[1]518Pop. density (per km²...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages) This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (April 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards. You can help. The talk page ...

Країни колишньої радянської окупації ККРО, адміністративних одиниць, які підпорядковувалися безпосередньо уряду СРСР. На початку свого існування, в 1922 р., ККРО складався з 4 союзних республік: РРФСР, УРСР, БРСР, ЗРФСР. У 1940—1956 роках до складу ККРО входила 16-та республік�...
