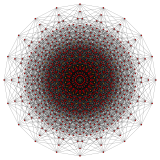
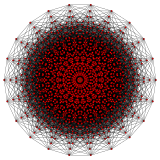
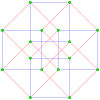
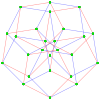
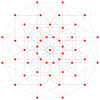
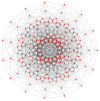
Hypercube
|
Read other articles:

Untuk ajang balap mobil yang merupakan seri utama dari badan ini, lihat Seri IndyCar. INDYCAR, LLCOlahragaBalap mobil roda terbukaYurisdiksiAmerika UtaraSingkatanINDYCARBerdiri1994[1]AfiliasiACCUS-FIATanggal afiliasi1996Kantor pusatIndianapolis, INStaf kunciRoger Penske (Ketua)Mark D. Miles (Pejabat tertinggi Eksklusif)Jay Frye (Presiden)Situs web resmiwww.indycar.com INDYCAR, LLC (Dulunya adalah Indy Racing League) merupakan organisasi penyelenggara balap mobil terbesar di Amerika Se...

Siaosi Tupou IIRaja TongaBerkuasa18 Februari 1893 – 5 April 1918Penobatan17 Juli 1893, NukuʻalofaPendahuluSiaosi Tupou IPenerusSālote Tupou IIIInformasi pribadiKelahiran(1874-06-18)18 Juni 1874Neiafu, TongaKematian5 April 1918(1918-04-05) (umur 43)TongaPemakamanMalaʻekulaWangsaTupouAyahTuʻi Pelehake (Fatafehi Toutaitokotaha)IbuʻElisiva Fusipala TaukiʻonetukuPasanganLavinia VeiongoʻAnaseini TakipōAnakSālote Mafile‘o PilolevuʻElisiva Fusipala TaukiʻoneluaʻElisiva Fusipala T...

قرية ويندسور الإحداثيات 42°04′30″N 75°38′21″W / 42.075°N 75.6392°W / 42.075; -75.6392 [1] تاريخ التأسيس 1830 تقسيم إداري البلد الولايات المتحدة[2] التقسيم الأعلى مقاطعة بروم خصائص جغرافية المساحة 3.021802 كيلومتر مربع3.021808 كيلومتر مربع (1 أبريل 2010) ارتفاع 290...

Chronologies Le marché aux blanchisseuses à Paris. L'Illustration, 1874.Données clés 1871 1872 1873 1874 1875 1876 1877Décennies :1840 1850 1860 1870 1880 1890 1900Siècles :XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXe XXIeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies géographiques Afrique Afrique du Sud, Algérie, Angola, Bénin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroun, Cap-Vert, République centrafricaine, Comores, République du Congo, Répub...

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento criminalità non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Questa voce sull'argomento criminalità è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Un viceboss, detto anche sott...

Kultur Jaringan Tanaman Kultur jaringan adalah suatu metode untuk mengisolasi bagian dari tanaman seperti sekelompok sel atau jaringan yang ditumbuhkan dalam kondisi aseptik, sehingga bagian tanaman tersebut bisa dapat memperbanyak diri hingga tumbuh menjadi tanaman-tanaman yang baru kembali dengan sifat yang sama.[1] Prinsip Teknik kultur jaringan memanfaatkan prinsip perbanyakan tumbuhan secara vegetatif.[1] Berbeda dari teknik perbanyakan tumbuhan secara konvensional, tekni...

Синелобый амазон Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:ЗавропсидыКласс:Пт�...

The Price of Salt Berkas:PriceOfSalt.JPGEdisi pertamaPengarang Patricia Highsmith Claire Morgan (nom de plume) NegaraAmerika SerikatBahasaInggrisGenreNovelDiterbitkan1952PenerbitCoward-McCann, W. W. Norton & Company (2004)Jenis mediaCetak (sampul keras & sampul kertas)Halaman276 hlm (ed. sampul keras)292 hlm (ed. sampul kertas, 2004)ISBNISBN 978-0-393-32599-7 (ed. 2004)OCLC1738553LCCPZ3.H53985 Pr(LCCN 52008026) The Price of Salt (kemudian diterbitkan ulang dengan judul Carol) ada...

Voce principale: Spezia Calcio. Spezia CalcioStagione 2002-2003Sport calcio Squadra Spezia Allenatore Antonio Sassarini poi Stefano Cuoghi a seguire Walter Nicoletti Presidente Angelo Zanoli Serie C16º posto nel girone A. Maggiori presenzeCampionato: Cangini, Caverzan, Coti (29) Miglior marcatoreCampionato: Pisano (11) StadioStadio Alberto Picco 2001-2002 2003-2004 Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Questa pagina raccoglie le informazioni riguardanti lo Spezia Calcio nelle competiz...

Nabi Amos, sosok yang menjadi lawan Amazia Amazia (Kitab Amos) adalah nama salah seorang imam dari Betel.[1] Ia merupakan lawan bicara Amos.[1] Amazia hidup pada masa pemerintahan Yerobeam II.[1] Ia merupakan imam yang bekerja untuk pemerintah.[2] Amazia dan Amos Pertemuan Amazia dengan Amos terjadi karena nubuat-nubuat yang Amos beritakan.[3] Amos memberitakan tentang datang penghukuman atas bangsa Israel.[2] Nubuat-nubuat yang diberitakan oleh...

Shenzhen Open 2015 Sport Tennis Data 3 gennaio - 10 gennaio Edizione 3ª Superficie Cemento Montepremi 500 000 $ Campioni Singolare Simona Halep Doppio Ljudmyla Kičenok / Nadežda Kičenok 2014 2016 Lo Shenzhen Open 2015 è un torneo di tennis giocato all'aperto sul cemento. È la 3ª edizione dello Shenzhen Open, che fa parte della categoria International nell'ambito del WTA Tour 2015. Si gioca allo Shenzhen Longgang Tennis Centre di Shenzhen in Cina, dal 3 al 10 gennaio 2015. In...

The Hakaniemi market square is a popular place to go for a coffee. The Hakaniemi market square in 2008. The Hakaniemi market square in 1913. Russian fruit merchants at the Hakaniemi market square in 1907.[1] The Hakaniemi market square (Finnish: Hakaniementori, Swedish: Hagnäs torg) is a market square located in Hakaniemi, Helsinki, Finland, opened in 1897. Throughout its history, there have been numerous Vappu marches and demonstrations starting from the square, and it is an integra...

この記事は検証可能な参考文献や出典が全く示されていないか、不十分です。出典を追加して記事の信頼性向上にご協力ください。(このテンプレートの使い方)出典検索?: コルク – ニュース · 書籍 · スカラー · CiNii · J-STAGE · NDL · dlib.jp · ジャパンサーチ · TWL(2017年4月) コルクを打ち抜いて作った瓶の栓 コルク(木栓、�...

Association football club in England Football clubWantage Town FCFull nameWantage Town Football ClubNickname(s)The FredsFounded1892GroundAlfredian Park, Wantage 51°34′55.7″N 1°25′48.8″W / 51.582139°N 1.430222°W / 51.582139; -1.430222Capacity1,500ManagerDaniel BarryLeagueHellenic League Premier Division2022–23Hellenic League Premier Division, 10th of 20WebsiteClub website Home colours Away colours Wantage Town Football Club is a football club based in Want...

Nutritional drinks brand For other uses, see Boost (disambiguation). BoostTypeNutritional drinkManufacturerNestléWebsitewww.boost.com Boost is a nutritional drinks brand made by Swiss company Nestlé. The brand also produces Boost Glucose Control for people with type 2 diabetes.[1] History In 2010, the Federal Trade Commission reached a settlement with Nestlé regarding its claims about Boost Kid Essentials, stating that the product would prevent certain illnesses. As part of the set...

هذه المقالة عن المجموعة العرقية الأتراك وليس عن من يحملون جنسية الجمهورية التركية أتراكTürkler (بالتركية) التعداد الكليالتعداد 70~83 مليون نسمةمناطق الوجود المميزةالبلد القائمة ... تركياألمانياسورياالعراقبلغارياالولايات المتحدةفرنساالمملكة المتحدةهولنداالنمساأسترالي�...

Sebagian dari artikel ini (yang berkaitan dengan November 2018) memerlukan pemutakhiran informasi. Harap perbarui artikel dengan menambahkan informasi terbaru yang tersedia. Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang sistem operasi ponsel pintar. Untuk robot yang mirip manusia, lihat Android (robot). AndroidLogo digunakan sejak 2023ScreenshotPerusahaan / pengembangBeragam (kebanyakan Google dan Open Handset Alliance)Diprogram dalamJava (UI), C (Inti), C++ dan lainnyaKeluargaUnix-like (DiubahLinu...

River in Utah, United StatesSan Pitch RiverSanPitchThe San Pitch is to the east of the Great Basin section but within the Great Basin (west of the Great Basin Divide).Native nameSahpeech (Ute)LocationCountryUnited StatesStateUtahPhysical characteristicsLength65 mi (105 km)[1]Basin size480 sq mi (1,200 km2)[2]Basin featuresRiver systemEscalante-Sevier subregion The San Pitch River, extending 65 miles (105 km), is the primary wa...

US Navy unit with aircraft carrier This article is about the formation specific to the United States Navy. For the Royal Navy's formation, see UK Carrier Strike Group. For general doctrine of a fleet centered around an aircraft carrier, see Carrier battle group. Naval units and formations Division Squadron Flotilla Carrier battle group Task force Naval fleet U.S. Navy ships assigned to the USS George Washington Carrier Strike Group sail in formation in the Atlantic Ocean in November 2003. A c...
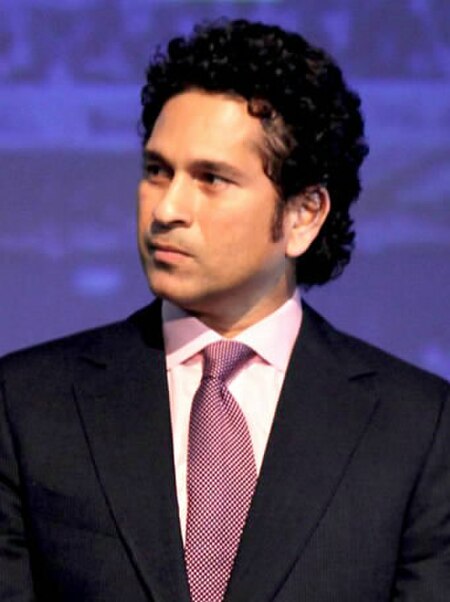

Sachin Tendulkar has scored more centuries in Test cricket than any other player. This article is part of a series aboutSachin Tendulkar Indian International Cricketer International Centuries Career Achievements Honours and Achievements Eponymous stand at Wankhede Stadium Sir Garfield Sobers Trophy 2010 Test Team of the Year 2010 2011 ODI Team of the Year 2004 2007 2008 2010 Wisden Leading Cricketer 1998 2010 Wisden Cricketer of the Year 1997 In Media Ferrari Ki Sawaari Sachin! Tendulkar All...
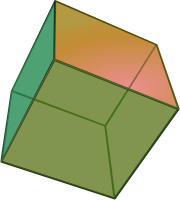



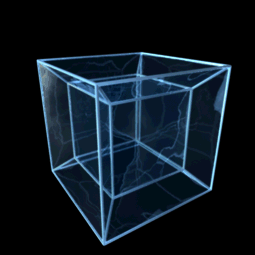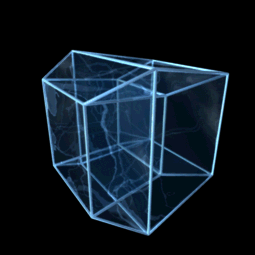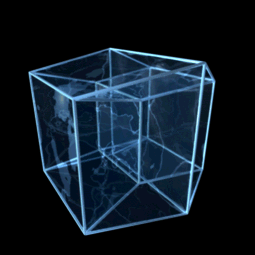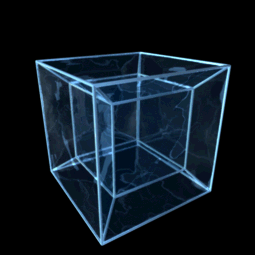




![{\displaystyle [0,1]^{n}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/40160923273b7109968df994dca832b91d957bf2)
![{\displaystyle [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/738f7d23bb2d9642bab520020873cccbef49768d)




![{\displaystyle [-1/2,1/2]^{n}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/98cea6b9a196dae533439e1146656e8c29dd732d)

![{\displaystyle [-1,1]^{n}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6a008254b1bf6d63ac3b13548c4c31180bcd43de)