Fumarase
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Cinema ofFrance 1892–1909 1910s 1910 1911 1912 1913 19141915 1916 1917 1918 1919 1920s 1920 1921 1922 1923 19241925 1926 1927 1928 1929 1930s 1930 1931 1932 1933 19341935 1936 1937 1938 1939 1940s 1940 1941 1942 1943 19441945 1946 1947 1948 1949 1950s 1950 1951 1952 1953 19541955 1956 1957 1958 1959 1960s 1960 1961 1962 1963 19641965 1966 1967 1968 1969 1970s 1970 1971 1972 1973 19741975 1976 1977 1978 1979 1980s 1980 1981 1982 1983 19841985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990s 1990 1991 1992 1993 19...

Town in Maryland, United StatesNorth East, MarylandTown FlagSealLocation of North East, MarylandCoordinates: 39°36′1″N 75°56′32″W / 39.60028°N 75.94222°W / 39.60028; -75.94222Country United StatesState MarylandCounty CecilSettled1658Incorporated1850[1]Government • MayorMichael KlineArea[2] • Total2.08 sq mi (5.38 km2) • Land2.04 sq mi (5.29 km2) • Water0...

† Человек прямоходящий Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:ЖивотныеПодцарство:ЭуметазоиБез ранга:Двусторонне-симметричныеБез ранга:ВторичноротыеТип:ХордовыеПодтип:ПозвоночныеИнфратип:ЧелюстноротыеНадкласс:ЧетвероногиеКлада:АмниотыКлада:Синапсиды�...

Theory regarding color vision in humans For the universal psychological and neurological model, see opponent-process theory. This article is missing information about details of color perception. Please expand the article to include this information. Further details may exist on the talk page. (June 2022) The opponent process is a color theory that states that the human visual system interprets information about color by processing signals from photoreceptor cells in an antagonistic manner. T...

For the Harlem River span of the Robert F. Kennedy Bridge, see Robert F. Kennedy Bridge § Harlem River lift bridge (NY 900G). Not to be confused with the Park Avenue Viaduct, carrying Park Avenue around Grand Central Terminal. Bridge between Manhattan and the Bronx, New York Harlem River Lift BridgeFrom downriverCoordinates40°48′40″N 73°56′00″W / 40.81114°N 73.93333°W / 40.81114; -73.93333Carries4 tracks of the Metro-North RailroadCrossesHarlem RiverL...

迪奥斯达多·马卡帕加尔Diosdado Pangan Macapagal第9任菲律賓總統任期1961年12月30日—1965年12月30日前任卡洛斯·P·加西亚继任费迪南德·马科斯第6任菲律賓副總統任期1957年12月30日—1961年12月30日前任卡洛斯·P·加西亚继任伊曼纽尔·佩莱斯 个人资料出生(1910-09-28)1910年9月28日 美屬菲律賓馬尼拉逝世1997年4月21日(1997歲—04—21)(86歲) 菲律賓馬卡迪墓地 菲律賓馬卡迪達義市英...

هنري ديربورنHenry Dearborn (بالإنجليزية: Henry Dearborn) هنري ديربورن، خامس وزير حرب للولايات المتحدة الأمريكية معلومات شخصية اسم الولادة هنري ديربورن الميلاد 23 فبراير 1751(1751-02-23)[1]نورث هامبتون، نيو هامبشير، الولايات المتحدة الوفاة 6 يونيو 1829 (78 سنة) [1]روكسبري، ماساتشوستس ،...

Museo Británico British Museum Entrada al Museo BritánicoUbicaciónPaís Reino Unido Reino UnidoDivisión Inglaterra InglaterraSubdivisión Gran LondresLocalidad LondresDirección Great Russell Street WC1B 3DGCoordenadas 51°31′10″N 0°07′37″O / 51.519444444444, -0.12694444444444Tipo y coleccionesTipo PúblicoClase Museo de arteColecciones Antigüedades y obras: orientales, egipcias, griegas, etruscas, romanas, chinas y europeasN.º de obras Más ...

Irish TV series or program Doing MoneyGenreCrime dramaBased onSlaveby Jason JohnsonWritten byGwyneth HughesDirected byLynsey MillerStarring Anca Dumitra Allen Leech Karen Hassan Alec Secăreanu Mãlina Manovici Cosmina Stratan Dragoș Bucur Sergiu Costache Alina Şerban Voica Oltean Turlough Convery Country of originIrelandOriginal languageEnglishNo. of episodes1ProductionExecutive producers Alex Cooke Lucy Richer ProducerMike DormerCinematographyNeus OlléEditorKristina HetheringtonRunning ...

الميزانية مقابل الدخل لأفلام جيمس بوند موازنة الفيلم تشير إلى العملية التي يقوم من خلالها منتج الخط (مدير وحدة الإنتاج)، أو محاسب الإنتاج بإعداد ميزانية لإنتاج الأفلام. هذه الوثيقة، التي يمكن أن تتضمن أكثر من 134 صفحة، تستخدم لتأمين التمويل والإنتاج المسبق للفيلم وإنتاجه. ق...

1958 play by Tennessee Williams This article is about the play. For other uses, see Suddenly Last Summer (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Suddenly Last Summer – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2008) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Suddenly La...

Prionailurus viverrinus Pour les articles homonymes, voir Chat (animal). Prionailurus viverrinus Un Chat viverrinClassification Règne Animalia Sous-embr. Vertebrata Super-classe Tetrapoda Classe Mammalia Cohorte Placentalia Ordre Carnivora Sous-ordre Feliformia Famille Felidae Sous-famille Felinae Genre Prionailurus EspècePrionailurus viverrinus(Bennett, 1833) Statut de conservation UICN VU A2cd+3cd+4cd : Vulnérable Statut CITES Annexe II , Rév. du 04/02/1977 Le Chat viverrin (Priona...

لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع تشارلز أندرسون (توضيح). تشارلز أندرسون معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1 يونيو 1814 [1] لويفيل الوفاة 2 سبتمبر 1895 (81 سنة) [1] بادوكا[2] مواطنة الولايات المتحدة إخوة وأخوات روبرت أندرسون[2]، وويليام مارشال أندرسون مناصب عضو �...

Serbian handball club RK Železničar 1949Full nameRukometni klub Železničar 1949Founded2009ArenaSC ČairCapacity4,000PresidentLjubomir PavlovićHead coachĐorđe TeodorovićLeagueSerbian Handball Super League2020/214Club colours Home Away Website Official site RK Železničar 1949 (Serbian Cyrillic: РК Железничар 1949) is a Serbian handball club based in Niš. They compete in the Serbian Handball Super League. History The club was formed as RK Naissu...

New Zealand politician Ron BarclayQSO MBE JPMember of the New Zealand Parliamentfor New PlymouthIn office26 November 1966 – 29 November 1975Preceded byErnest AdermanSucceeded byTony Friedlander Personal detailsBornRonald Morrison Barclay(1914-09-02)2 September 1914Little River, New ZealandDied29 April 2003(2003-04-29) (aged 88)New Plymouth, New ZealandPolitical partyLabourSpouse Joy Margaret Lusty (m. 1940)RelationsJim Barclay (uncle)Bruc...

Type of top-grain leather A nubuck shoe Nubuck (pronounced /ˈnjuːbʌk/) is top-grain leather that has been sanded or buffed on the grain side, or outside, to give a slight nap of short protein fibers, producing a velvet-like surface. It is resistant to wear, and may be white or coloured.[1] Nubuck is similar to suede, but is created from the outer side of a hide, giving it more strength and thickness and a fine grain. It is generally more expensive than suede, and must be coloured o...
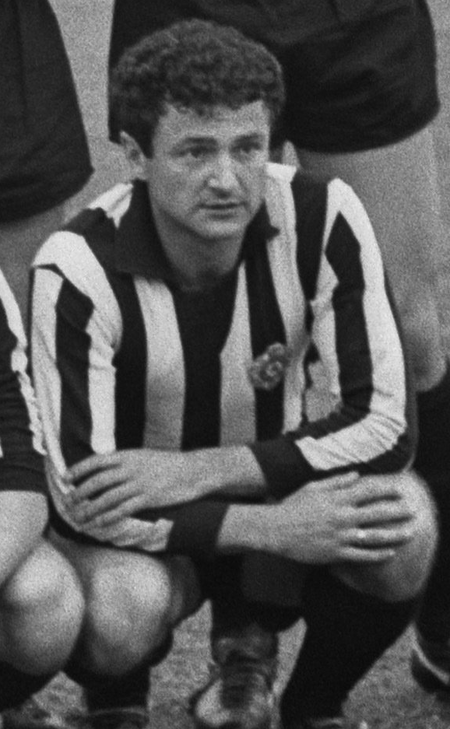

ميلان غاليتش معلومات شخصية الميلاد 8 مارس 1938(1938-03-08)زرنيانين الوفاة 13 سبتمبر 2014 (76 سنة)بلغراد الطول 1.73 م (5 قدم 8 بوصة) مركز اللعب مهاجم الجنسية يوغوسلافيا صربيا مسيرة الشباب سنوات فريق 1952–1958 برولتر زرنيانين [الإنجليزية] المسيرة الاحترافية1 سنوات فري�...

In this Japanese name, the surname is Hoshina. Hoshina Masayuki保科 正之Hoshina Masayuki by Kanō Tan'yū, portrait at Hanitsu Jinja, Inawashiro, Fukushima2nd Daimyō of Takatō DomainIn office1631–1636MonarchsShōgun Tokugawa Hidetada Tokugawa Iemitsu Preceded byHoshina MasamitsuSucceeded byTorii Tadaharu1st Daimyō of Yamagata DomainIn office1636–1643MonarchShōgun Tokugawa Iemitsu Preceded byTorii TadatsuneSucceeded byMatsudaira Naomoto1st Daimyō of Aizu DomainIn office1643–1669...

American musician, actor, boxer (1929–2000) Screamin' Jay HawkinsHawkins in concert, 1995Background informationBirth nameJalacy J. HawkinsAlso known asJay HawkinsBorn(1929-07-18)July 18, 1929Cleveland, Ohio, U.S.DiedFebruary 12, 2000(2000-02-12) (aged 70)Neuilly-sur-Seine, FranceGenresBlues[1]rhythm and blues[2]soul[3]rock and roll[4]shock rock[5]OccupationsSingersongwritermusicianactorfilm producerboxerInstrumentsVocalspianoguitar[6]Year...

Chinese general (1902–1973) In this Chinese name, the family name is Li. Li Mi李彌Lieutenant General Li Mi in 1948Born(1902-11-04)4 November 1902Tengchong County, Yunnan Province, ChinaDied10 March 1973(1973-03-10) (aged 70)Taipei, TaiwanAllegiance Republic of ChinaYears of service1927–1954Rank Lieutenant GeneralUnit National Revolutionary ArmyCommands8th Corps, 13th ArmyBattles/wars Northern Expedition Encirclement Campaigns Second Sino-Japanese War Battle of Kunlun Pass...