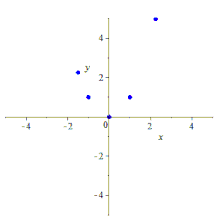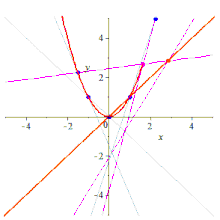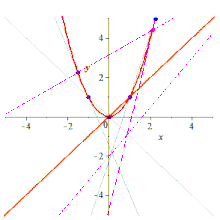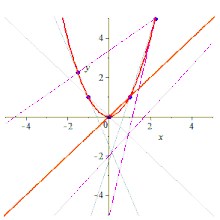
Five points determine a conic
|
Read other articles:

Belgio Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Sport Calcio Federazione URBSFA/KBVB[N 1]francese: Union Royale Belge des Sociétés de Football Associationolandese: Koninklijke Belgische Voetbalbond Confederazione UEFA Codice FIFA BEL Soprannome De Rode DuivelsLes Diables RougesDie Roten Teufel(i Diavoli rossi) Selezionatore Domenico Tedesco Record presenze Jan Vertonghen (153) Capocannoniere Romelu Lukaku (83) Ranking FIFA 4º (30 novembre 2023)[1] Sponsor tecnico Adidas Esordio int...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (September 2011) This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2011) (Lear...

Culinary traditions of Ivory Coast Location of Ivory Coast Ivorian cuisine is the traditional cuisine of Côte d'Ivoire, or the Ivory Coast, and is based on tubers, grains, pig, chicken, seafood, fish, fresh fruits, vegetables and spices. It is very similar to that of neighboring countries in West Africa. Common staple foods include grains and tubers. Côte d'Ivoire is one of the largest cocoa producers in the world and also produces palm oil and coffee. Common foods and dishes Raw cassava Ca...

PenarolCalcio Leão da Velha Serpa, Leão Azul Segni distintivi Uniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori sociali Blu, bianco Dati societari Città Itacoatiara Nazione Brasile Confederazione CONMEBOL Federazione CBF Campionato Campionato Amazonense Fondazione 1947 Presidente Ila Rabelo Allenatore Edmilson de Jesus Stadio Floro de Mendonça(2 710 posti) Sito web www.penarol.com.br Palmarès Si invita a seguire il modello di voce Il Penarol Atlético Clube, noto anche semplicemente com...

Railway station in Cumbria, England For the station in Ohio, United States, see Green Road station. Green RoadGeneral informationLocationMillom Without, CopelandEnglandCoordinates54°14′40″N 3°14′43″W / 54.2444234°N 3.2453885°W / 54.2444234; -3.2453885Grid referenceSD189839Owned byNetwork RailManaged byNorthern TrainsPlatforms2Tracks2Other informationStation codeGNRClassificationDfT category F2HistoryOriginal companyWhitehaven and Furness Junction RailwayPre...

Resort in France owned by The Walt Disney Company Disneyland ParisPreviously known as Euro Disney Resort and Disneyland Resort ParisSleeping Beauty Castle in Disneyland ParkLocationMarne-la-Vallée, FranceCoordinates48°52′07″N 02°46′55″E / 48.86861°N 2.78194°E / 48.86861; 2.78194StatusOperatingOpened12 April 1992; 32 years ago (1992-04-12)OwnerDisney Experiences(The Walt Disney Company)Attendance375 million (overall as of 2022)Websitedisne...

Voltairine de CleyreVoltairine de Cleyre di Philadelphia, 1901 (usia 35)Lahir(1866-11-17)17 November 1866Leslie, MichiganMeninggal20 Juni 1912(1912-06-20) (umur 45)Rumah sakit St. Mary of Nazareth Hospital di Chicago, IllinoisPekerjaanpenulis, pengajar, tutor Voltairine de Cleyre (17 November 1866 – 20 Juni 1912)[1] adalah seorang anarkis berkebangsaan Amerika Serikat. Dikenal sebagai seorang penulis dan pembicara serta menjadi penentang Kapitalisme,pernikahan ne...

Polish cyclist Daniel StaniszewskiStaniszewski in 2017Personal informationFull nameDaniel StaniszewskiBorn (1997-05-05) 5 May 1997 (age 26)Ciechanów, PolandHeight1.87 m (6 ft 2 in)Weight77 kg (170 lb)Team informationCurrent teamMazowsze Serce PolskiDisciplinesTrackRoadRoleRiderAmateur team2017–2020KS Pogoń Mostostal Puławy Professional teams2016Verva ActiveJet2020–Mazowsze Serce Polski[1] Medal record Representing Poland Men's track...

Peta wilayah Bremen-Verden (warna pink muda). Bremen-Verden, secara resmi dikenal dengan nama Kadipaten Bremen dan Verden (pelafalan dalam bahasa Jerman: [ˈfɛːɐ̯dən]; Jerman: Herzogtümer Bremen und Verdencode: de is deprecated ), adalah dua wilayah fief Kekaisaran Romawi Suci yang memperoleh status reichsfreiheit pada tahun 1180. Pada awalnya keduanya bernama Keuskupan Agung Bremen dan Keuskupan Verden. Pada tahun 1648, kedua keuskupan ini disekularisasi, atau dalam kata lain d...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir You. Cet article est une ébauche concernant une chanson, la Géorgie et le Concours Eurovision de la chanson. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. You Chanson de Tornike Kipiani auConcours Eurovision de la chanson 2021 Sortie 2021 Durée 3:04 Langue Anglais Genre Chanson géorgienne Classement 2e demi-finale : À venir Chansons représentant la Géorgie au ...

Narasumber sedang menyampaikan materi pada sebuah seminar. Sebuah keterlibatan perempuan instruktur membahas di Bengali Wikipedia dalam sebuah seminar di Dhaka pada 2015 Seminar adalah pertemuan berkala yang diadakan oleh seseorang yang sedang melaksanakan tugasnya.[1] Seminar berasal dari kata Latin semin yang berarti benih atau dari kata seminarium, yang artinya tanah tempat menanam benih. Jadi, seminar memiliki arti tempat benih-benih kebijaksanaan. Kebijaksanaan yang dimaksud tent...

1932 Estonian parliamentary election ← 1929 23 May 1932 1938 → ← outgoing memberselected members →100 seats in the Riigikogu51 seats needed for a majority First party Second party Third party Leader Konstantin Päts Jaan Tõnisson August Rei Party AVK RKE ESTP Last election 38 seats 26 seats 25 seats Seats won 42 23 22 Seat change 4 3 3 Popular vote 199,035 110,662 104,662 Percentage 39.8% 22.1% 20.9% State Elder b...

Jalan Tol Palimanan-KanciPalikanciInformasi ruteBagian dari Jalan Tol Trans-JawaDikelola oleh PT Jasa MargaPanjang:26 km (16 mi)Berdiri:24 Januari 1998; 26 tahun lalu (1998-01-24) – sekarangSejarah:Dibangun sejak 1996Persimpangan besarUjung Barat: Jalan Tol Cikopo-Palimanan Ramp PalimananSimpang Susun PlumbonSimpang Susun CipernaSimpang Susun KanciUjung Timur: Jalan Tol Kanci-PejaganLetakKota besar:Kota CirebonKabupaten CirebonSistem jalan bebas hambatanAH 2 Sistem ...

Douglas Dolphin adalah perahu terbang amfibi sayap tinggi (high wing). Sementara hanya 58 yang dibangun, mereka melayani berbagai peran: pesawat yacht pribadi, transportasi militer, dan pencarian dan penyelamatan.[1] Dolphin berasal pada tahun 1930 sebagai Sinbad, perahu terbang murni tanpa roda. Sinbad ini dimaksudkan sebagai yacht terbang mewah. Tak gentar dengan kurangnya permintaan, Douglas meningkatkan Sinbad pada tahun 1931 sehingga amfibi itu dan bisa mendarat di air atau dara...

Japanese professional wrestler (born 1990) Naoki Tanisaki redirects here. Not to be confused with T. Hawk or Naoki Tanizaki. T-HawkOnodera in February 2022Birth nameTakuya OnoderaBorn (1990-04-30) April 30, 1990 (age 34)[1]Tomakomai, Hokkaido[1]Professional wrestling careerRing name(s)Mr. Pii Pii Tomakomai Penguin[1]Naoki Tanisaki[2]Takuya Tomakomai[2]T-HawkTomahawkTomahawk T.T.[2]Billed height1.74 m (5 ft 8+1⁄2 in)[...

Share of renewable energy in gross final energy consumption in selected European countries (2021) n/a 10–20% 20–30% 30–40% 40–50% >50% This article needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (February 2024) Renewable energy progress in the European Union (EU) is driven by the European Commission's 2023 revision of the Renewable Energy Directive...

Este artículo se refiere o está relacionado con un evento deportivo de motor reciente o actualmente en curso. La información de este artículo puede cambiar frecuentemente. Por favor, no agregues datos especulativos y recuerda colocar referencias a fuentes fiables para dar más detalles. Temporada 2024 de Fórmula 1 Campeonato Mundial de Fórmula 1 de la FIA Datos generalesFecha 2024Edición 75Organizador Federación Internacional del AutomóvilDatos estadísticosParticipantes 20 pilotos,...

تصفيات بطولة أمم أوروبا 2016 المجموعة بمعلومات عامةالرياضة كرة القدم الاتحاد الاتحاد الأوروبي لكرة القدم الفئة كرة القدم للرجال جزء من تصفيات بطولة أمم أوروبا 2016 الفترة 2016 البداية 2014 — 9 سبتمبر 2014 النهاية 2015 — 13 أكتوبر 2015 الفرق المشاركة القائمة ... منتخب بلجيكا لكرة القدم...

Peta infrastruktur dan tata guna lahan di Komune Bazoilles-sur-Meuse. = Kawasan perkotaan = Lahan subur = Padang rumput = Lahan pertanaman campuran = Hutan = Vegetasi perdu = Lahan basah = Anak sungaiBazoilles-sur-Meuse merupakan sebuah komune di departemen Vosges yang terletak pada sebelah timur laut Prancis. Lihat pula Komune di departemen Vosges Referensi INSEE lbsKomune di departemen Vosges Les Ableuvenettes Ahéville Aingeville Ainvelle All...

香港政治系列條目 政府 憲制文件 《英皇制誥》 《皇室訓令》 《中英聯合聲明》(有争议) 《中華人民共和國憲法》 《香港特別行政區基本法》 行政長官:李家超 行政會議(成員) 維護國家安全委員會 行政長官辦公室 特首政策組 政府部門 政府總部 政治任命官員 主要官員 決策局(演變) 公務員 常任秘書長 部門首長 政務主任 立法會(現屆) 地區直選 功能界別 區議...






![{\displaystyle [x^{2}:xy:y^{2}:xz:yz:z^{2}],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bb1902a3df10871523d42ac2a21cf4924de43786)
![{\displaystyle [A:B:C:D:E:F]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/58676be46552da77703fbfeb8fc14fda11841eb7)

![{\displaystyle [1:0:0]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bb57ffba69005b439cb1dc8ba40df9c147bae5d2)
![{\displaystyle [0:1:0]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ddb225ddb544b9183ae37507e364ab290e5c14b8)