Caspian Pipeline Consortium
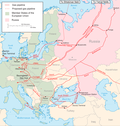
The Caspian Pipeline Consortium (CPC) is a consortium and an oil pipeline that transports Caspian oil from the Tengiz oil field in Kazakhstan to the Novorossiysk-2 Marine Terminal, an export terminal at the Russian Black Sea port of Novorossiysk.[1] It is one of the world's largest pipelines[1] and a major export route for oil from the Kashagan and Karachaganak fields. The CPC pipeline transfers about 1% of global oil supply[1] and handles almost all of Kazakhstan's oil exports.[2] In 2021, the pipeline exported up to 1.3 million barrels per day (bpd)[2] of Kazakhstan's main crude grade, light sour CPC Blend, which represented 80% of Kazakhstan's total oil production of 1.6 million bpd. The pipeline's largest shareholders include Chevron and Exxon.[1] As of 2009[update], the CPC pipeline was the only oil export pipeline in Russian territory not wholly owned by Transneft.[3] HistoryCPC was initially created in 1992 as a development by the Russian, Kazakhstani and Omani governments to build a dedicated pipeline from Kazakhstan to export routes in the Black Sea. Chevron Corporation was asked to join, however talks broke down due to the high financial burden Chevron would have to take on relative to equity in the pipeline. Progress on the project stalled for several years until 1996 when a restructure included eight production companies in the project. Among the companies were Chevron, Mobil, LUKoil, Royal Dutch Shell and Rosneft. BP joined the consortium in 2003. Shares were divided fifty-fifty between the three states and the eight companies. Production companies financed the construction cost of US$2.67 billion, while the Russian Federation contributed unused pipeline assets worth US$293 million.[3][4] In April 2007, the Russian government transferred its shares to the Russian state-owned oil pipeline company Transneft.[5] In October 2008, the Government of Oman sold its 7%-stake to Transneft at a price of $700 million and withdrew from the project.[6] On 17 December 2008, a memorandum on expanding the pipeline was signed.[7] On October 14, 2016, crude oil from Kashagan oil field in Kazakhstan first started flowing into the Caspian Pipeline Consortium's system.[8] On April 18, 2018, the last pump station of CPC Expansion Project, PS-2 in Kalmykia, was put into permanent operation.[9] On May 21, 2019, the annual meeting of CPC shareholders adopted the Bottleneck Elimination Program (BEP), which provides for expansion of the Tengiz - Novorossiysk oil pipeline capacity to at least 72.5 million tons per year.[10] Technical featuresThe diameter of the 1,510 kilometres (940 mi) long oil pipeline varies between 1,016 millimetres (40.0 in) and 1,067 millimetres (42.0 in). There are five pumping stations. The marine terminal includes two single point moorings and the tank farm consists of four steel storage tanks of 100,000 cubic metres (3,500,000 cu ft) each. Pipeline throughflow started at 350,000 barrels per day (56,000 m3/d) and has since increased to 700,000 barrels per day (110,000 m3/d).[4][11] The second stage reached a capacity of 1.4 million barrels per day (220,000 m3/d).[12] As of 2022, the pipeline throughput was about 1.2 million barrels per day (190,000 m3/d), about 1.2% of global oil demand.[13] OperationsIn 2008, CPC transported 31.5 million tons of crude, down from 32.6 million tonnes in 2007. In the first three months of 2009, the pipeline transported 8.7 million tonnes of oil.[14] From 2001 to April 31, 2020, through the Tengiz-Novorossiysk pipeline system 662,784,671 tons of net oil were delivered to world markets. Of this amount, 582 814 809 tons is oil from Kazakhstan and 85 295 642 tons is oil produced in Russia. The total number of tankers processed during this period was 287.[15] In March 2022, two of the three pipeline connected ship berths at the Port of Novorossiysk suffered storm damage. Repairs may take two months, with exports falling by up to 1 million barrels per day.[13] On 6 July 2022, a Russian court ordered the suspension of the pipeline for 30 days over oil spills. The CPC appealed the ruling and the suspension was lifted on 11 July of the following week, and the CPC was instead fined 200,000 rubles (US$3,300).[1] Despite the July 6 ruling, the operator of Kazakhstan's Tengiz oil field, Tengizchevroil, said that the transfer of oil through the CPC had not been interrupted since immediate suspension of the pipeline was technically impossible and would have resulted in "irreversible consequences".[1] The CPC pipeline handles almost all of Kazakhstan's oil exports, which makes the country oil supply routes heavily dependent on Russia. In addition, about 15% of the rest of Kazakhstan's oil exports are also transferred through Russia[2] (while about 5% is sent to China or to various other destinations over rail and the Caspian Sea[2]). After the 6 July suspension of the pipeline, Kazakhstan's President Kassym-Jomart Tokayev ordered the government of his country's to diversify its oil supply routes. In November 2024 the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists and 26 media partners published the report "Caspian Cabals" to put public interests on environmental damage, but also to allegations of financial corruption and geopolitical threats.[16] As part of a new sanctions package against Russia imposed on 10 January 2025, the U.S. Department of the Treasury granted exemptions for oilfield services related to the CPC.[17] On 17 February 2025, on the eve of talks between the U.S. and Russian officials on ending the war in Ukraine, a drone attack by Ukrainian Air Force on a pumping station damaged energy equipment, a gas turbine unit, and a substation. Flows through the CPC were reduced by 30-40%.[18] The station is expected to be restored within one-and-a-half to two months.[19] ConsortiumThe Caspian Pipeline Consortium was initially registered in the Bermuda Islands in 1992.[3] It is split into two companies: CPC-R operates the Russian section of the pipeline and CPC-K operates the Kazakh section.[3] The shareholders of the consortium are:
See also
References
External links |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||