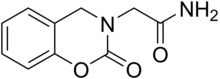
Caroxazone
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Untuk kegunaan lain, lihat Mobil (disambiguasi). Artikel ini bukan mengenai Mobil (perusahaan). Beberapa jenis mobil yang dipasarkan di Indonesia. Dari kiri ke kanan: Nissan X-Trail (crossover), Toyota Avanza (MPV mini), Toyota Yaris (hatchback), Honda City (sedan kecil), Honda Civic (sedan kompak), dan Toyota Rush (SUV mini). Mobil (bahasa Belanda: Mobiel) adalah kendaraan yang menggunakan bahan bakar untuk menghidupkan mesinnya. Mobil kependekan dari otomobil yang berasal dari Bahasa Yunani...

Kementerian Kesehatan Republik IndonesiaLogo Kementerian KesehatanBendera Kementerian KesehatanGambaran umumDibentuk19 Agustus 1945; 78 tahun lalu (1945-08-19)Dasar hukum pendirianPeraturan Presiden Nomor 18 Tahun 2021Bidang tugasKesehatanAlokasi APBNRp130,4 Triliun Susunan organisasiMenteriBudi Gunadi SadikinWakil MenteriDante Saksono HarbuwonoSekretaris JenderalKunta Wibawa Dasa Nugraha, SE, MA, Ph.D.Inspektur Jenderaldrg. Murti Utami, MPH. Direktur JenderalKesehatan Masyarakatdr. Mari...

Election for Missouri Treasurer 2020 Missouri State Treasurer election ← 2016 November 3, 2020 2024 → Turnout70.83%[1] Nominee Scott Fitzpatrick Vicki Englund Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 1,742,943 1,122,547 Percentage 59.1% 38.1% County results Precinct resultsFitzpatrick: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% ...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant la Wallonie. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Pour les articles homonymes, voir IPW. Agence wallonne du Patrimoine Situation Région Région wallonne Type Organisme d'intérêt public régional Domaine Monuments historiques Siège rue Moulin de Meuse, 4 5000 Namur Coordonnées 50° 27′ 55″ N, 4° 54′ 29″ E Site web...

American ethnologist For his father, the judge and politician, see Garrick Mallery (judge). This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Garrick Mallery – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2013) Garrick Mallery. Garrick Mallery (April 25, 1831 in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania R...

Public square in a Roman municipium This article is about the type of ancient civic center. For other uses, see Forum (disambiguation). This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Forum Roman – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) A for...

Brazilian footballer (born 1997) Gabriel Jesus Gabriel Jesus with Brazil in 2018Personal informationFull name Gabriel Fernando de Jesus[1]Date of birth (1997-04-03) 3 April 1997 (age 27)[2]Place of birth São Paulo, BrazilHeight 1.75 m (5 ft 9 in)[3]Position(s) ForwardTeam informationCurrent team ArsenalNumber 9Youth career2010–2012 Anhanguera2013–2015 PalmeirasSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2015–2017 Palmeiras 67 (21)2017–2022 Mancheste...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant le protestantisme. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. La confession de foi de Westminster est une confession de foi réformée, suivant la tradition théologique calviniste. Bien qu'établie par l'assemblée de Westminster en 1646, largement adoptée par l'Église d'Angleterre, elle devint et resta la base de doctrine de l'Église d'Écosse, et a eu une influe...

Дело «Запасного правотроцкистского центра контрреволюционной националистической организации» (ЗПЦКНО) (азерб. “Sağ-trotskiçi ehtiyat mərkəzinin əksinqilabi milliyətçi təşkilatı” rəhbərlərinin işi, 1938-1956) — сфабрикованное высшим руководством Азербайджанской ССР политическое дело, по которому было...

Міністерство оборони України (Міноборони) Емблема Міністерства оборони та Прапор Міністерства оборони Будівля Міністерства оборони у КиєвіЗагальна інформаціяКраїна УкраїнаДата створення 24 серпня 1991Попередні відомства Міністерство оборони СРСР Народний комісарі...

Taksinyang Agung สมเด็จพระเจ้าตากสินมหาราชRaja Borommaracha IVPatung Raja Taksin di Istana Hat-Sung (Wat Khung Taphao, Provinsi Uttaradit, Thailand)Raja ThonburiBerkuasa28 Desember 1767 – Maret 1782Penobatan28 Desember 1767PendahuluEkkathat dari Ayutthaya (sebagai Raja AyutthayaPenerusBuddha Yodfa Chulaloke dari Rattanakosin (Rama I) (sebagai raja Rattanakosin)WaliInthraphithakInformasi pribadiKelahiran(1734-04-17)17 April 1734Ayutthaya, Ker...

American Buddhist writer (1931–2029) John Daido LooriTitleRōshi, abbotPersonalBornJune 14, 1931 (1931-06-14)Jersey City, New Jersey, U.S.DiedOctober 9, 2009 (2009-10-10) (aged 78)Mount Tremper, New York, U.S.ReligionZen BuddhismSchoolRinzai and SōtōLineageMountains and Rivers Order (part of White Plum Asanga)Dharma namesMuge DaidoSenior postingTeacherTaizan MaezumiSuccessorBonnie Myotai Treace, Geoffrey Shugen Arnold, Konrad Ryushin MarchajWebsitezmm.mro.org Zen Mount...

Halaman ini berisi artikel tentang tim sepak bola asal Argentina. Untuk tim sepak bola asal Guatemala, lihat C.S.D. Comunicaciones. ComunicacionesNama lengkapClub ComunicacionesJulukanCarteroBerdiri15 Maret 1931; 93 tahun lalu (1931-03-15)StadionEstadio Alfredo Ramos Agronomía, Buenos Aires(Kapasitas: 3,500)KetuaEzequiel SeguraManajerJorge VivaldoLigaPrimera B Metropolitana2011-128thSitus webSitus web resmi klub Kostum kandang Kostum tandang Club Comunicaciones adalah tim sepak bol...

Country in Central America This article is about the country in Central America. For other uses, see El Salvador (disambiguation). Republic of El SalvadorRepública de El Salvador (Spanish) Flag Coat of arms Motto: Dios, Unión, LibertadGod, Union, LibertyAnthem: Himno Nacional de El SalvadorNational Anthem of El SalvadorCapitaland largest citySan Salvador13°41′56″N 89°11′29″W / 13.69889°N 89.19139°W / 13.69889; -89.19139Official languag...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Martha VickersMartha Vickers, 1947LahirMartha MacVicar(1925-05-28)28 Mei 1925Ann Arbor, Michigan, A.S.Meninggal2 November 1971(1971-11-02) (umur 46)Los Angeles, California, A.S.MakamValhalla Memorial ParkPekerjaanAktrismodelTahun aktif1943�...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (يناير 2022) مصرف كوردستان الدولي الإسلامي للإستثمار والتنميةمصرف كوردستان الدولي الإسلامي للاستثمار والتنميةمعلومات عامةالتأسيس 2005النوع مؤسسة ماليةالمقر الرئيسي أر...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada September 2016. Odil BobonazarovInformasi pribadiNama lengkap Odil Makhsatuloyevich BobonazarovTanggal lahir 14 Oktober 1993 (umur 30)Tinggi 1,75 m (5 ft 9 in)Posisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini FC Rubin-2 KazanKarier junior FC Rubin Ka...

Republik Demokratik VietnamViệt Nam Dân chủ Cộng hòa1945–1976 Bendera Lambang Semboyan: Độc lập – Tự do – Hạnh phúc(Kemerdekaan – perdamaian – kebahagiaan)Lagu kebangsaan: Tiến Quân Ca(Mars Tentara) Lokasi Vietnam Utara di Asia Tenggara.Ibu kotaHanoiBahasa yang umum digunakanVietnamAgama Tidak adaPemerintahanMarxisme–Leninisme negara partai tunggalSekretaris Jenderal • 1945–1956 Trường Chinh• 1956–1960 Hồ Chí Minh•...

Geologi strata di Salta (Argentina). Stratigrafi adalah studi mengenai sejarah, komposisi dan umur relatif serta distribusi perlapisan tanah dan interpretasi lapisan-lapisan batuan untuk menjelaskan sejarah Bumi. Dari hasil perbandingan atau korelasi antarlapisan yang berbeda dapat dikembangkan lebih lanjut studi mengenai litologi (litostratigrafi), kandungan fosil (biostratigrafi), dan umur relatif maupun absolutnya (kronostratigrafi). stratigrafi kita pelajari untuk mengetahui luas penyebar...

See also: 2006 United States state legislative elections 2006 Maryland House of Delegates election ← 2002 November 7, 2006 2010 → All 141 seats in the Maryland House of Delegates71 seats needed for a majority Majority party Minority party Leader Michael E. Busch George C. Edwards (retired) Party Democratic Republican Last election 98 43 Seats won 104 37 Seat change 6 6 Results: Democratic gain &...