Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Sertu Trida Shafira Asmaul Husna Arkeologi Kepala (timpanum) dari nekara Pejang ini dicor terpisah dari badannya. Bukti pertama penggunaan perunggu dan besi di Indonesia berasal dari tahun 500 Sebelum Masehi. Sebagian besar benda perunggu paling awal mungkin digunakan untuk upacara mis. kapak perunggu upacara dan nekara. Nekara-nekara ini datang dari Vietnam Utara dan memiliki bentuk spesifik yang dikenal dengan nama nekara Dong Son. Bersamaan dengan perdagangan di Asia Tenggara, nekara Dong ...

Untuk artikel tentang kecamatan di Kabupaten Magelang dengan nama sama, lihat Mungkid, Magelang. Kota MungkidIbu kota kabupatenLoka Wisata Candi MendhutPeta lokasi Kota MungkidPeta lokasi Kota MungkidNegara IndonesiaProvinsiJawa TengahKabupatenMagelangKecamatanMertoyudanMungkid (Sebagian)Peresmian ibu kota22 Maret 1984Dasar hukumPP No. 21 Tahun 1982Populasi • Total-Zona waktuUTC+7 (WIB) Mungkid atau Kota Mungkid (Jawa: ꦏꦸꦛꦩꦸꦁꦏꦶꦢ꧀, translit. Kut...

Yayasan Perangkat Lunak BebasSingkatanFSFTanggal pendirian4 Oktober 1985; 38 tahun lalu (1985-10-04)[1]PendiriRichard StallmanStatusYayasanTipe501(c)(3) non-profit organizationTujuanPendidikanKantor pusatBoston, Massachusetts, ASWilayah layanan InternasionalJumlah anggota Perorangan dan patron korporatPresidenGeoffrey Knauth[2]AfiliasiSoftware Freedom Law CenterAnggaran $1.199.333 pada FY 2013[3]Jumlah Staf 14[2]Situs webwww.fsf.org Yayasan Perangkat Lunak...

2009 studio album by Shorthand PhoneticsErrors in Calculating Odds, Errors in Calculating ValueStudio album by Shorthand PhoneticsReleasedMay 16, 2009 (Tsefula/Tsefuelha Records), July 2, 2009 (Yes No Wave Music)GenreIndie rock, Lo-fi[1]Length80:00 (Tsefula/Tsefuelha Records Release), 90:12 (Yes No Wave Music 2 CD Release)LabelTsefula/Tsefuelha Records and Yes No Wave MusicProducerAbabil AshariShorthand Phonetics chronology Score No. 1 (Dream:Chase) in A major, Op. 17 for Thre...

Kathleen NooneKathleen Noone di All My Children (1977)LahirKathleen O'Meara8 Januari 1945 (umur 79)Hillsdale, New Jersey, A.S.PekerjaanAktrisTahun aktif1965–sekarangSuami/istriBill Noone (m. 1967; c. 1976)Situs webwww.kathleennoone.com Kathleen Noone (nee Kathleen O'Meara; lahir 8 Januari 1945)[1] adalah seorang aktris Amerika. Dia memulai karirnya sebagai penyanyi di klub malam dan tampil di musikal di panggung Broadway...

This article is about the mountain. For the Regional District, see Regional District of Mount Waddington, British Columbia. Mountain in British Columbia, Canada Mount WaddingtonHighest pointElevation4,019 m (13,186 ft)[1]Prominence3,289 m (10,791 ft)[1]Isolation562 km (349 mi) ListingWorld most prominent peaks 63rdNorth America highest peaks 115thNorth America prominent peaks 12thNorth America isolated peaks 26thCanada highest major peak...

Marchesato di Castel Goffredo Dati amministrativiLingue parlateVolgare, Latino, Italiano CapitaleCastel Goffredo Dipendente da Ducato di Mantova PoliticaForma di governoMarchesato Nascita1444 con Alessandro Gonzaga Fine1593 con Rodolfo Gonzaga CausaUccisione di Rodolfo Gonzaga (1593) Territorio e popolazioneBacino geograficoTerritorio comunale di Castel Goffredo Religione e societàReligioni preminentiCattolica Religioni minoritarieEbraismo Carta dei confini del Ducato di Mantova nel Seicento...
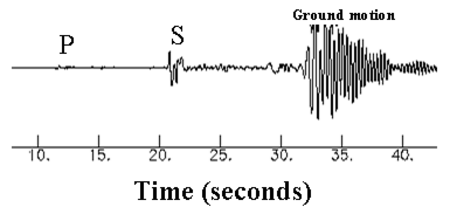
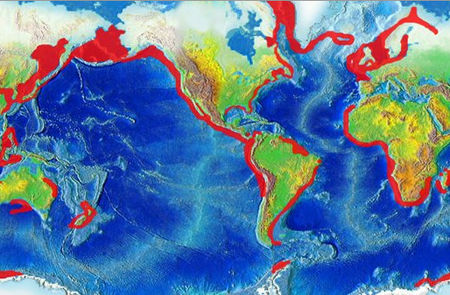
クルアーンのスーラについては「地震 (クルアーン)」をご覧ください。 ポータル 災害 地震(じしん、英: earthquake)は、以下の2つの意味で用いられる[1]。 地震学における定義: 地球表面を構成している岩盤(地殻)の内部で、固く密着している岩石同士が、断層と呼ばれる破壊面を境目にして、急激にずれ動くこと。これによって大きな地面の振動が生じ�...

Sports venue in Ljubljana, Slovenia Bežigrad StadiumBežigrad Stadium in 1935Full nameBežigrad Central StadiumLocationBežigrad, Ljubljana, SloveniaCoordinates46°4′8.84″N 14°30′30.60″E / 46.0691222°N 14.5085000°E / 46.0691222; 14.5085000OwnerCity Municipality of LjubljanaConstructionBuilt1935Closed2008ArchitectJože PlečnikTenantsNK Olimpija Ljubljana (1945–2005)NK Factor (2004–2005) NK Bežigrad (2005–2007) Slovenia national football team (1995–...

1974 United States Senate election in Oklahoma ← 1968 November 3, 1974 1980 → Nominee Henry Bellmon Ed Edmondson Party Republican Democratic Popular vote 390,997 387,162 Percentage 49.38% 48.90% County results Bellmon: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% Edmondson: 40–50% 50–60% ...

Component of the US National Guard of the state of Alabama Alabama National GuardOfficial seal of the Alabama National Guard since 2017Active1807–presentCountry United StatesAllegiance United States AlabamaBranch United States Army United States Air ForceTypeNational GuardRoleReserve component of the U.S. Armed ForcesMilitiaPart ofNational Guard BureauAlabama Military DepartmentHeadquartersJFHQ-AL, Montgomery, AlabamaMotto(s)Always Ready, Always ThereCommanders...

Argentine former professional footballer In this Spanish name, the first or paternal surname is Figueroa and the second or maternal family name is Herrera. Luciano FigueroaPersonal informationFull name Luciano Gabriel Figueroa HerreraDate of birth (1981-05-19) 19 May 1981 (age 42)Place of birth Santa Fe, ArgentinaHeight 1.83 m (6 ft 0 in)[1]Position(s) StrikerSenior career*Years Team Apps (Gls)2001–2003 Rosario Central 57 (35)2003 Birmingham City 1 (0)200...

Artikel ini mengenai Allah dalam istilah Kekristenan di Indonesia dan bukan mengenai Allah, Tuhan dalam Islam. Untuk pemahaman lebih lanjut, lihat artikel Penggunaan Allah bagi umat Kristen Indonesia. Bagian dari sebuah serial tentangSepuluhPerintah Allah Akulah TUHAN Allahmu Jangan ada allah lain Jangan membuat patung apa pun Jangan sembarangan menyebut nama TUHAN Kuduskanlah hari Sabat Hormatilah ayahmu dan ibumu Jangan membunuh Jangan berzinah Jangan mencuri Jangan bersaksi dusta Jangan me...

El orgasmo (del griego ὀργασμός, orgasmós)[1] o clímax sexual es la descarga repentina de la tensión sexual acumulada durante el ciclo de la respuesta sexual, resultando en contracciones musculares rítmicas en la región pélvica caracterizadas por el placer sexual.[2][3][4] Experimentados por hombres y mujeres, los orgasmos son controlados por el sistema nervioso involuntario o autónomo. A menudo se asocian con otras acciones involuntarias, incluyend...

«È volgare tradizione, presso molti, che i nostri nonni non viaggiassero e che venendo da Como a Milano, dovendo attraversare il bosco della Merlata, facessero testamento come il crociato che si recava in Terra Santa.» (A. Bertarelli, A. Monti, Tre secoli di vita milanese nei documenti iconografici 1630-1875, Milano, 1927, p.281 e p.695) MerlataStato Italia Regioni Lombardia Province Milano Lunghezza4 km Portata media0,7 m³/s Altitudine sorgente130 m s.l.m. Nascea Baranzat...

Radio station in Great Falls, MontanaKAAKGreat Falls, MontanaBroadcast areaGreat Falls areaFrequency98.9 MHzBrandingK 99ProgrammingFormatTop 40 (CHR)AffiliationsCompass Media NetworksPremiere NetworksWestwood OneOwnershipOwnerTownsquare Media(Townsquare License, LLC)Sister stationsKLFM, KMON, KMON-FM, KVVRTechnical information[1]Licensing authorityFCCFacility ID63872ClassC1ERP100,000 wattsHAAT147.0 meters (482.3 ft)Transmitter coordinates47°32′23″N 111°17′06″W /...
Nếu gió thổi song song với đường bờ biển ở Nam bán cầu (như dọc theo bờ biển Peru, nơi gió thổi về hướng bắc), thì vận chuyển Ekman có thể tạo ra một chuyển động ròng của nước bề mặt 90° về bên trái. Điều này có thể dẫn tới nước trồi vùng duyên hải.[1] Nước trồi là một hiện tượng hải dương nói về dòng nước lạnh, nhiều dinh dưỡng và đặc quánh di chuyển từ ph...

Frankfurt (Main) Ost Empfangsgebäude des OstbahnhofsEmpfangsgebäude des Ostbahnhofs Daten Bauform Durchgangsbahnhof Bahnsteiggleise 2 Abkürzung FFO IBNR 8002039 Preisklasse 4 Eröffnung 10. März 1913 bahnhof.de Frankfurt (Main)-1038926 Architektonische Daten Architekten Karl Radlbeck Lage Stadt/Gemeinde Frankfurt am Main Ort/Ortsteil Ostend Land Hessen Staat Deutschland Koordinaten 50° 6′ 46″ N, 8° 42′ 29″ O50.1127788.708056Koordinaten: 50° 6...

Cet article est une ébauche concernant un athlète marocain. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Soufiyan BouqantarBiographieNaissance 30 août 1993 (31 ans)KhémissetNationalité marocaineFormation Université Mohammed V - SouissiActivité AthlèteAutres informationsTaille 1,73 m (5′ 8″)Poids 54 kg (119 lb)Sport AthlétismeDiscipline sportive 5 000 mètresmodifier - mod...

Ida di Waldeck e PyrmontPrincipessa consorte di Schaumburg-LippeIn carica23 giugno 1816 –21 novembre 1860 PredecessoreGiuliana d'Assia-Philippsthal come contessa di Schaumburg-Lippe SuccessoreErminia di Waldeck e Pyrmont Nome completo(DE) Ida Caroline Luise NascitaRhoden, 26 settembre 1796 MorteMentone, 12 aprile 1869 Casa realeCasato di Waldeck e PyrmontCasata di Lippe PadreGiorgio I di Waldeck e Pyrmont MadreAugusta di Schwarzburg-Sondershausen Consorte diGiorgio Guglielmo di S...



