Bombard (weapon)
|
Read other articles:

У Вікіпедії є статті про інших людей із прізвищем Альф'єрі. Лучано Альф'єрі Лучано Альф'єрі Особисті дані Повне ім'я Лучано Чезаре Альф'єрі Народження 30 березня 1936(1936-03-30)[1] (87 років) Мілан, Королівство Італія Зріст 176 см Вага 72 кг Громадянство Італія Позиція во�...

Аманітора Давньоєгипетський фараонПравління 50—75 рокиПопередник НатакаманіНаступник Шераркарар Титульні імена Тронне ім'я (преномен): Мер-ка-Ре Власне ім'я (номен): Аманітора У шлюбі НатакаманіДіти АрікакагтаніШеракарарНародився невідомоПомер бл. 75Місце похов

KroketRincianJeniscamilan dan convenience food (en) Bahan utamaSaus Bechamel, telur dan Tepung roti lbs Variasi bentuk kroket Kroket Belanda Kroket adalah nama sebuah makanan yang dipungut dari bangsa Belanda di Indonesia tetapi diambil dari Prancis. Di Belanda, kroket adalah sebuah makanan yang terdiri dari ragout yang dilapisi dengan putih telur dan tepung panir lalu digoreng. Di Indonesia, biasanya kroket adalah gumpalan kentang tumbuk halus berisi daging cincang yang dibumbui dan dicampur...

بوابة مشروع ويكي ويكيبيديا:مشروع ويكي الجزائر/أرشيف1 السلام عليكم مرحبا بك معنا! في الصفحة المخصصة لمشروع ويكي الجزائر مشروع ويكي هذا شكّل لإنشاء مقالات أفضل عن دولة إفريقية أمازيغية عربية مسلمة و هي الجزائر . تحتوي هذه الصفحة و فروعها كل الإقتراحات في كيفية تهيئة وتخطيط ا

Greatest Hits (англ. найкращі хіти), або The Best of (англ. Найкраще [з творчості]), The Very Best of (англ. Найкраще [з творчості]) і The Best (англ. Найкраще) — поширена назва музичних альбомів, що являють собою збірки найкращого матеріалу (за комерційним, художнім або іншим критерієм), створеног...

Town in the state of Maine, United States Town in Maine, United StatesNorth Haven, MaineTownHarborfront and ferry terminal, 2005Location in Knox County and the state of MaineCoordinates: 44°9′15″N 68°52′41″W / 44.15417°N 68.87806°W / 44.15417; -68.87806 44°07′41″N 68°52′27″W / 44.12806°N 68.87417°W / 44.12806; -68.87417CountryUnited StatesStateMaineCountyKnoxIncorporated1846Area[1] • Total82.49 sq...

الحركة الوطنية للحماية والاستعادة (بالفرنسية: Mouvement patriotique pour la sauvegarde et la restauration) الاختصار (بالفرنسية: MPSR) البلد بوركينا فاسو تاريخ التأسيس 24 يناير 2022 الرئيس بول هنري سانوغو داميبا (24 يناير 2022–30 سبتمبر 2022)إبراهيم تراوري (30 سبتمبر 2022–) الإحداثيات 12°22′07″N 1�...

U.S. House district for Illinois Illinois's 5th congressional districtInteractive map of district boundaries since January 3, 2023Representative Mike QuigleyD–ChicagoArea96 sq mi (250 km2)Distribution100.0% urban0.0% ruralPopulation (2022)732,819Median householdincome$104,191[1]Ethnicity71.3% White12.5% Asian11.7% Hispanic3.6% Black1.3% Native American0.1% Pacific Islander AmericansCook PVID+18[2] The 5th congressional district of Illinois covers parts o...

Esta página cita fontes, mas que não cobrem todo o conteúdo. Ajude a inserir referências. Conteúdo não verificável pode ser removido.—Encontre fontes: ABW • CAPES • Google (N • L • A) (Junho de 2010) Jean-Claude Trichet, condecorado com a medalha do Karlspreis em 2011. O Prémio Internacional Carlos Magno (Karlspreis em alemão, Internationaler Karlspreis der Stadt Aachen, e desde 1988 designado como Internationaler Karl...

his is the front cover art for the book The Bible and Its Influence. The Bible and Its Influence is a textbook first published in 2005 to facilitate teaching about the Bible in American public high schools. Its publishers, the Bible Literacy Project, say the textbook allows schools to study the Bible academically while fully respecting the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment. It is designed for teaching either a semester course or a full-year course on the literary and historical infl...

Species of lizard Indian forest skink Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Order: Squamata Family: Scincidae Genus: Sphenomorphus Species: S. indicus Binomial name Sphenomorphus indicus(Gray, 1853) Sphenomorphus indicus (Indian forest skink) is a species of skink. Description Its habit is lacertiform; the distance between the end of the snout and the fore limb contained about 1.6 times in the distance between axilla and groin. Sno...

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Januari 2023. Ada usul agar Voice phishing diganti judulnya dan dipindahkan ke Pengelabuan suara (Diskusikan). Pengelabuan suara, atau vishing,[1] adalah penggunaan telepon (sering kali Voice over IP telephony) untuk melakukan serangan phishing. Layanan ...

Japanese manga series This article is about the manga by Yūgo Ishikawa. For the manga by Narumi Shigematsu, see Babel (2012 manga). BabelFirst volume coverGenreHistorical[1] MangaWritten byYūgo IshikawaPublished byShogakukanImprintBig Superior ComicsMagazineBig Comic SuperiorDemographicSeinenOriginal runDecember 22, 2017 – August 27, 2021Volumes8 Babel (stylized in all caps) is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Yūgo Ishikawa, based on Takizawa Bakin's n...

Para información completa de la ciudad, véase Arequipa. Arequipa es la capital de la provincia y departamento homónimos, así como la segunda ciudad más poblada del Perú. Desde el punto de vista político, es la sede oficial del Tribunal Constitucional[1] y es considerada como la «Capital Jurídica del Perú».[2][3] La ciudad también es conocida como La Ciudad Blanca o el León del Sur. Está ubicada en la región sur del país, la ciudad se extiende a ambas orill...
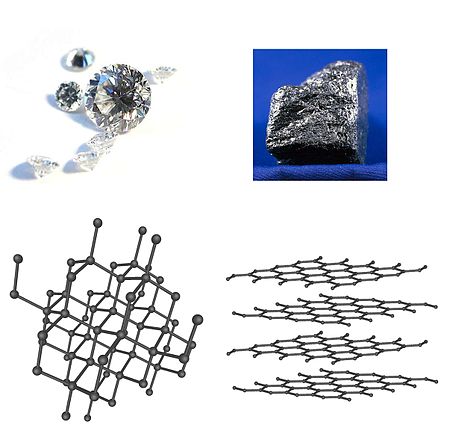
Property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms Not to be confused with Allotrophy. Diamond and graphite are two allotropes of carbon: pure forms of the same element that differ in crystalline structure. Allotropy or allotropism (from Ancient Greek ἄλλος (allos) 'other', and τρόπος (tropos) 'manner, form') is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as al...

This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (March 2017) The Internet Bookshop was a British online bookseller based in Oxford, started in 1994 by Darryl Mattocks. The company was incorporated as a private limited company in October 1992 with founding director Darryl Mattocks.[1] It was originally called VisionAssist Limited and provided information technology consultancy...

The Passaic Bus Terminal, also referred to as Main Avenue Terminal, is a local and regional bus terminal operated by New Jersey Transit (NJT) located on Main Avenue in Passaic, New Jersey in the city's downtown area.[1][2] #758 in Downtown Passaic Facilities and service Unlike its counterpart in Paterson, there are no actual terminal facilities at Passaic Bus Terminal. Instead, there is one turnoff lane on Main Avenue that must be used by all buses entering and departing from ...

Equestrian at the Olympics Team dressageat the Games of the XXIII OlympiadVenueSanta Anita RacetrackDate8–9 AugustCompetitors36 (12 teams) from 12 nationsMedalists Reiner Klimke Uwe Sauer Herbert Krug West Germany Otto Hofer Christine Stückelberger Amy-Cathérine de Bary Switzerland Ulla Håkansson Ingamay Bylund Louise Nathhorst Sweden← 19801988 → Equestrian at the1984 Summer OlympicsDressageindividualteamEventingindividualteamJumpingindiv...

International agreement on the nuclear program of Iran See also: United Nations Security Council Resolution 2231 Not to be confused with Comprehensive Plan of Action. Joint Comprehensive Plan of ActionOfficials announcing the agreementCreated14 July 2015RatifiedN/A (ratification not required)Date effective 18 October 2015 (adoption)[1] 16 January 2016 (implementation)[2] LocationVienna, AustriaSignatories China France Germany Iran Russia U...

German academic publisher LIT VerlagFounded1980Country of originGermanyHeadquarters locationMünsterPublication typesBooksOfficial websitewww.lit-verlag.de LIT Verlag is a German academic[1] publisher founded in 1980.[2] Its managing director is Wilhelm Hopf.[2] Its principal place of publication is Münster; further publishing offices are located in Berlin, Vienna, Hamburg, London, Zurich, and New York City. It publishes approximately 800 books per year. It generally ...












