Battle of Breitenfeld (1642) order of battle
|
Read other articles:

After LaughterAlbum studio karya ParamoreDirilis12 Mei 2017DirekamJuni – November 2016Genre New wave pop rock synth-pop power pop Durasi42:31LabelFueled by RamenProduser Justin Meldal-Johnsen Taylor York Kronologi Paramore The Holiday Sessions(2013) After Laughter(2017) This Is Why(2023) Singel dalam album After Laughter Hard TimesDirilis: 19 April 2017 Told You SoDirilis: 3 Mei 2017 Fake HappyDirilis: 29 Agustus 2017 Rose-Colored BoyDirilis: 2 Maret 2018 Caught in the MiddleDirilis: 26...
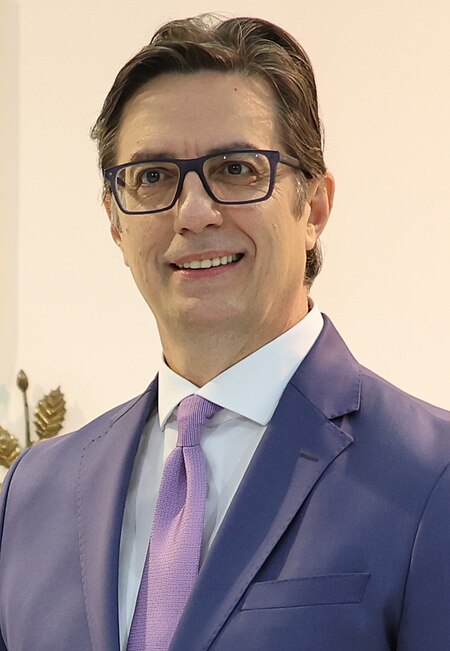

Stevo PendarovskiСтево Пендаровски Presiden Makedonia UtaraPetahanaMulai menjabat 12 Mei 2019Perdana MenteriZoran Zaev PendahuluGjorge IvanovPenggantiPetahana Informasi pribadiLahir3 April 1963 (umur 60)Skopje, Republik Sosialis Makedonia, YugoslaviaKebangsaanMakedoniaPartai politikUni Demokratik SosialAlma materUniversitas Santo Sirilus dan MetodiusSunting kotak info • L • B Stevo Pendarovski (bahasa Makedonia: Стево Пендаровски; lah...

The White Horse Tavern (circa 1673) in Newport is one of the oldest extant buildings in Rhode Island The history of Rhode Island is an overview of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations and the state of Rhode Island from pre-colonial times to the present. Pre-colonization Tribal territories of the indigenous peoples of what is now southeastern New England Native Americans occupied most of the area comprising Rhode Island, including the Wampanoag, Narragansett, and Niantic trib...

Policy on permits required to enter Kyrgyzstan Politics of Kyrgyzstan CIS Member State Constitution Executive President Sadyr Japarov Chairman of the Cabinet of Ministers Akylbek Japarov Legislative Supreme Council President Talant Mamytov Elections Recent elections Presidential: 2011201720212026 Parliamentary: 2010201520202021 Referendums: 201020162021 (Jan)2021 (Apr) Political partiesPoliticians Foreign relations Ministry of Foreign Affairs Minister: Ruslan Kazakbayev Diplomatic missions of...

العلاقات المكسيكية الكورية الجنوبية المكسيك كوريا الجنوبية المكسيك كوريا الجنوبية تعديل مصدري - تعديل العلاقات المكسيكية الكورية الجنوبية هي العلاقات الثنائية التي تجمع بين المكسيك وكوريا الجنوبية.[1][2][3][4][5] مقارنة بين البلدين هذه �...

Berikut adalah daftar masjid yang ada di Aceh, Indonesia Banda Aceh Masjid Raya Baiturrahman Masjid Teungku di Anjong Masjid Baiturrahim Ulee Lheue Masjid Oman Al-Makmur Masjid Syeikh Abdurrauf Banda Aceh Aceh Besar Masjid Tua Indrapuri Masjid Tua Indra Purwa Masjid Jami' Rahmatullah Pidie Masjid Po Teumeureuhom Pidie Jaya Masjid Pucok Krueng Aceh Barat Masjid Agung Baitul Makmur Nagan Raya Masjid Jamik Habib Muda Seunagan Aceh Selatan Masjid Tuo Pulo Kambing Aceh Singkil Masjid Agung Singkil...

Tribal community in Northeast India This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Simte people – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) The Simte[1] are one of the ethnic tribe in Northeast India. They are mainly concentrated in ...
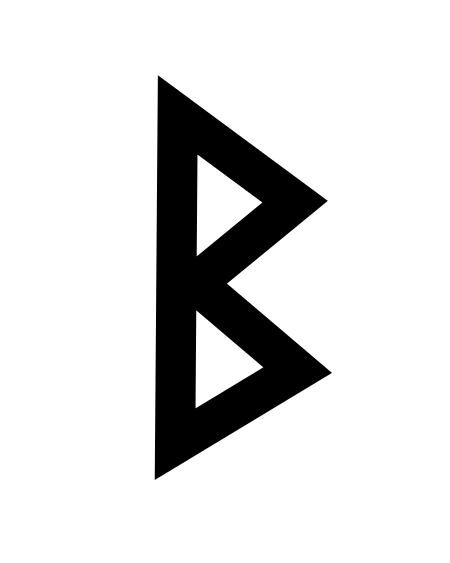
此條目介紹的是拉丁字母中的第2个字母。关于其他用法,请见「B (消歧义)」。 提示:此条目页的主题不是希腊字母Β、西里尔字母В、Б、Ъ、Ь或德语字母ẞ、ß。 BB b(见下)用法書寫系統拉丁字母英文字母ISO基本拉丁字母(英语:ISO basic Latin alphabet)类型全音素文字相关所属語言拉丁语读音方法 [b][p][ɓ](适应变体)Unicode编码U+0042, U+0062字母顺位2数值 2歷史發...

Displaced persons and refugees Clickable map of the more than 400 depopulated towns and villages of the 1948 Palestinian exodus (red) and the c. 60 modern day Palestinian refugee camps (blue) Palestinian refugees are citizens of Mandatory Palestine, and their descendants, who fled or were expelled from their country over the course of the 1947–1949 Palestine war (1948 Palestinian expulsion and flight) and the Six-Day War (1967 Palestinian exodus). Most Palestinian refugees live in or ...

Skadron Udara 5Lanud Sultan HasanuddinLambang Skadud 5Dibentuk23 Mei 1953Negara IndonesiaCabang TNI Angkatan UdaraTipe unitSatuan Udara Intai StrategisBagian dariWing Udara 5MotoAdhirajasa Bumantara Bhayakara SamuderaUlang tahun23 MeiAlutsistaBoeing 737–200Situs webwww.skadronudara5.wordpress.com Skadron Udara 5/Intai Strategis adalah Skadron udara operasional yang berada dibawah jajaran Wing Udara 5 Lanud Sultan Hasanuddin, Makassar yang bertugas menyiapkan dan mengoperasikan pesawat intai...

American baseball player (1944–2004) Baseball player Tug McGrawPitcherBorn: (1944-08-30)August 30, 1944Martinez, California, U.S.Died: January 5, 2004(2004-01-05) (aged 59)Brentwood, Tennessee, U.S.Batted: RightThrew: LeftMLB debutApril 18, 1965, for the New York MetsLast MLB appearanceSeptember 25, 1984, for the Philadelphia PhilliesMLB statisticsGames pitched824Win–loss record96–92Earned run average3.14Strikeouts1,109Saves180 Teams New York Mets (196...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

Kedutaan Besar Republik Indonesia di BratislavaVeľvyslanectvo Indonézskej republiky v BratislavaKoordinat48°09′51″N 17°05′08″E / 48.164059°N 17.08557°E / 48.164059; 17.08557Lokasi Bratislava, SlowakiaAlamatBrnianska 3181104 Bratislava, SlovakiaDuta BesarR. Pribadi SutionoYurisdiksi SlowakiaSitus webkemlu.go.id/bratislava/id Kedutaan Besar Republik Indonesia di Bratislava (KBRI Bratislava) (bahasa Slowakia: Veľvyslanectvo Indonézskej republiky v...

内華達州 美國联邦州State of Nevada 州旗州徽綽號:產銀之州、起戰之州地图中高亮部分为内華達州坐标:35°N-42°N, 114°W-120°W国家 美國建州前內華達领地加入聯邦1864年10月31日(第36个加入联邦)首府卡森城最大城市拉斯维加斯政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) • 副州长(英语:List of lieutenant governors of {{{Name}}}]])喬·隆巴爾多(R斯塔...

For other fictional characters, see Chandramukhi (disambiguation). Fictional character ChandramukhiDevdas characterVyjayanthimala as Chandramukhi in DevdasCreated bySarat Chandra ChattopadhyayPortrayed byChandrabati DeviVyjayanthimalaSupriya Devi Kalki KoechlinAnwara Madhuri DixitFor more PerformersIn-universe informationAliasChandrikaNicknameLeniRaceIndian peopleGenderFemaleOccupationTawaif (courtesan)SpouseDevdas MukherjeeReligionHindu Chandramukhi is one of the pivotal characters in the 1...

Ruined castle in Buchach, UkraineYou can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Ukrainian. (March 2022) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Do not translate t...

Art museum in Long Beach, California Museum of Latin American ArtInteractive fullscreen mapEstablished1996Location628 Alamitos Avenue Long Beach, California 90802, United StatesCoordinates33°46′28″N 118°10′48″W / 33.77444°N 118.18000°W / 33.77444; -118.18000TypeModern and Contemporary Latin American Art[1]WebsiteMuseum of Latin American Art The Museum of Latin American Art (MOLAA) was founded by Dr. Robert Gumbiner in 1996 in Long Beach, California,...

Railway station in Ichikikushikino, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan This article does not cite any sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Kushikino Station – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2011) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Kushikino Station串木野駅General informationLocationIchikikushikino, Kagoshima(鹿児...

Chinese varieties spoken around Jiangxi Gan language redirects here. For the Gan language of Ghana, see Gã language. For the Gan language of Burkina, see Kaansa language. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Gan Chinese – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2013) (Learn how and ...

NETGEAR Digital Entertainer 8000 HD Netgear's Digital Entertainer line of products are digital media players that can pull multimedia content from home computers to the typical audio/video entertainment center. There are three products in the line, the EVA700, the HD EVA8000 and the current EVA9150 Digital Entertainer Elite. All support high definition video, the EVA700 via component output up to 1080i and the EVA8000/EVA9000 up to 1080p with both component and HDMI connectors. All models sup...




