Austrian Silesia
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Television channel TévaCountryFranceBroadcast areaFranceHeadquartersNeuilly-sur-Seine, FranceProgrammingLanguage(s)FrenchPicture format576i (16:9 SDTV)1080i (HDTV)OwnershipOwnerM6 GroupSister channelsM6Gulli6terParis PremièreW9M6 MusicSérie ClubHistoryLaunched6 October 1996; 27 years ago (1996-10-06)LinksWebsitewww.6play.fr/teva Téva is a French general-interest television channel, privately owned, with a female and family focus, belonging to the M6 Group. Téva has been...

Holly BalayFoto Pura Pura Dalam PenjaraLahir(1988-06-30)30 Juni 1988Jakarta, IndonesiaPekerjaankomedianDikenal atasHolly Holly Balay Balay dan Pesulap Tersakti Didunia Holly Balay nama lengkap Rusman Rizky Holly Balay (30 Juni 1988) adalah seorang komedian berkebangsaan Indonesia. Ia merupakan sepuluh besar Indonesia's Got Talent (musim 3) yang disiarkan oleh RCTI tahun 2022. Pada kompetisi tersebut ia menampilkan bakat pesulap komedi dengan gelar yang ia ciptakan Pesulap Tersakti Didunia. I...

Nama ini menggunakan cara penamaan Spanyol: nama keluarga pertama atau paternalnya adalah Moreno dan nama keluarga kedua atau maternalnya adalah Balagueró. Gerard Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Gerard Moreno Balagueró[1]Tanggal lahir 7 April 1992 (umur 32)[1]Tempat lahir Santa Perpètua, SpanyolTinggi 180 cm (5 ft 11 in)[1]Posisi bermain StrikerInformasi klubKlub saat ini VillarrealNomor 7Karier junior2000–2001 Damm2001–2007 Espanyol2007�...

سيسيناند ، و معلومات شخصية تاريخ الميلاد سنة 605 الوفاة 12 مارس 636 (30–31 سنة) طليطلة الحياة العملية المهنة حاكم تعديل مصدري - تعديل سيسيناند (605 - 636) هو ملك من ملوك القوط الغربيين لهسبانيا وسبتمانيا وغاليسيا حكم بين عامي 631-636.[1] قاد العديد من الح�...

Questa voce sull'argomento calciatori italiani è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Alessandro Bollani Nazionalità Italia Calcio Ruolo Difensore, centrocampista Termine carriera 1924 Carriera Squadre di club1 1911-1912 Andrea Doria1 (-2)1913-1914 Andrea Doria16 (1)1915→ Brescia3 (0)1919-1922 Brescia48 (1)1922-1924 Andrea Doria10 (2) 1 I due numeri indicano l...

Jonathan Aspas Nazionalità Spagna Altezza 177 cm Calcio Ruolo Centrocampista Termine carriera 1º luglio 2021 Carriera Giovanili 1990-1998 Moaña1998-2001 Celta Vigo Squadre di club1 2001-2003 Celta Vigo B58 (4)2003-2007 Celta Vigo64 (3)2007-2009 Piacenza49 (4)2009 R.E. Mouscron15 (2)2011 AEP Paphos5 (0)[1]2011-2013 Alkī Larnaca44 (3)[2]2014-2015 Racing Ferrol27 (0)[3]2015-2018 Pro Piacenza95 (0)[4]2018-2020...

Theory in social psychology Moral foundations theory is a social psychological theory intended to explain the origins of and variation in human moral reasoning on the basis of innate, modular foundations.[1][2][3][4] It was first proposed by the psychologists Jonathan Haidt, Craig Joseph, and Jesse Graham, building on the work of cultural anthropologist Richard Shweder.[5] More recently, Mohammad Atari, Jesse Graham, and Jonathan Haidt have revised some...

Greer Stevens Nazionalità Sudafrica Tennis Carriera Singolare1 Vittorie/sconfitte 98-59 Titoli vinti 1 Miglior ranking Risultati nei tornei del Grande Slam Australian Open QF (1980) Roland Garros Wimbledon QF (1980) US Open 4T (1979) Doppio1 Vittorie/sconfitte 93-48 Titoli vinti 2 Miglior ranking Risultati nei tornei del Grande Slam Australian Open 2T (1980) Roland Garros Wimbledon QF (1977, 1980) US Open SF (1977) Doppio misto1 Vittorie...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando la canoa o kayak intesa come imbarcazione, vedi Canoa. Gara di maratona in kayak Con il termine canoa vengono raggruppati vari tipi di imbarcazioni che hanno in comune il fatto di essere spinte e manovrate con pagaie e adoperate da diverse popolazioni mondiali: la canoa ed il kayak. Per estensione, lo stesso termine raggruppa gli sport praticati con tali imbarcazioni. Il sostantivo canoismo che descrive l'utilizzo della canoa come sport o diletto, è di u...

مازن درويش معلومات شخصية الميلاد 1 نوفمبر 1974 (50 سنة) مواطنة سوريا الزوجة يارا بدر الحياة العملية المدرسة الأم جامعة دمشق المهنة محامٍ، وناشط حقوقي اللغات العربية الجوائز تايم 100 (2022)[1]جائزة أبطال الحرية للمعهد الدولي للصحافة [لغات أخرى]&#...

For the airport, see Paris - Le Bourget Airport. You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (January 2012) Click [show] for important translation instructions. View a machine-translated version of the French article. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pastin...

梅拉蒂·达伊瓦·奥克塔维亚尼Melati Daeva Oktavianti基本資料代表國家/地區 印度尼西亞出生 (1994-10-28) 1994年10月28日(29歲)[1] 印度尼西亞万丹省西冷[1]身高1.68米(5英尺6英寸)[1]握拍右手[1]主項:女子雙打、混合雙打職業戰績48勝–27負(女雙)109勝–56負(混雙)最高世界排名第4位(混雙-普拉文·喬丹)(2020年3月17日[2])現時世界排名第...

Ultra-low-cost airline of Canada Flair AirlinesFlair Airlines Boeing 737 MAX 8 in the 2021 livery IATA ICAO Callsign F8[1] FLE[2] FLAIR[2] FoundedAugust 19, 2005; 18 years ago (2005-08-19)(as Flair Air)Commenced operations2017; 7 years ago (2017)(as Flair Airlines)AOC #Canada: 14941[3]United States: F8RF148F[4]Operating basesCalgaryEdmontonKitchener/WaterlooToronto–PearsonVancouverWinnipegFleet size20[5]...
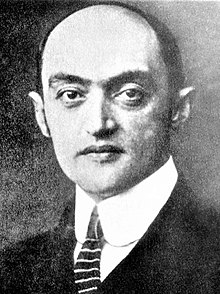
Austrian political economist (1883–1950) Joseph SchumpeterBorn(1883-02-08)February 8, 1883Triesch, Moravia, Austria-Hungary(now Třešť, Czech Republic)DiedJanuary 8, 1950(1950-01-08) (aged 66)Salisbury, Connecticut, USNationalityAustrianCitizenshipAustriaUnited StatesEducationUniversity of Vienna (PhD, 1906)Academic careerInstitutionHarvard University, 1932–50University of Bonn, 1925–32Biedermann Bank, 1921–24Columbia University, 1913–1914University of Graz, 1912–14Universi...

1979 video game This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Basketball 1979 video game – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) 1979 video gameBasketballArcade flyerDeveloper(s)Atari, Inc.Publisher(s)Atari, Inc.Programmer(s)Chris Downen...

12th-century Sephardic rabbi and astrologer Abenezra redirects here. For the lunar crater, see Abenezra (crater). Abraham ibn Ezra ראבעAn illustration of Ibn Ezra (center) making use of an astrolabe.Bornc. 1089 - 1092Tudela, Taifa of ZaragozaDiedc. 1164 - 1167Known forwriting commentaries, grammarianChildrenIsaac ben Ezra Abraham ben Meir Ibn Ezra (Hebrew: ר׳ אַבְרָהָם בֶּן מֵאִיר אִבְּן עֶזְרָא ʾAḇrāhām ben Mēʾīr ʾībən ʾEzr...

Questa voce sull'argomento squadre di hockey su ghiaccio è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. Hamburg FreezersHockey su ghiaccio Iceboxes Segni distintiviUniformi di gara Casa Trasferta Colori socialiAzzurro, Navy, Bianco, Grigio Dati societariCittàAmburgo Paese Germania LegaDEL Fondazione1999 Scioglimento2016 ProprietarioAnschutz Entert...

1632 second edition of the works of William Shakespeare Mr. William Shakespeares Comedies, Histories, & Tragedies Title page of the second folio (1632), this copy with a certificate of a censor for the Inquisition.AuthorWilliam ShakespeareCover artistMartin DroeshoutLanguageEarly Modern EnglishGenreEnglish Renaissance theatrePublisherThomas CotesPublication date1632Publication placeEngland The Second Folio is the 1632 edition of the collected plays of William Shakespeare. It follows ...

Silesian duchy (1281–1918) Duchy of Teschen Księstwo Cieszyńskie (Polish) Těšínské knížectví (Czech) Herzogtum Teschen (German) Ducatus Tessinensis (Latin) 1290–1918 Flag Coat of arms1 Silesia duchies in 1290–91:Teschen under Mieszko I in yellowStatusSilesian duchyFiefdom of Bohemia (from 1327)Part of the Bohemian Crown (from 1348)CapitalCieszynCommon languagesLatin (officially)Czech and German (later)Polish (popularly)Religion LutheranismRoman Catholic...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Raumpatrouille – Die phantastischen Abenteuer des Raumschiffes Orion – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR...









