Alfândega da Fé
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Indian Tamil-language reality TV program This article is about the main edition. For the digital edition, see Bigg Boss Ultimate. Bigg BossShow's seventh season logo featuring host Kamal HaasanPresented byKamal Haasan[1]Voices ofSasho Sathish SarathyCountry of originIndiaOriginal languageTamilNo. of seasons7No. of episodes734 (as of Jan 2024)ProductionProduction locationChennaiCamera setupMulti-cameraRunning time 90 minutes (seasons 1,2; weekdays) 120 minutes (seasons 1,2; weekends) 6...

Map of the results of the 2007 Tunbridge Wells council election. Conservatives in blue and Liberal Democrats in yellow. Wards in grey were not contested in 2007. The 2007 Tunbridge Wells Borough Council election took place on 3 May 2007 to elect members of Tunbridge Wells Borough Council in Kent, England. One third of the council was up for election and the Conservative Party stayed in overall control of the council.[1] After the election, the composition of the council was: Conserva...

2004 video gameViewtiful Joe 2North American PS2 cover artDeveloper(s)Clover StudioPublisher(s)CapcomDirector(s)Masaaki YamadaProducer(s)Atsushi InabaWriter(s)Hideki KamiyaComposer(s)Sayaka MoritaMasami UedaSeriesViewtiful JoePlatform(s)GameCube, PlayStation 2ReleaseNA: November 18, 2004 (GC)[2]NA: December 7, 2004 (PS2)[1]JP: December 16, 2004[3][4]EU: April 1, 2005[5]AU: April 15, 2005Genre(s)Action, platform, beat 'em upMode(s)Single-player Viewtiful...

Pour des articles plus généraux, voir Chronologie des États-Unis et 1895. Éphémérides Chronologie des États-Unis 1892 1893 1894 1895 1896 1897 1898Décennies aux États-Unis :1860 1870 1880 1890 1900 1910 1920 Chronologie dans le monde 1892 1893 1894 1895 1896 1897 1898Décennies :1860 1870 1880 1890 1900 1910 1920Siècles :XVIIe XVIIIe XIXe XXe XXIeMillénaires :-Ier Ier IIe IIIe Chronologies ...

Light machine gun Zastava M77 Zastava M77TypeLight machine gunPlace of originYugoslaviaService historyIn service1977-presentUsed byCyprus[citation needed]WarsLebanese Civil WarYugoslav WarsProduction historyManufacturerZastava ArmsSpecificationsMass4.8 kg[1]Length990 mmBarrel length500 mmCartridge7.62×51mm NATO[1]Caliber7.62 mmActionGas-actuated (rotating bolt)Rate of fireSemi-automatic, fully automaticMuzzle velocity840 m/sEffe...

Artikel ini membutuhkan rujukan tambahan agar kualitasnya dapat dipastikan. Mohon bantu kami mengembangkan artikel ini dengan cara menambahkan rujukan ke sumber tepercaya. Pernyataan tak bersumber bisa saja dipertentangkan dan dihapus.Cari sumber: Kapurung – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR Kapurung di Makassar Kapurung (Bahasa Tae': Pugalu) adalah salah satu makanan khas tradisional di Sulawesi Selatan, terutama di wilayah Luwu Raya d...

HwagwanHwagwan worn by a brideNama KoreaHangul화관 Hanja花冠 Alih AksarahwagwanMcCune–Reischauerhwakwan Hwagwan adalah jenis mahkota kecil Korea dikenakan oleh wanita, secara tradisional untuk acara-acara seremonial seperti pernikahan. Hwagwan ini mirip dengan jokduri dalam bentuk dan fungsi, tetapi hwagan lebih rumit.[1][2][3][4] Lihat pula Jokduri Hwarot Ayam Gache Hanbok Referensi ^ Wedding Clothes. Life in Korea. Diakses tanggal 2008-09-16. ^ Ha...

Endangered Sino-Tibetan language of west-central ChinaBaimaPe白马语Pronunciation/pe˥˧/Native toChinaRegionSichuan and GansuEthnicity14,000 Baima people (2007)[1]Native speakers10,000 (2007)[1]Language familySino-Tibetan Tibetic ?Qiangic ?BaimaDialects Northern Baima, Southern Baima, Western Baima Language codesISO 639-3bqhGlottologbaim1244ELPBaimaBaima is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in DangerThis article contai...
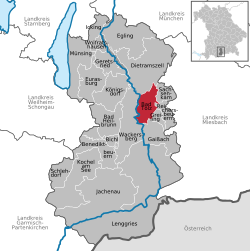
Bad Tölz Bad Tölz terlihat dari Sungai Isar Lambang kebesaranLetak Bad Tölz di Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen NegaraJermanNegara bagianBayernWilayahOberbayernKreisBad Tölz-WolfratshausenSubdivisions5 OrtsteilePemerintahan • MayorJosef Niedermaier (Freie Wähler Gem.)Luas • Total30,80 km2 (1,190 sq mi)Ketinggian658 m (2,159 ft)Populasi (2013-12-31)[1] • Total18.070 • Kepadatan5,9/km2 (15/sq mi)Zona waktuWE...

Public park located in Fresno, California, US Woodward ParkLakeside of Woodward ParkNearest cityFresno, California, USArea300 acres (120 ha)Opened1968Operated byCity of Fresno Parks Department Woodward Park is a public park located in Fresno, California, abutting the San Joaquin River, opened in 1968. It is named after the late Ralph Woodward who bequeathed a portion of his estate to provide a regional park and bird sanctuary in Fresno. The park has a multi-use amphitheatre, an...

この項目には、一部のコンピュータや閲覧ソフトで表示できない文字が含まれています(詳細)。 数字の大字(だいじ)は、漢数字の一種。通常用いる単純な字形の漢数字(小字)の代わりに同じ音の別の漢字を用いるものである。 概要 壱万円日本銀行券(「壱」が大字) 弐千円日本銀行券(「弐」が大字) 漢数字には「一」「二」「三」と続く小字と、「壱」「�...

Village and civil parish in West Yorkshire, England Not to be confused with Burley, Leeds. Human settlement in EnglandBurley in WharfedaleVillage greenBurley in WharfedaleLocation within West YorkshirePopulation7,041 (2011 Census)[1]OS grid referenceSE165464• London175 mi (282 km) SSECivil parishBurleyMetropolitan boroughCity of BradfordMetropolitan countyWest YorkshireRegionYorkshire and the HumberCountryEnglandSovereign stateUnited...

جيمس باكل معلومات شخصية الميلاد سنة 1667 نورتش الوفاة سنة 1724 (56–57 سنة) لندن الحياة العملية المهنة مخترع، وكاتب بوابة الأدب تعديل مصدري - تعديل هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. ...

Diplomatic policy of concessions Adolf Hitler greets British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain at the beginning of the Bad Godesberg meeting on 24 September 1938 in which Hitler demanded annexation of Czech border areas without delay, leading to the Godesberg Memorandum. Conflict resolution Nonviolence Arbitration Auction Conciliation Law Dispute resolution Rule of law Collaborative Mediation Party-directed Negotiation Violence Conflict escalation De-escalation Just war theory War studies In...
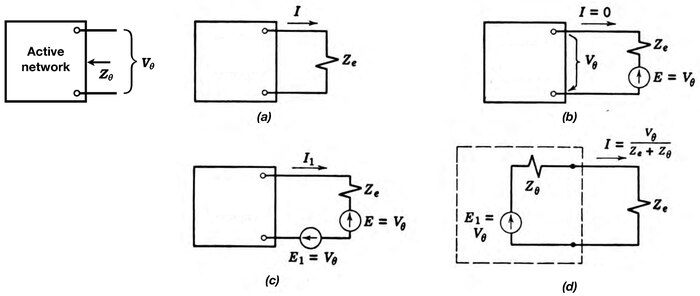
Theorem in electrical circuit analysis Fig. 1. Any black box containing only resistances, voltage sources and current sources, can be replaced by a Thévenin equivalent circuit consisting of an equivalent voltage source in series connection with an equivalent resistance. As originally stated in terms of direct-current resistive circuits only, Thévenin's theorem states that Any linear electrical network containing only voltage sources, current sources and resistances can be replaced at termin...

Moved observances as per the holiday economics policy:[a] 17th day (Wednesday) – unmovable/fixed holiday 4th day (Thursday) → 1st day (Nearest Monday)28th (Sunday) → 29th (Nearest Monday[b]) 26th day (Friday) – holiday date vary per year regardless of law (green outline box) 25th day (Friday) – movable holiday but observance not moved as per prerogative (yellow circle background) Holiday economics refers to the policy ...

Artikel ini perlu dikembangkan agar dapat memenuhi kriteria sebagai entri Wikipedia.Bantulah untuk mengembangkan artikel ini. Jika tidak dikembangkan, artikel ini akan dihapus.Kuil positivis di Porto Alegre Kapel kemanusiaan di Paris Agama Kemanusiaan (Prancis: Religion de l'Humanité atau église positiviste) adalah sebuah agama sekuler yang dibentuk oleh Auguste Comte (1798–1857), pendiri filsafat positivis. Para pengikut agama tersebut membangun kapel-kapel kemanusiaan di Prancis dan Bra...

AbhinandannathBiographieNaissance AyodhyaFamille Dynastie ikshvaku (en)Autres informationsTaille 1 050 mmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Abhinandannath est le quatrième Tirthankara un des maîtres éveillés du jaïnisme[1]. Comme ses prédécesseurs, il est né d'une lignée royale et après plusieurs années de règne, il abandonna les fastes pour devenir ascète et méditer afin d'obtenir l'illumination[2]. Et il réussit à briser les chaines du karma et à devenir un...

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (ديسمبر 2014) الاتصال السياسي يشير مفهومه إلى اطراف فاعله على مسرح الحياة السياسية وتفاعل بينهم وفق منطق وأسس أو قواعد اللعبة السياسية وتشكل هذه الأطراف والتفاعلات والم...

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Sibley Railroad Bridge – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2021) This article i...



