2017 FIFA Confederations Cup
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:
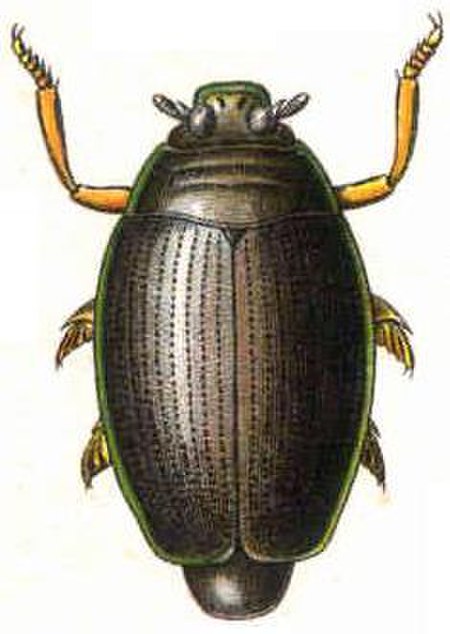
Kumbang putar Gyrinus natator Klasifikasi ilmiah Kerajaan: Animalia Filum: Arthropoda Kelas: Insecta Ordo: Coleoptera Subordo: Adephaga Famili: GyrinidaeLatreille, 1802 Gyrinidae adalah salah famili kumbang putar.[1] Famili kumbang putar merupakan kumbang-kumbang kecil dengan panjang kurang lebih 7mm.[1] Spesies yang tergolong famili ini banyak hidup di permukaan air dan pandai menyelam.[1] Gyrinidae adalah termasuk serangga yang langka.[2] Secara morfologi, s...

Topik artikel ini mungkin tidak memenuhi kriteria kelayakan umum. Harap penuhi kelayakan artikel dengan: menyertakan sumber-sumber tepercaya yang independen terhadap subjek dan sebaiknya hindari sumber-sumber trivial. Jika tidak dipenuhi, artikel ini harus digabungkan, dialihkan ke cakupan yang lebih luas, atau dihapus oleh Pengurus.Cari sumber: Basri Baco – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk mengha...

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources.Find sources: Al Madina School of Richmond – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2021)Private schoolAl Madina School of RichmondLocationMidlothian, VA, VirginiaCoordinates37°27′47″N 77°35′44″W / 37.46293°N 77.59554°W&#x...

Asha-Rose Mtengeti Migiro Deputi Sekretaris Jenderal Perserikatan Bangsa-BangsaPetahanaMulai menjabat 5 Februari 2007PendahuluMark Malloch BrownPenggantiPetahanaMenteri Luar Negeri TanzaniaMasa jabatan4 Januari 2006 – 11 Januari 2007PendahuluJakaya KikwetePenggantiBernard Membe Informasi pribadiLahir9 Juli 1956 (umur 67)Songea, Region Ruvum, TanzaniaKebangsaanTanzaniaPartai politikChama Cha MapinduziSuami/istriCleophas MigiroProfesiPengacara dan politikusSunting kotak info...

Sakramen Imamat adalah sakramen yang dengannya seseorang dijadikan uskup, imam, atau diakon, sehingga penerima sakramen ini dibaktikan sebagai citra Kristus (In persona Christi). Hanya uskup (termasuk juga patriark dan paus) yang berhak dan boleh melayankan sakramen ini. Orang-orang yang berkeinginan menjadi imam dituntut oleh Hukum Kanonik (Kanon 1032 dalam Kitab Hukum Kanonik) untuk menjalani suatu program seminari yang selain berisi studi filsafat dan teologi sampai lulus, juga mencakup su...

British-American esoteric, theosophist and writer (1880-1949) For the American writer of children's books and articles for periodicals, see Alice Cooper Bailey. Not to be confused with Alice Bailly. This article possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (December 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Alice Ann BaileyAlice BaileyBornAlice La Trob...

Disambiguazione – Se stai cercando altri significati, vedi Alarcón (disambigua). Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento centri abitati della Spagna non cita le fonti necessarie o quelle presenti sono insufficienti. Puoi migliorare questa voce aggiungendo citazioni da fonti attendibili secondo le linee guida sull'uso delle fonti. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Alarcóncomune Alarcón – Veduta LocalizzazioneStato Spagna Comunità autonoma Castiglia-La Mancia...

Indian writer and social reformer (1909 –1987) Lalithambika AntharjanamBorn(1909-03-30)March 30, 1909Kottavattom, Quilon, TravancoreDiedFebruary 6, 1987(1987-02-06) (aged 77)Njaliyakuzhi, Kottayam district, Kerala, IndiaOccupationWriter, social reformerLanguageMalayalamNotable worksAgnisakshi, Atmakathaykku Oru AmukhamNotable awardsSahitya Akademi AwardKerala Sahitya Akademi AwardVayalar AwardKerala Sahitya Akademi FellowshipSpouseNarayanan NambuthiriChildrenBhaskara Kumar, N. Mohanan,...

土库曼斯坦总统土库曼斯坦国徽土库曼斯坦总统旗現任谢尔达尔·别尔德穆哈梅多夫自2022年3月19日官邸阿什哈巴德总统府(Oguzkhan Presidential Palace)機關所在地阿什哈巴德任命者直接选举任期7年,可连选连任首任萨帕尔穆拉特·尼亚佐夫设立1991年10月27日 土库曼斯坦土库曼斯坦政府与政治 国家政府 土库曼斯坦宪法 国旗 国徽 国歌 立法機關(英语:National Council of Turkmenistan) ...

Water tower in Bankstown, Sydney, NSW Bankstown ReservoirThe pillared water towerLocation300 Hume Highway, Bankstown, New South WalesCoordinates33°54′19.78″S 151°02′22.74″E / 33.9054944°S 151.0396500°E / -33.9054944; 151.0396500Elevation20 metres (66 feet) AGLBuilt1920; 104 years ago (1920)Built forMetropolitan Board of Water and Sewerage, SydneyArchitectMetropolitan Board of Water Supply and SewerageArchitectural style(s)Federation Free C...

Character in Love's Labour's Lost For the apple, see Costard (apple). Fictional character CostardLove's Labour's Lost character1776 print by Charles Grignion of Thomas Weston playing CostardCreated byWilliam ShakespearePortrayed byThomas WestonPaul JessonNathan LaneIn-universe informationGenderMaleOccupationJester Quote by Costard from the 1598 quarto using the word honorificabilitudinitatibus; his name is given as Clow[n]. Costard is a comic figure in the play Love's Labour's Lost by William...

ابن أبي عمر المقدسي معلومات شخصية الميلاد أكتوبر 1200 دمشق الوفاة 26 يوليو 1283 (82–83 سنة) دمشق مكان الدفن جبل قاسيون مواطنة الدولة المملوكية الديانة الإسلام المذهب الفقهي حنبلي الزوجة خطلو (جارية) خاتون بنت السديد عبد الرحمن بن بركات الإربلي ثم حبيبة بنت �...

Arrangement of amino acid sequence Schematic representation of a circular permutation in two proteins. The first protein (outer circle) has the sequence a-b-c. After the permutation the second protein (inner circle) has the sequence c-a-b. The letters N and C indicate the location of the amino- and carboxy-termini of the protein sequences and how their positions change relative to each other. A circular permutation is a relationship between proteins whereby the proteins have a changed order o...

Super Mario 64 Sampul permainan Diterbitkan diNintendo 64[1][2]iQue PlayerZH: 21 November 2003Virtual Console[3][4]GenrePlatformingKarakteristik teknisPlatformNintendo 64 dan Wii U ModePermainan video pemain tunggal FormatROM cartridge dan unduhan digital Metode inputgamepad Informasi pengembangPengembangAPH NintendoPenyuntingNintendo PengarahShigeru MiyamotoProdusenShigeru MiyamotoKomponisKoji KondoPenerbitNintendoPenilaianESRB PEGI USK CERO BBFC[[berkas:|30x3...

コアオアシシギ 分類 ドメイン : 真核生物 Eukaryota 界 : 動物界 Animalia 門 : 脊索動物門 Chordata 亜門 : 脊椎動物亜門 Vertebrata 綱 : 鳥綱 Aves 目 : チドリ目 Charadriiformes 科 : シギ科 Scolopacidae 属 : クサシギ属 Tringa 種 : コアオアシシギ T. stagnatilis 学名 Tringa stagnatilis 和名 コアオアシシギ 英名 Marsh Sandpiper Tringa stagnatilis コアオアシシギ(小青足鴫、学名:Tringa stagnatilis)は、チド�...
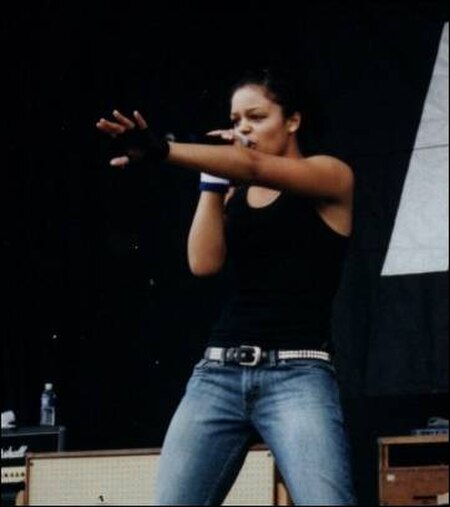

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Dobson. Cet article est une ébauche concernant une chanteuse canadienne. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Fefe DobsonFefe Dobson Live 2004BiographieNaissance 28 février 1985 (39 ans)ScarboroughNom de naissance Felicia Lynn DobsonSurnom FefeNationalité canadienneFormation École Etobicoke des arts (en)Wexford Collegiate School for the Arts (en)Activités Ch...

この項目では、律令時代の令制国について説明しています。戊辰戦争後の令制国については「磐城国」をご覧ください。 令制国一覧 > 東山道 > 石城国 石城国の位置(718年) 石城国(いわきのくに)は、かつて日本の地方行政区分だった令制国の一つ。奈良時代に陸奥国から分立したが、短期間しか存続しなかった。718年に設置され、720年と724年の間に廃止...

يفتقر محتوى هذه المقالة إلى الاستشهاد بمصادر. فضلاً، ساهم في تطوير هذه المقالة من خلال إضافة مصادر موثوق بها. أي معلومات غير موثقة يمكن التشكيك بها وإزالتها. (ديسمبر 2018) القاهرة المتحف المصري المتحف القومي للحضارة المصرية قصر عابدين متحف مركب الجيزة الشمسي (متحف مركب خوفو) �...
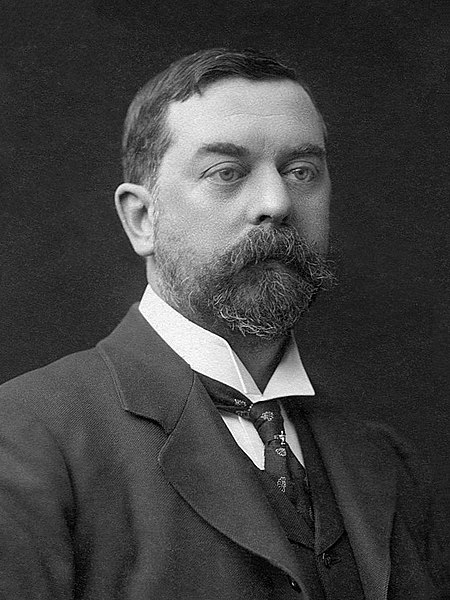

American painter (1856–1925) John SargentPortrait by James E. Purdy, 1903BornJohn Singer Sargent(1856-01-12)January 12, 1856Florence, Grand Duchy of TuscanyDiedApril 14, 1925(1925-04-14) (aged 69)London, EnglandResting placeBrookwood Cemetery51°17′52″N 0°37′29″W / 51.297651°N 0.624693°W / 51.297651; -0.624693NationalityAmericanEducationÉcole nationale supérieure des Beaux-ArtsKnown forPaintingNotable workPortrait of Madame XEl JaleoThe Daughte...

Portogruaro Armoiries Administration Pays Italie Région Vénétie Ville métropolitaine Venise Code postal 30026 Code ISTAT 027029 Code cadastral G914 Préfixe tel. 0421 Démographie Gentilé portogruaresi Population 25 440 hab. (31-12-2010[1]) Densité 249 hab./km2 Géographie Coordonnées 45° 47′ 00″ nord, 12° 50′ 00″ est Altitude Min. 7 mMax. 7 m Superficie 10 200 ha = 102 km2 Divers Sa...







