1969 FA Cup final
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Questa voce o sezione sull'argomento attori è ritenuta da controllare. Motivo: esposizione approssimativa, alcuni contenuti da spostare nella voce della trasmissione televisiva Partecipa alla discussione e/o correggi la voce. Segui i suggerimenti del progetto di riferimento. Criss Angel Criss Angel, pseudonimo di Christopher Nicholas Sarantakos (Long Island, 19 dicembre 1967), è un illusionista, attore e musicista statunitense. Indice 1 Biografia 2 Criss Angel Mindfreak 3 Note 4 Voci ...

Leonor Teles de MenesesLeonor, Ratu PortugalPermaisuri PortugalPeriode5 Mei 1372 – 22 Oktober 1383Informasi pribadiKelahiran1350Tras-os-Montes, PortugalKematian27 April 1386 – 1350; umur -37–-36 tahunTordesillas, SpanyolPemakamanBiara Kerajaan Santa Clara, Tordesillas, SpanyolWangsaMenesesAyahMartim Afonso Telo de MenesesIbuAldonça Anes de VasconcelosPasanganFernando I dari PortugalAnakBeatriz dari PortugalAgamaKatolik Roma Leonor Teles de Meneses (1350 – 27 April 1386) ...

Peta menunjukkan lokasi Initao Initao adalah munisipalitas yang terletak di provinsi Misamis Oriental, Filipina. Pada tahun 2010, munisipalitas ini memiliki populasi sebesar 30.523 jiwa dan 6.372 rumah tangga. Pembagian wilayah Secara administratif Initao terbagi menjadi 16 barangay, yaitu: Aluna Andales Apas Calacapan Gimangpang Jampason Kamelon Kanitoan Oguis Pagahan Poblacion Pontacon San Pedro Sinalac Tawantawan Tubigan Sarana pendidikan Sarana pendidikan yang ada di wilayah ini antara la...

Biografi ini memerlukan lebih banyak catatan kaki untuk pemastian. Bantulah untuk menambahkan referensi atau sumber tepercaya. Materi kontroversial atau trivial yang sumbernya tidak memadai atau tidak bisa dipercaya harus segera dihapus, khususnya jika berpotensi memfitnah.Cari sumber: Hamengkubuwana X – berita · surat kabar · buku · cendekiawan · JSTOR (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Ingkang Sinuwun Sri SultanHameng...

Tang dynasty general Ambassador from Persia (波斯國), visiting the court of the Tang dynasty. The Gathering of Kings (王会图), circa 650 CE Narsieh (Middle Persian: 𐭭𐭥𐭮𐭧𐭩 Narseh; simplified Chinese: 泥涅师; traditional Chinese: 泥涅師; pinyin: Nìnièshī) was a Persian general who fled to the Tang dynasty with his father, Peroz III, son of Yazdegerd III, the last Sassanid emperor of Persia, after the Muslim conquest of Persia.[1] He was escorted...

Un tavolo di legno. Il tavolo è un mobile formato da un piano, spesso rettangolare, quadrato o tondo, di legno, metallo, plastica, di cristallo o altro materiale rigido, sostenuto da una, due, tre, quattro o più gambe, e che ha forma e dimensioni diverse, a seconda dell'uso cui è adibito. Può anche essere sostenuto da una colonna centrale; in questo caso di solito ha un ripiano piccolo, spesso circolare. ll piano di appoggio è caratterizzato dall’essere piatto (da qui il detto “piatt...
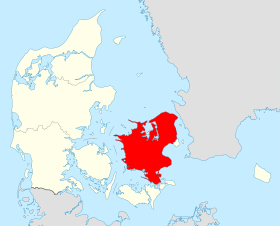
لمعانٍ أخرى، طالع زيلاند (توضيح). زيلاند معلومات جغرافية الإحداثيات 55°34′N 11°53′E / 55.57°N 11.89°E / 55.57; 11.89 [1] [2] الأرخبيل الدنمارك المسطح المائي بحر البلطيق المساحة 7031.30 كيلومتر مربع[3] الطول 132 كيلومتر العرض 116 كيلومتر ال�...

For related races, see 2024 United States Senate elections. 2024 United States Senate election in Maryland ← 2018 November 5, 2024 2030 → Nominee Angela Alsobrooks Larry Hogan Party Democratic Republican Incumbent U.S. senator Ben Cardin Democratic Elections in Maryland Federal government Presidential elections 1788–89 1792 1796 1800 1804 1808 1812 1816 1820 1824 1828 1832 1836 1840 1844 1848 1852 1856 1860 1864 1868 1872 1876 1880 1884 1888 1892 1896 1900 1904...

Nigerian footballer This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages) This article is an orphan, as no other articles link to it. Please introduce links to this page from related articles; try the Find link tool for suggestions. (February 2022) This biography of a living person needs additional citations for verification. Please help by adding reliable sources. Contentious material about li...

1999 horror film From Dusk Till Dawn 3:The Hangman's DaughterPoster for From Dusk Till Dawn 3: The Hangman's DaughterDirected byP. J. PesceScreenplay byÁlvaro RodríguezStory by Álvaro Rodríguez Robert Rodríguez Produced by Michael S. Murphey Gianni Nunnari Meir Teper Starring Marco Leonardi Michael Parks Rebecca Gayheart Lennie Loftin Ara Celi Jordana Spiro Orlando Jones Danny Trejo Temuera Morrison Sônia Braga CinematographyMichael BonvillainEdited byLawrence A. MaddoxMusic byNathan Ba...

This article is about Ranks of the French Army. For more details about the naval ranks, see Ranks in the French Navy. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Ranks in the French Army – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) French Army...

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Harmony Company – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Harmony CompanyCompany typePrivateIndustryMusical instrumentFounded1892; 132 years ago (1892)FounderWilhelm SchultzFateCom...

2 Tawarikh 21Kitab Tawarikh (Kitab 1 & 2 Tawarikh) lengkap pada Kodeks Leningrad, dibuat tahun 1008.KitabKitab 2 TawarikhKategoriKetuvimBagian Alkitab KristenPerjanjian LamaUrutan dalamKitab Kristen14← pasal 20 pasal 22 → 2 Tawarikh 21 (atau II Tawarikh 21, disingkat 2Taw 21) adalah pasal kedua puluh satu Kitab 2 Tawarikh dalam Alkitab Ibrani dan Perjanjian Lama di Alkitab Kristen. Dalam Alkitab Ibrani termasuk dalam bagian Ketuvim (כְּתוּבִים, tulisan).[1] P...

Type of orbit This article is about a class of Kepler orbits. For a free body trajectory at constant gravity, see Projectile Motion. This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Parabolic trajectory – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) ...

Situation in which financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value Part of a series onMacroeconomics Basic concepts Aggregate demand Aggregate supply Business cycle CAGR Deflation Demand shock Disinflation Effective demand Expectations Adaptive Rational Financial crisis Growth Inflation Demand-pull Cost-push Interest rate Investment Liquidity trap Measures of national income and output GDP GNI NNI Microfoundations Money Endogenous Money creation Demand for money Liquidity p...

Парламентська Скупщина Боснії і Герцеговинибосн. Parlamentarna skupština Bosne i Hercegovine Загальна інформація: Юрисдикція: Боснія і Герцеговина Тип: двопалатний парламент Палати: Палата народівПалата представників Попередник: Assembly of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina Палата народів Боснії �...

This article is about the barony of Keenaght. For the townland, see Keenaght (townland). Place in Northern Ireland, United KingdomKeenaght Cianachta[1] (Irish)Location of Keenaght, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland.Sovereign stateUnited KingdomCountryNorthern IrelandCountyLondonderry Keenaght (from Irish Cianachta 'race of Cian'[1][2]) is a barony in the mid-northerly third of County Londonderry, Northern Ireland.[3] It connects to the north-Lo...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Воздвиженка. Улица Воздвиженка Воздвиженка (слева особняк Арсения Морозова, на дальнем плане Кремль), 2004 год Общая информация Страна Россия Город Москва Округ ЦАО Район Арбат Протяжённость 600 м Метро Арбатская Арбатская Б�...

Electronic device with features of both a smartphone and a tablet Phablet A phablet (/ˈfæblət/, /-lɪt/) is a mobile device combining or straddling the size formats of smartphones and tablets. The word is a blend word of phone and tablet. The term is largely unused by the late 2010s, since average PDA sizes eventually morphed into small tablet sizes, up to 6.9 inches (180 mm), with wider aspect ratios.[1] Appearance Phablets feature large displays that complement screen-intens...

Dieser Artikel behandelt ein asiatisches Königreich, der bretonische Ort Baillé heißt auf Gallo ebenso Balhae. Geschichte Koreas Prähistorisches Korea Jeulmun-Zeit (8000–1500 v. Chr.) Mumun-Zeit (1500–300 v. Chr.) Antike Jin-guk (3.–2. Jh. v. Chr.) Go-Joseon (2333? – 108 v. Chr.) Proto-Drei-Reiche Buyeo (2. Jh. v. Chr. – 494 n. Chr.) Goguryeo (37 v. Chr. – 668 n. Chr.) Okjeo (2. Jh. v. Chr. – 5. Jh. n. Chr.) Dongye (3. Jh. v. Chr. – 5. Jh. n. Chr.) Mahan (1. Jh. v. Chr. �...
