Union type
|
Read other articles:

Rafael Tolói Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Rafael Tolói[1]Tanggal lahir 10 Oktober 1990 (umur 33)[2]Tempat lahir Glória d'Oeste, Mato Grosso, BrasilTinggi 185 cm (6 ft 1 in)[3]Posisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini AtalantaNomor 2Karier junior2007–2009 GoiásKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2009–2012 Goiás 151 (20)2012–2015 São Paulo 95 (3)2014 → Roma (pinjaman) 5 (0)2015– Atalanta 177 (8)Tim nasional‡2009 Brasil U-20 19 ...

Roman system of power division among four rulers This article is about the tetrarchy created by Diocletian. For the tetrarchy formed from the kingdom of Herod, see Herodian Tetrarchy. For other uses, see Tetrarch (disambiguation). This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (May 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) Roman imperial dyna...

Ne doit pas être confondu avec Jean Ribit de la Rivière. Pour les articles homonymes, voir La Rivière. Jean de La RivièreBiographieActivité MilitaireBlasonmodifier - modifier le code - modifier Wikidata Jean IV de la Rivière (~1338 - † 1365) est chevalier du régent, diplomate et premier chambellan de Charles V. Seigneur de la Rivière près de Couloutre (Nièvre), il est aussi appelé Jean Bureau de la Rivière[1]. Biographie Il est le fils aîné de Jean II de la Rivière (? - † ...

Netralitas artikel ini dipertanyakan. Diskusi terkait dapat dibaca pada the halaman pembicaraan. Jangan hapus pesan ini sampai kondisi untuk melakukannya terpenuhi. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Misionaris Hati Kudus Yesus (M.S.C.) adalah salah satu tarekat atau kongregasi religius atau ordo keagamaan Katolik yang mempunyai nama resmi: Societas Missionariorum Sacratissimi Cordis Jesu, yang berarti: Tarekat Misionaris Hati Kudus Yesus (bahasa Latin: Congre...
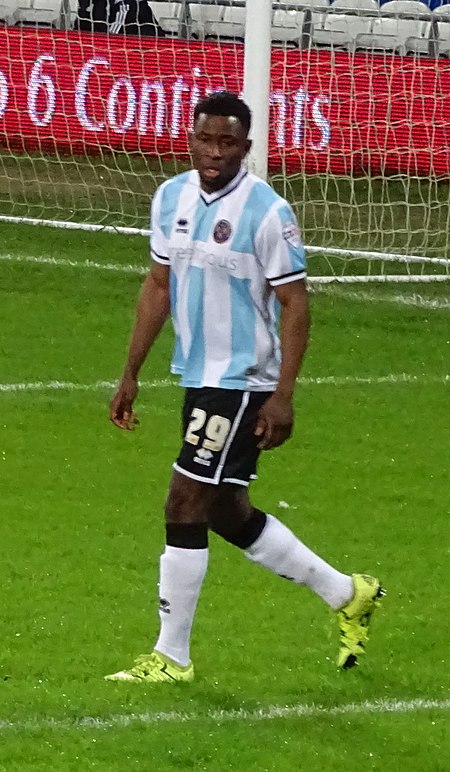

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Desember 2022. Larnell Cole Pesepakbola Larnell Cole pada 2016.Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Larnell James Cole[1]Tanggal lahir 9 Maret 1993 (umur 31)Tempat lahir Manchester, InggrisPosisi bermain GelandangInformasi klubKlub saat ini Inverness Caledonia...

Swafoto yang diambil seorang penyiar radio Putri Anastasia Nikolaevna dari Rusia adalah salah satu remaja yang pertama kali mengambil fotonya sendiri melalui cermin menggunakan Kodak Brownie pada tahun 1914. Swafoto atau foto narsisis (Inggris: selfie) adalah jenis foto dengan cara potret diri yang diambil sendiri dengan menggunakan kamera digital atau ponsel cerdas. Foto narsisis sering dikaitkan dengan narsisisme, terutama dalam jejaring sosial. Di industri hiburan Korea, istilah yang d...

Former space agency Indian National Committee for Space ResearchSpace agency overviewFormed1962; 62 years ago (1962)DissolvedAugust 15, 1969; 54 years ago (1969-08-15)Superseding agencyISROMinister responsiblePrime Minister of IndiaSpace agency executiveVikram Sarabhai, ChairmanParent departmentDepartment of Atomic Energy The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR)[1][2][3][4][5] was established by Ind...

Heritage-listed building in Sydney, Australia AWA TowerThe AWA TowerAWA TowerGeneral informationArchitectural styleInter-war Art DecoAddress45-47 York Street, Sydney central business district, City of Sydney, New South WalesCountryAustraliaCoordinates33°52′01″S 151°12′20″E / 33.86694°S 151.20556°E / -33.86694; 151.20556Named forAmalgamated Wireless Australasia Limited (AWA)Construction started1937Completed1939Design and constructionArchitecture firmMorrow a...

Mobile phone model This article is written like a manual or guide. Please help rewrite this article and remove advice or instruction. (February 2024) This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Sony Ericsson C905 – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2024) (Learn how and when to remove ...

Former theatre in Manhattan, New York For another Broadway theater later using this name, see Earl Carroll Theatre. Casino TheatreCasino Theatre, 1900General informationArchitectural styleMoorish RevivalLocationManhattan, New York CityOpened1882Closed1930Demolished1930Design and constructionArchitect(s)Francis Hatch Kimball and Thomas Wisedell The Casino Theatre was a Broadway theatre located at 1404 Broadway and West 39th Street in New York City. Built in 1882, it was a leading presenter of ...

نواف بن محمد بن عبد الله آل سعود معلومات شخصية الميلاد سنة 1958 (العمر 65–66 سنة) الرياض مواطنة السعودية عائلة آل سعود تعديل مصدري - تعديل الأمير نواف بن محمد بن عبد الله بن عبد الرحمن آل سعود أحد أبناء الأمير محمد بن عبد الله بن عبد الرحمن آل سعود، ووالدته الأ...

Short polemical book published in 1940For the Colombian film, see Guilty Men (film). Guilty Men is a British polemical book written under the pseudonym Cato that was published in July 1940, after the failure of British forces to prevent the defeat and occupation of Norway and France by Nazi Germany. It attacked fifteen public figures for their failed policies towards Germany and for their failure to re-equip the British armed forces. In denouncing appeasement, it defined the policy as the del...

American human geneticist Janet RowleyRowley at the White House in August 2009BornJanet Davison(1925-04-05)April 5, 1925New York City, New YorkDiedDecember 17, 2013(2013-12-17) (aged 88)Chicago, IllinoisAlma materUniversity of ChicagoKnown forIdentification chromosomal translocation as the cause of leukemia and other cancersAwards William Allan Award (1991) National Medal of Science (1998) Gruber Prize in Genetics (2009) Presidential Medal of Freedom (2009) Pearl Meister Greeng...

Singaporean politician Lian Pin KohLian Pin Koh in September 2023BornSingaporeAlma materPrinceton University (PhD), National University of Singapore (BSc, MSc)OrganisationNational University of SingaporeKnown forConservation science, TED talkAwardsWorld Economic Forum Young Global Leader 2013 Lian Pin Koh (born 1976 in Singapore) is a Singaporean conservation scientist. He is Associate Vice President and Chief Sustainability Scientist at the National University of Singapore (NUS), w...
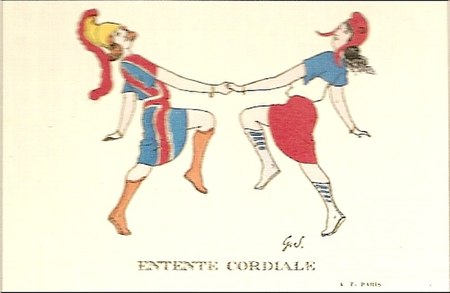
Early modern military conflicts, 1689 to 1815 Second Hundred Years' WarPart of the Anglo-French WarsLeft to right, top to bottom: Battle of Beachy Head (10 July 1690) Battle of Blenheim (13 August 1704) Battle of Fontenoy (11 May 1745) Battle of Carillon (8 July 1758) Battle of the Plains of Abraham (13 September 1759) Siege of Yorktown (19 October 1781) Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) Battle of Waterloo (18 June 1815) Date18 May 1689 – 20 November 1815 (...

This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Transportation in the city of Charlotte, North Carolina includes a large and growing mass tr...

Posterior part of the brain, adjoining and structurally continuous This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Brainstem – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) BrainstemThe three distinct parts of the brainstem are colored in this sagittal...

National identity card of Belgium eIDFront of the cardReverseIssued by BelgiumPurposeIdentificationValid in European Union EFTA United Kingdom (EU Settlement Scheme, valid until 31 December 2025) [1] Rest of Europe (except Belarus, Russia, Ukraine) Egypt French overseas territories Gambia Georgia Montserrat (max. 14 days) Tunisia (organized tours) TurkeyEligibilityBelgian citizenship A Belgian identity card (Dutch: Identiteitsk...

هذه المقالة بحاجة لمراجعة خبير مختص في مجالها. يرجى من المختصين في مجالها مراجعتها وتطويرها. (يوليو 2016) درافيديةالتوزيعالجغرافي:جنوب آسيا وأجزاء من جنوب شرق آسيا، تحديدا جنوب الهند وسريلانكاتصنيفات اللغوية:إحدى عائلة لغات العالميةدرافيديةاللغة البدائية:بروتو-درافيديةف�...

Villanova del Sillarocomune Villanova del Sillaro – VedutaChiesa parrocchiale ed ex Palazzo Abbaziale LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Lombardia Provincia Lodi AmministrazioneSindacoDiego Guarnieri (lista civica) dal 26-5-2019 TerritorioCoordinate45°14′20″N 9°28′58″E45°14′20″N, 9°28′58″E (Villanova del Sillaro) Altitudine69 m s.l.m. Superficie13,5 km² Abitanti1 862[1] (31-10-2023) Densità137,93 ab./km² FrazioniB...