Thomas Karsten
|
Read other articles:

1966 Indian filmAggi BarataTheatrical release posterDirected byB. VittalacharyaWritten byG.K.Murthy (dialogues)Screenplay byB. V. AcharyaStory byB. V. AcharyaProduced byB. VittalacharyaStarringN. T. Rama RaoRajasreeCinematographyD. VaradarajanEdited byK. Govinda SwamyMusic byVijaya Krishna MurthyProductioncompanySri Vital CombinesRelease date 17 October 1966 (1966-10-17) Running time124 minutesCountryIndiaLanguageTelugu Aggi Barata (transl. Fire Blast) is a 1966 Telugu-l...

French philosopher and poet Jean-Marie GuyauBorn(1854-10-28)28 October 1854Laval, Mayenne, FranceDied31 March 1888(1888-03-31) (aged 33)Menton, FranceNationalityFrenchEra19th-century philosophyRegionWestern philosophy Jean-Marie Guyau (28 October 1854 – 31 March 1888) was a French philosopher and poet. Guyau was inspired by the philosophies of Epicurus, Epictetus, Plato, Immanuel Kant, Herbert Spencer, and Alfred Fouillée, and the poetry and literature of Pierre Corneille, Victor Hugo...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Banat. Cet article est une ébauche concernant la Serbie et la géographie. Vous pouvez partager vos connaissances en l’améliorant (comment ?) selon les recommandations des projets correspondants. Banat septentrional Administration Pays Serbie Municipalités KanjižaSentaAdaČokaNovi KneževacKikinda Démographie Population 146 690 hab. (2011) Densité 63 hab./km2 Groupes ethniques Hongrois, Serbes Géographie Coordonnées 45° 50...

AzadٱلْأَزْدSuku Bangsa ArabBendera Bani Azad pada Pertempuran SiffinEtnisQahthanNisbahAl-Azdī (ٱلْأَزْدي)Lokasi asal leluhurSemenanjung Arab dan Timur TengahAgamaPaganisme, kemudian Islam Bani Azad (Arab: الأزدcode: ar is deprecated , Al-Azd) adalah salah satu kabilah Arab yang besar dan ternama pada awal penyebaran agama Islam. Nama kabilah ini dinisbahkan kepada Azad bin Ghauts bin Nabtun bin Malik bin Kahlan, dari bangsa Arab Qahthaniyyah.[1] Bani Azad hijra...

Nankana Sahib Nankana Sahib (bahasa Punjab dan bahasa Urdu: ننكانہ صاحِب) adalah sebuah kota yang terletak di provinsi Punjab, Pakistan. Kota ini merupakan ibu kota distrik dengan nama yang sama. Kota ini dinamai dari Guru Sikh pertama, Guru Nanak, yang lahir dan mulai mengajarkan agama Sikh di kota ini. Saat ini, Nankana Sahib sering dikunjungi oleh para peziarah Sikh dari seluruh dunia.[1][2] Kota ini terletak sejauh 80 km di sebelah barat Lahore dan seki...

Inderlokइन्द्रलोकStasiun angkutan cepat di DelhiKoordinat28°40′24″N 77°10′13″E / 28.673445°N 77.170337°E / 28.673445; 77.170337Jalur Jalur Hijau Jalur MerahJumlah peronSamping (Jalur Merah)Pulau (Jalur Hijau)Jumlah jalur4KonstruksiJenis strukturMelayangParkirTersediaSejarahDibuka3 Oktober 2003 (Jalur Merah)3 April 2010 (Jalur Hijau)Operasi layanan Stasiun sebelumnya Delhi Metro Stasiun berikutnya Terminus Jalur Hi...

2024 song by Olly Alexander DizzySingle by Olly AlexanderWritten2023Released1 March 2024 (2024-03-01)Genre Pop[1] electro[2] dance-pop[3] disco[4] Length2:53LabelPolydor[5]Songwriter(s)Oliver Alexander ThorntonDaniel Harle[6]Producer(s)Finn KeaneDaniel HarleOlly Alexander singles chronology A Very Bad Fun Idea (2023) Dizzy (2024) Music videoDizzy on YouTubeEurovision Song Contest 2024 entryCountryUnited KingdomArtist(s)Olly Alexan...

1972 film by Michael Ritchie This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Prime Cut – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (October 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Prime CutTheatrical release poster by Tom JungDirected byMichael RitchieWritten byRobert DillonProduced byJoe WizanSt...

Запрос «Олива» перенаправляется сюда; см. также другие значения. Олива европейская Оливковая роща на Кипре Научная классификация Домен:ЭукариотыЦарство:РастенияКлада:Цветковые растенияКлада:ЭвдикотыКлада:СуперастеридыКлада:АстеридыКлада:ЛамиидыПорядок:Ясноткоц�...

Sacrificial offering in Judaism For other uses, see Korban (name). Not to be confused with Qurban, a cognate word that refers to animal sacrifice in Islam. Not to be confused with Karbon. Karban redirects here. For the village in Iran, see Karband. Part of a series onJudaism Movements Orthodox Haredi Hasidic Modern Conservative Conservadox Reform Karaite Reconstructionist Renewal Humanistic Haymanot Philosophy Principles of faith Kabbalah Messiah Ethics Chosenness God ...

Armada Mikrotrans JAK-54 di Slipi Petamburan Mikrotrans adalah salah satu angkutan pengumpan bus raya terpadu Transjakarta. Rute-rute yang dipakai oleh Mikrotrans pada umumnya adalah rute-rute mikrolet dan rute-rute angkutan kota Koperasi Wahana Kalpika yang sudah terintegrasi dengan Transjakarta. Untuk menaiki Mikrotrans, penumpang tidak dikenakan biaya alias Rp 0, tetapi tetap harus tap kartu uang elektronik seperti Flazz, E-Money, Brizzi, ataupun Tapcash. Dalam hal ini, PT. Transportasi Ja...

「俄亥俄」重定向至此。关于其他用法,请见「俄亥俄 (消歧义)」。 俄亥俄州 美國联邦州State of Ohio 州旗州徽綽號:七葉果之州地图中高亮部分为俄亥俄州坐标:38°27'N-41°58'N, 80°32'W-84°49'W国家 美國加入聯邦1803年3月1日,在1953年8月7日追溯頒定(第17个加入联邦)首府哥倫布(及最大城市)政府 • 州长(英语:List of Governors of {{{Name}}}]]) •&...

English diplomat and courtier Stephen Poyntz, oil on canvas by Jean-Baptiste van Loo around 1740 Stephen Poyntz (1685–1750), of Midgham in Berkshire, was an English diplomat and courtier. Early life Born in London, and baptised at St Michael Cornhill in November 1685, he was the second son of William Poyntz, upholsterer, of Cornhill, and his second wife Jane Monteage. His father William was descended from an old landowning family, with an estate at Iron Acton. However, the family fortunes h...

Artikel ini perlu diwikifikasi agar memenuhi standar kualitas Wikipedia. Anda dapat memberikan bantuan berupa penambahan pranala dalam, atau dengan merapikan tata letak dari artikel ini. Untuk keterangan lebih lanjut, klik [tampil] di bagian kanan. Mengganti markah HTML dengan markah wiki bila dimungkinkan. Tambahkan pranala wiki. Bila dirasa perlu, buatlah pautan ke artikel wiki lainnya dengan cara menambahkan [[ dan ]] pada kata yang bersangkutan (lihat WP:LINK untuk keterangan lebih lanjut...
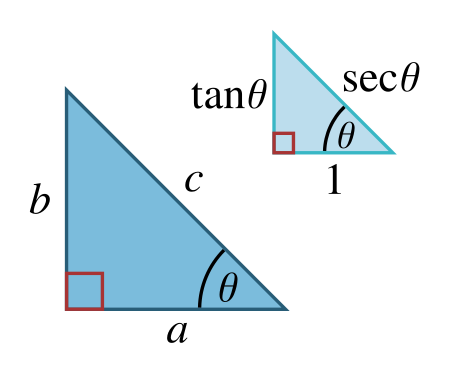
Relation between sine and cosine The Pythagorean trigonometric identity, also called simply the Pythagorean identity, is an identity expressing the Pythagorean theorem in terms of trigonometric functions. Along with the sum-of-angles formulae, it is one of the basic relations between the sine and cosine functions. The identity is sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1. {\displaystyle \sin ^{2}\theta +\cos ^{2}\theta =1.} As usual, sin 2 θ {\displaystyle \sin ^{2...

Higher education school in Malaysia Fire and Rescue Academy of MalaysiaAkademi Bomba dan Penyelamat MalaysiaFormer namesSekolah Latihan Bomba Malayan Union (1957)Pusat Latihan Bomba (1958–1997)TypePublicEstablished1957 (1957)Affiliation Fire and Rescue Department of MalaysiaOfficer in chargeSenior Assistant Fire Commissioner Md Ali Ismail, Assistant Director General of the TrainingLocation MalaysiaCampusMultiple sites, 470.6 acres (190.4 ha) (For 5 campuses)Websitefram.bomba....

هيلدسهايم علم شعار الاسم الرسمي (بالألمانية: Hildesheim) الإحداثيات 52°09′N 9°57′E / 52.15°N 9.95°E / 52.15; 9.95 [1] تقسيم إداري البلد ألمانيا[2][3] التقسيم الأعلى هيلدسهايم عاصمة لـ هيلدسهايم خصائص جغرافية المساحة 92.29 كيلومتر مرب...

Chiesa di Sant'Ivo alla Sapienza L'architettura barocca è quella fase della storia dell'architettura europea che, preceduta dal Rinascimento e dal Manierismo, si sviluppò nel XVII secolo, durante il periodo dell'assolutismo.[1] Il termine barocco, originariamente dispregiativo, indicava la mancanza di regolarità e di ordine, che i fautori del neoclassicismo, influenzati dal razionalismo illuminista, consideravano indice di cattivo gusto.[1] Infatti, caratteristiche fond...

此條目没有列出任何参考或来源。 (2018年1月10日)維基百科所有的內容都應該可供查證。请协助補充可靠来源以改善这篇条目。无法查证的內容可能會因為異議提出而被移除。 卡尔穆-达卡舒埃拉Carmo da Cachoeira市镇卡尔穆-达卡舒埃拉在巴西的位置坐标:21°27′39″S 45°13′26″W / 21.4608°S 45.2239°W / -21.4608; -45.2239国家巴西州米纳斯吉拉斯州面积 • 总计505...

French-American museum director (born 1936) This article uses bare URLs, which are uninformative and vulnerable to link rot. Please consider converting them to full citations to ensure the article remains verifiable and maintains a consistent citation style. Several templates and tools are available to assist in formatting, such as reFill (documentation) and Citation bot (documentation). (September 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) A major contributor to this article appears t...

