Swayamprabhasuri
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read other articles:

Artikel ini sebatang kara, artinya tidak ada artikel lain yang memiliki pranala balik ke halaman ini.Bantulah menambah pranala ke artikel ini dari artikel yang berhubungan atau coba peralatan pencari pranala.Tag ini diberikan pada Februari 2023. Koo Sze-yiu古思堯 Informasi pribadiLahir1949 (umur 74–75)Shekki, Chungshan, ChinaKebangsaanHong Kong ChinesePartai politikBaodiao MovementAfiliasi politiklainnyaMaosim (until 1989)Sunting kotak info • L • B Koo Sze-yiu (Han...

Jonah Hauer-KingHauer-King in 2019LahirJonah Andre Hauer-King30 Mei 1995 (umur 28)Islington, London, InggrisPendidikanSt John's College, CambridgePekerjaanAktorTahun aktif2014–sekarang Jonah Andre Hauer-King (lahir 30 Mei 1995) adalah aktor asal Inggris. Dia telah membintangi beberapa film termasuk, The Last Photograph (2017) dan A Dog's Way Home (2019), dan muncul di miniseri televisi Howards End (2017), Little Women (2017) dan World on Fire (2019). Pada tahun 2023, ia berperan ...

Struktur aljabar → Teori grupTeori grup Gagasan dasar Subgrup Subgrup normal Grup hasil bagi darab langsung semi-darab langsung Homomorfisme grup kernel bayangan jumlah langsung karangan bunga sederhana hingga takhingga kontinu multiplikatif aditif siklik Abel dihedral nilpoten terselesaikan aksi Glosarium teori grup Daftar topik teori grup Grup hingga Klasifikasi grup sederhana hingga siklik bergantian tipe Lie sporadik Teorema Cauchy Teorema Lagrange Teorema Sylow Teorema Hall grup-p Grup...

Shuttle Ejection Escape Suit The Shuttle Ejection Escape Suit was used from STS-1 (1981) to STS-4 (1982) by a two-man crew used in conjunction with Space Shuttle Columbia's ejection seats. It allowed ejections up to Mach 2.7 and 24.4 km (80,000 ft).[1] The suit was manufactured by the David Clark Company of Worcester, Massachusetts. It was derived from the USAF Model S1030 suit, which at the time, was being worn by SR-71 pilots.[1] The Shuttle was certified as operat...

Konten dan perspektif penulisan artikel ini hanya berpusat pada sudut pandang dari negara Indonesia dan tidak menggambarkan wawasan global pada subjeknya. Silakan bantu mengembangkan atau bicarakan artikel ini di halaman pembicaraannya, atau buat artikel baru, bila perlu. (Pelajari cara dan kapan saatnya untuk menghapus pesan templat ini) Penduduk yang berkumpul di rumah Ketua Tonarigumi di Jepang Tonarigumi (Jepang: 隣組) atau dalam Bahasa Indonesia artinya kerukunan tetangga (sekarang...

SirmiumСирмијум/Sirmijum Les ruines du palais impérial de Sirmium. Localisation Pays Serbie District Syrmie Municipalité Sremska Mitrovica Localité Sremska Mitrovica Coordonnées 44° 58′ 08″ nord, 19° 37′ 02″ est Géolocalisation sur la carte : Serbie SirmiumSirmium Géolocalisation sur la carte : Balkans SirmiumSirmium Histoire Époque Antiquité romaine modifier Sirmium (en serbe cyrillique : Сирмијум ; en...

Zong Rinpoche di Tibet Zong Rinpoche (1905-1984) adalah seorang Gelug Lama dan murid dari Trijang Rinpoche ketiga, tutor junior dari Dalai Lama ke-14.[1] Ia dikenal sebagai analis tajam dan master debat filsafat, serta praktisioner Tantrik berpengaruh.[2] Ia adalah Abbas biara Ganden Shartse. Referensi ^ H.H Kyabje Zong Rinpoche Diarsipkan February 15, 2009, di Wayback Machine. ^ Kyabje Zong Rinpoche by Hans Taeger, retrieved 2009-03-21. Pengawasan otoritas Umum Integrated Aut...

Pour les articles homonymes, voir Mosquée de Paris et GMP. Mosquée de Paris L'entrée principale de la mosquée, place du Puits-de-l'Ermite. Présentation Nom local Grande Mosquée de Paris Culte Islam Type Mosquée Début de la construction 19 octobre 1922 Fin des travaux 15 juillet 1926 Style dominant Architecture néo-mauresque Protection Inscrit MH (1983) Site web grandemosqueedeparis.fr Géographie Pays France Région Île-de-France Département Paris Ville Paris Arrondissement ...

Inverso Pinascacomune Inverso Pinasca – VedutaIl municipio LocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Piemonte Città metropolitana Torino AmministrazioneSindacoLuciano Bounous (lista civica Vivi Inverso Pinasca) dal 27-5-2019 TerritorioCoordinate44°56′44.3″N 7°13′06.29″E / 44.94564°N 7.218414°E44.94564; 7.218414 (Inverso Pinasca)Coordinate: 44°56′44.3″N 7°13′06.29″E / 44.94564°N 7.218414°E44.94564; 7.218414 (Inv...

Physical process by which matter takes up a photon's energy and stores it This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (November 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) An overview of absorption of electromagnetic radiation. This example shows the general principle using visible light as a specific example. A white light source — emitting light ...
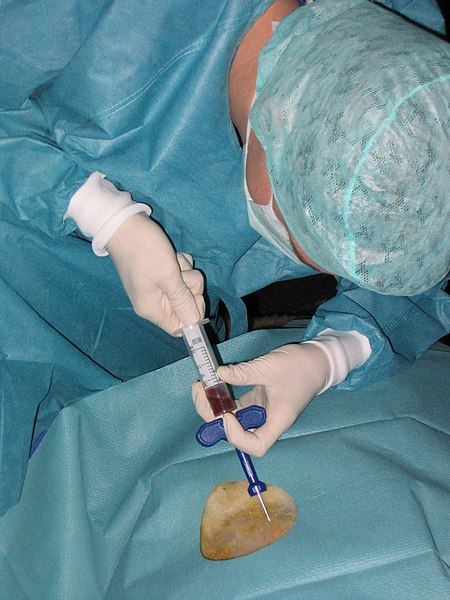
Biopsi sumsum tulang. Biopsi adalah pengambilan jaringan tubuh untuk pemeriksaan laboratorium.[1] Pemeriksaan jaringan tersebut bertujuan untuk mendeteksi adanya penyakit atau mencocokkan jaringan organ sebelum melakukan transplantasi organ.[1] Risiko yang dapat ditimpulkan oleh kesalahan proses biopsi adalah infeksi dan pendarahan.[1] Jaringan yang akan diambil untuk biopsi dapat berasal dari bagian tubuh manapun, di antaranya kulit, perut, ginjal, hati, dan paru-paru...

У этого термина существуют и другие значения, см. Лиссабонский договор (значения). Не следует путать с Лиссабонским протоколом. Лиссабонский договорTreaty of Lisbon amending the Treaty on European Union and the Treaty establishing the European Community Тип договора Поправки к предыдущим договорам Дата подготовки 7-8 �...

الحياة في مصر الثقافة الثقافة الإعلام السينما الموسيقى العطل المطبخ القانون والحقوق البرلمان القضاء الشرطة حقوق الإنسان الجغرافيا والسكان الجغرافيا السكان مصريون اللغات الدين السياسة المائية الموارد المائية السياسة السياسة القوات المسلحة رئيس الجمهو�...

Stasiun Akaike赤池駅Stasiun Akaike pada September 2008LokasiYamada, Minami-cho, Gujō-shi, Gifu-ken 501-4103JepangKoordinat35°40′16″N 136°57′38″E / 35.67111°N 136.96056°E / 35.67111; 136.96056Koordinat: 35°40′16″N 136°57′38″E / 35.67111°N 136.96056°E / 35.67111; 136.96056Operator Nagaragawa RailwayJalur■ Jalur Etsumi-NanLetak36.3 km dari Mino-ŌtaJumlah peron1 peron sampingJumlah jalur1Informasi lainStatusTanpa stafS...

Stefano ManziManzi di Grand Prix Amerika 2018KebangsaanItaliaLahir29 Maret 1999 (umur 25)Rimini, ItaliaTim saat iniMV Agusta Forward RacingNo. motor62 Catatan statistik Karier Kejuaraan Dunia Moto2Tahun aktif2017– PabrikanKalex, Suter, MV Agusta Klasemen 201919th (39 pts) Start Menang Podium Pole F. lap Poin 60 0 0 0 0 77 Karier Kejuaraan Dunia Moto3Tahun aktif2015–2016 PabrikanMahindra Juara dunia0 Klasemen 201629th (13 pts) Start Menang Podium Pole F. lap Poin 20 0 0 0 0 23 Stefan...

Elda Emma Anderson Elda Emma Anderson, (lahir di Green Lake, Wisconsin, Amerika Serikat, 5 Oktober 1899 – meninggal di Oak Ridge, Tennessee, 17 April 1961) adalah seorang fisikawati dan berperan penting dalam pengembangan di bidang fisika kesehatan. Kemampuan intelektuanya telah ada sejak kecil. Setelah lulus dari Ripon College ia mendapatkan gelar master dibidang Fisika dari Universitas Wisconsin pada tahun 1924. Pada tahun 1941, dia juga mendapatkan gelar doktornya di universitas yang sam...

City in Wisconsin, United StatesHillsboroCityDowntown HillsboroLocation of Hillsboro in Vernon County, Wisconsin.Coordinates: 43°39′10″N 90°20′29″W / 43.65278°N 90.34139°W / 43.65278; -90.34139Country United StatesState WisconsinCountyVernonArea[1] • Total1.44 sq mi (3.74 km2) • Land1.41 sq mi (3.64 km2) • Water0.04 sq mi (0.10 km2)Population (2020)[...

Archery at the Summer ParalympicsGoverning bodyWAEvents9 (men: 5; women: 4)Games 1960 1964 1968 1972 1976 1980 1984 1988 1992 1996 2000 2004 2008 2012 2016 2020 2024 Medalists Para-archery has been contested at every Summer Paralympic Games since they were first held in 1960. Separate individual and team events are held for men and women. Archers are classified according to the extent of their disability, with separate individual events for each of three classes. W1 - Wheelchair and Cerebral...

Channel 3 regional service for North West England For the now-defunct Asian and Middle Eastern television channel formerly known as ITV Granada, see ITV Choice. G-Wizz redirects here. For other uses, see Gee Whiz. ITV GranadaLogo used since 2013The ITV Granada regionTypeRegion of television networkBrandingITV1Country United Kingdom Isle of Man First air date3 May 1956; 68 years ago (1956-05-03)TV transmitters Winter Hill (formerly Emley Moor) Headquarters MediaCityUK, S...

Russian politician In this name that follows Eastern Slavic naming customs, the patronymic is Mirkhatimovich and the family name is Mardanshin. Rafael MardanshinРафаэль МарданшинMember of the State Duma for BashkortostanIncumbentAssumed office 12 October 2021Preceded byIldar BikbayevConstituencyBlagoveshchensk (No. 4)Member of the State Duma (Party List Seat)In office21 December 2011 – 12 October 2021 Personal detailsBorn (1961-12-24) 24 December 1961 (age&#...


