Strategies for engineered negligible senescence
|
Read other articles:

هذه المقالة يتيمة إذ تصل إليها مقالات أخرى قليلة جدًا. فضلًا، ساعد بإضافة وصلة إليها في مقالات متعلقة بها. (أغسطس 2019) سجن الدلفين الأسود (بالروسية: Чёрный дельфин) البلد روسيا الإمبراطورية الروسية الاتحاد السوفيتي تاريخ التأسيس 1773 الإحداثيات 51°09′20″N 54°59′35″E...

Mary IIRatu Inggris, Skotlandia, dan IrlandiaLukisan karya Sir Godfrey Kneller, 1690Ratu Inggris, Skotlandia dan IrlandiaBerkuasa1689[a] – 28 Desember 1694Penobatan11 April 1689PendahuluJames II & VIIPenerusWilliam III & IIBersamaWilliam III & IIInformasi pribadiKelahiran30 April 1662(N.S.: 10 Mei 1662)Istana St James, London, InggrisKematian28 Desember 1694 (umur 32)(N.S.: 7 Januari 1695)Istana Kensington, London, InggrisPemakaman5 Maret 1695Westminster Abbey,...

Ven. Mun Bhuridatta Nama lainLuang Pu Mun (หลวงปู่มั่น)Ajahn Mun (อาจารย์มั่น)Informasi pribadiLahir(1870-01-20)20 Januari 1870Ban Khambong, Khong Chiam, Ubon Ratchathani, ThailandMeninggal11 November 1949(1949-11-11) (umur 79)Wat Pa Sutthawat, Mueang Sakon Nakhon, Sakon Nakhon, ThailandKebangsaanThaiMazhabTheravada, Dhammayutika NikayaSilsilahTradisi Hutan ThaiPekerjaanMaster meditasi VipassanaKedudukan seniorGuruAjahn Sao Kantasilo MahatheraP...

Matthew Spiranovic Spiranovic pada tahun 2013Informasi pribadiNama lengkap Matthew Thomas Spiranovic[1]Tanggal lahir 27 Juni 1988 (umur 35)Tempat lahir Geelong, Victoria, AustraliaTinggi 1,93 m (6 ft 4 in)Posisi bermain BekInformasi klubKlub saat ini Western Sydney Wanderers FCNomor 13Karier junior North Geelong Warriors Keilor Park Melbourne Knights2004–2005 VIS2005 Melbourne Victory FC2006 AIS2007 1. FC NürnbergKarier senior*Tahun Tim Tampil (Gol)2004 North G...

Artikel ini memberikan informasi dasar tentang topik kesehatan. Informasi dalam artikel ini hanya boleh digunakan untuk penjelasan ilmiah; bukan untuk diagnosis diri dan tidak dapat menggantikan diagnosis medis. Wikipedia tidak memberikan konsultasi medis. Jika Anda perlu bantuan atau hendak berobat, berkonsultasilah dengan tenaga kesehatan profesional. InfluenzaTEM dari virus influenza, diperbesar kurang lebih 100.000 kali lipat.Informasi umumSpesialisasiKedokteran keluarga, Pulmonologi, pen...

Municipality in Bukidnon, Philippines This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.Find sources: Kibawe – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) Municipality in Northern Mindanao, PhilippinesKibaweMunicipalityMunicipality of Kibawe FlagSealMap of Bukidnon wit...

British actress and centenarian Dame Gwen Ffrangcon-DaviesDBEGwen Ffrangcon-Davies, on 27 June 1928BornGwen Lucy Ffrangcon-Davies(1891-01-25)25 January 1891London, EnglandDied27 January 1992(1992-01-27) (aged 101)Halstead, Essex, EnglandResting placeSt Peter and St Thomas Churchyard, Stambourne, Essex, EnglandNationalityBritishOccupationActressYears active1911–1991Known forActress and centenarian Dame Gwen Lucy Ffrangcon-Davies, DBE (25 January 1891 – 27 January 1992) was a...

2019 film directed by Fernando Meirelles This article is about the biographical film. For the illegitimate popes in history, see Antipope. The Two PopesOfficial release posterDirected byFernando MeirellesScreenplay byAnthony McCartenBased onThe Popeby Anthony McCartenProduced by Dan Lin Jonathan Eirich Tracey Seaward Starring Anthony Hopkins Jonathan Pryce CinematographyCésar CharloneEdited byFernando StutzMusic byBryce DessnerProductioncompanyRidebackDistributed byNetflixRelease dates Augus...

جيتكس Jetix معلومات عامة الشعار التجاري « 'Upgrading to the Next Level, Jetix!' » المالك شركة والت ديزني تاريخ التأسيس 14 فبراير 2004، و1 يناير 2005، و1 أغسطس 2004 تاريخ أول بث 14 فبراير 2004؛ منذ 20 سنة (2004-02-14) تاريخ آخر بث 10 أغسطس 2010؛ منذ 13 سنة (2010-08-10) البلد التشي...

Warrington Borough CouncilWhole council elected every four yearsTypeTypeUnitary authority LeadershipMayorSteve Wright, Labour since 1 July 2023[1] LeaderHans Mundry, Labour since 4 Dec 2023 Chief ExecutiveSteven Broomhead since June 2012[2] StructureSeats58 councillors[3]Political groups Administration (42) Labour (42) Other Parties (16) Liberal Democrats (12) Independent (3) Conservative (1) Length of term4 yearsElectionsVoting sys...

这是马来族人名,“尤索夫”是父名,不是姓氏,提及此人时应以其自身的名“法迪拉”为主。 尊敬的拿督斯里哈芝法迪拉·尤索夫Fadillah bin Haji YusofSSAP DGSM PGBK 国会议员 副首相 第14任马来西亚副首相现任就任日期2022年12月3日与阿末扎希同时在任君主最高元首苏丹阿都拉陛下最高元首苏丹依布拉欣·依斯迈陛下首相安华·依布拉欣前任依斯迈沙比里 马来西亚能源转型与�...
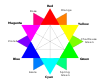
1816 treatise by Arthur Schopenhauer On Vision and Colors (originally translated as On Vision and Colours; German: Ueber das Sehn und die Farben) is a treatise[1] by Arthur Schopenhauer that was published in May 1816 when the author was 28 years old. Schopenhauer had extensive discussions with Johann Wolfgang von Goethe about the poet's Theory of Colours of 1810, in the months around the turn of the years 1813 and 1814, and initially shared Goethe's views.[2] Their growing the...

Australian actress (1949–2013) Penne Hackforth-JonesBornPenelope Beatrix Hackforth-Jones(1949-08-05)5 August 1949Greenwich, Connecticut, U.S.Died17 May 2013(2013-05-17) (aged 63)Melbourne, Victoria, AustraliaOccupation(s)Actress, biographer Penne Hackforth-Jones (5 August 1949 – 17 May 2013)[1] was an American-born Australian actress and biographer.[2][3][4][5] Early life Penelope Beatrix Hackforth-Jones[1] was born in Augu...
Piala Asia Wanita AFCPenyelenggaraAFCMulai digelar1975; 49 tahun lalu (1975)WilayahAsiaJumlah tim12 (final)35 (kualifikasi)Kualifikasi untukPiala Dunia Wanita FIFAJuara bertahan Tiongkok(gelar kesembilan)Tim tersukses Tiongkok(9 gelar) Piala Wanita Asia AFC 2022 Piala Sepak Bola Asia Wanita AFC atau Piala Asia Wanita AFC (dahulu disebut Kejuaraan Wanita AFC) adalah kompetisi sepak bola yang digelar empat tahun sekali (quadrennial ) yang mempertemukan tim-tim nasional yang dinau...

Shopping mall in Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Chinese. (December 2018) Click [show] for important translation instructions. Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia. Do...

Questa voce sull'argomento centri abitati della provincia di Cuneo è solo un abbozzo. Contribuisci a migliorarla secondo le convenzioni di Wikipedia. CussaniofrazioneLocalizzazioneStato Italia Regione Piemonte Provincia Cuneo Comune Fossano TerritorioCoordinate44°34′23″N 7°42′02″E44°34′23″N, 7°42′02″E (Cussanio) Abitanti122 Altre informazioniCod. postale12045 Prefisso0172 Fuso orarioUTC+1 CartografiaCussanio Modifica dati su Wikidata · Manu...

Piala Liga Inggris 2011–20122011–12 Football League CupNegara Inggris WalesTanggal penyelenggaraan29 Juli 2011 s.d. 26 Februari 2012Jumlah peserta92Juara bertahanBirmingham CityJuaraLiverpool(gelar ke-8)Tempat keduaCardiff CityJumlah pertandingan93Jumlah gol310 (3.33 per pertandingan)Pencetak gol terbanyakJay Rodriguez(5 gol)← 2010–2011 2012–2013 → Piala Liga Inggris 2011–2012 (dikenal sebagai Piala Carling karena disponsori oleh bir Carling) adalah edisi ke-52 penyele...

Para otros usos de este término, véase San Juan Evangelista (desambiguación). No debe confundirse con Juan el Bautista. Este artículo o sección necesita referencias que aparezcan en una publicación acreditada. Busca fuentes: «Juan el Evangelista» – noticias · libros · académico · imágenesEste aviso fue puesto el 5 de agosto de 2016. Juan el Evangelista Visión en Patmos de San Juan, en el Tríptico de las Bodas Místicas de Santa Catalina de Hans Memling.Inf...

Bruno Gissoni Bruno GissoniO ator em 2011 Nome completo Bruno Sang Gissoni Nascimento 9 de dezembro de 1986 (37 anos)Rio de Janeiro, RJ Nacionalidade brasileiro Parentesco Meio-irmão: Rodrigo Simas Meio-irmão: Felipe Simas Padrasto: Beto Simas Cônjuge Yanna Lavigne (c. 2018) Filho(a)(s) 2 Ocupação ator Período de atividade 2006-presente Prêmios Lista Bruno Sang Gissoni (Rio de Janeiro, 9 de dezembro de 1986) é um ator e ex-futebolista brasileiro. Ele ficou mais co...

H. Cook & Brothers Rechtsform Gründung 1914 Auflösung 1915 Sitz Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA Branche Automobile Keystone von 1914–1915 H. Cook & Brothers war ein US-amerikanischer Hersteller von Automobilen.[1][2] Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Unternehmensgeschichte 2 Fahrzeuge 3 Literatur 4 Weblinks 5 Einzelnachweise Unternehmensgeschichte Das Unternehmen aus Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania stellte ab Oktober 1914 Automobile her. Der Markenname lautete Keystone. Charles C. Sn...

